An automatic medical image segmentation method based on multi-atlas label fusion
A label fusion, medical image technology, applied in image analysis, image enhancement, image data processing and other directions, can solve the problem of reduced accuracy of fusion results, failure to consider local similarity information between target images and atlas grayscale images, and pixel label assignment errors. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] In this application, an MR image of a human brain is used as a segmentation object for description. It should be understood that the present invention is not limited to application to MR images of the human brain.
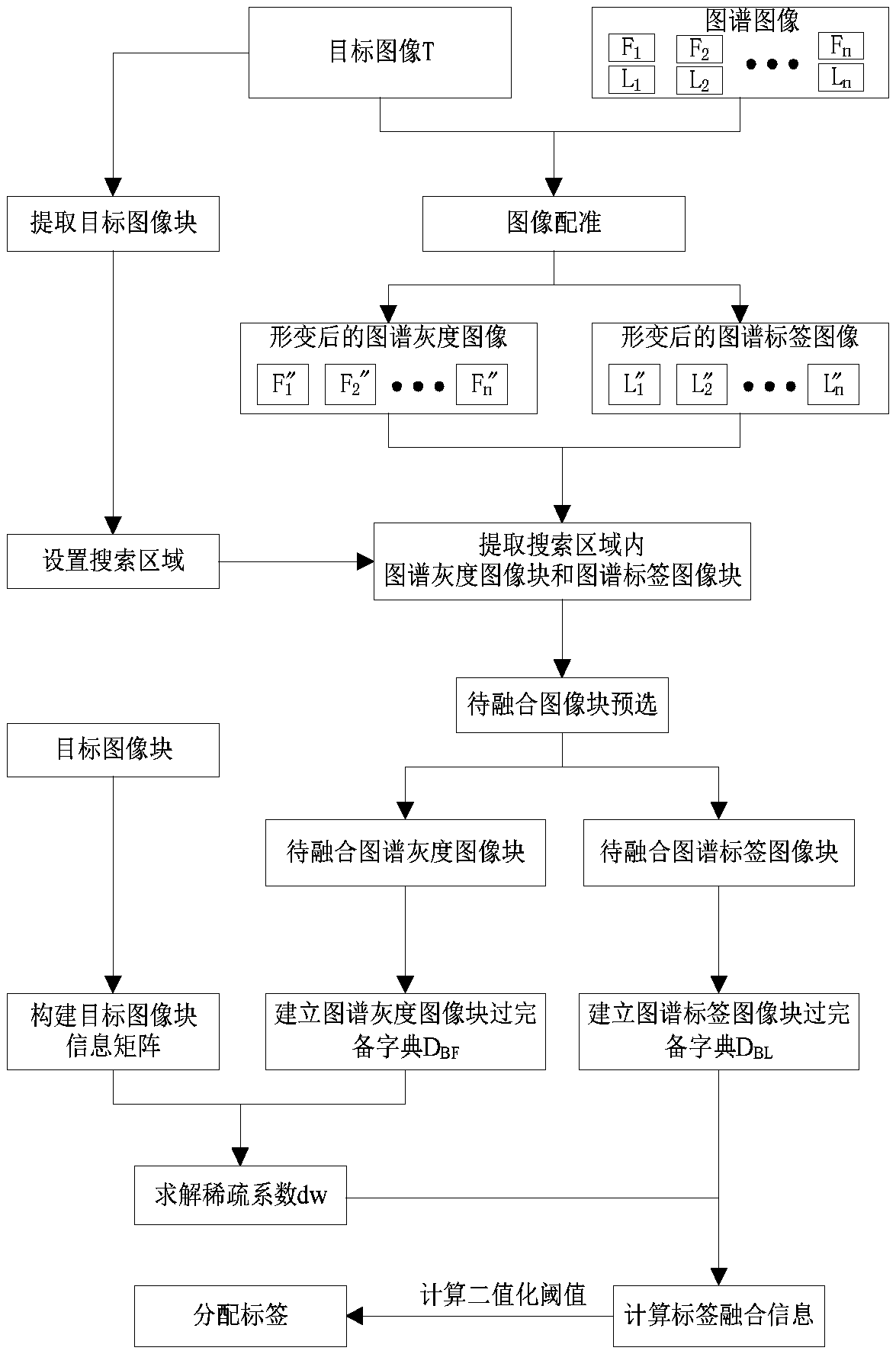
[0054] Such as figure 1 As shown, the specific implementation process of a medical image automatic segmentation method based on multi-atlas label fusion described in this embodiment is:
[0055] Step 1. Atlas registration;
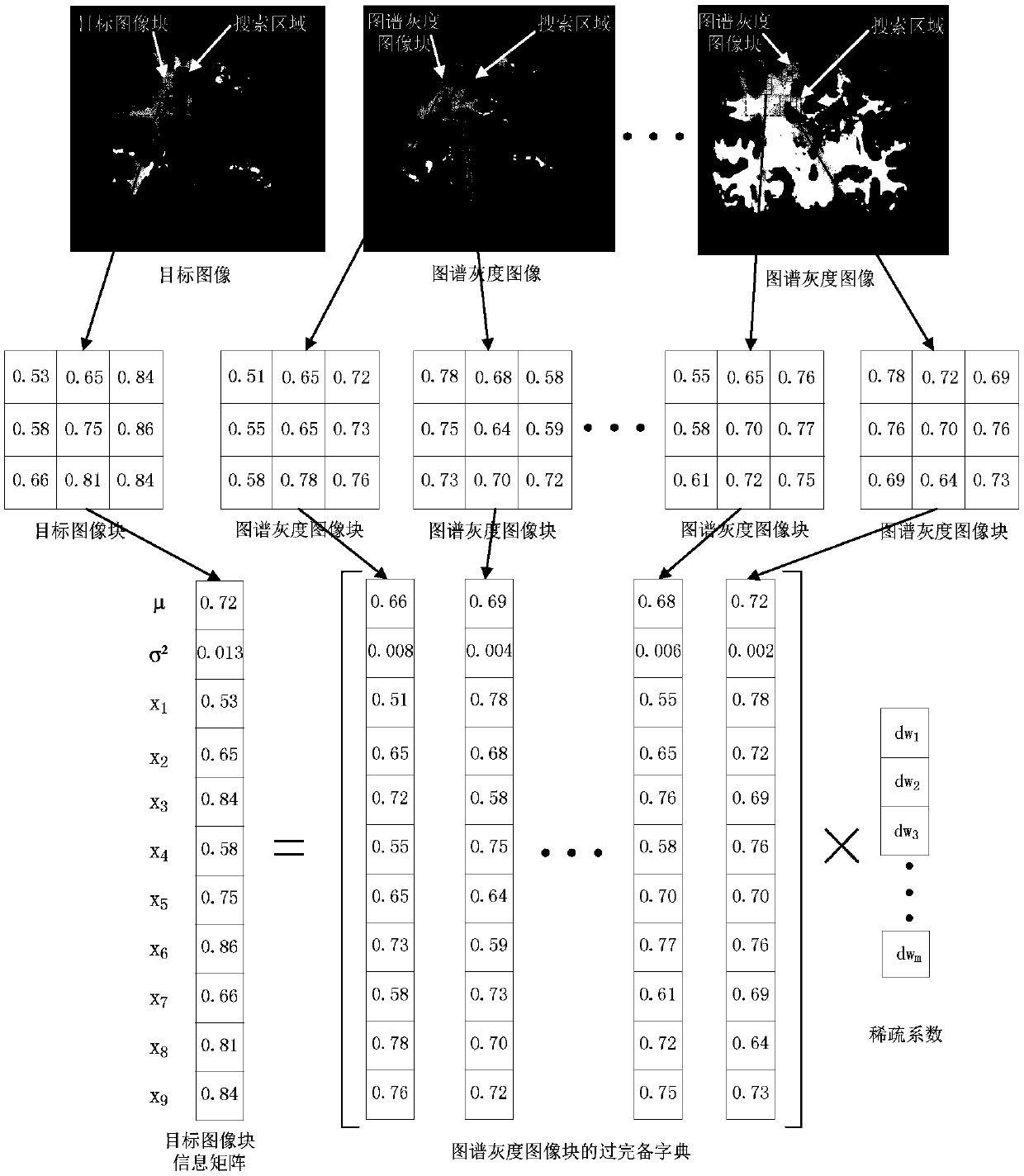
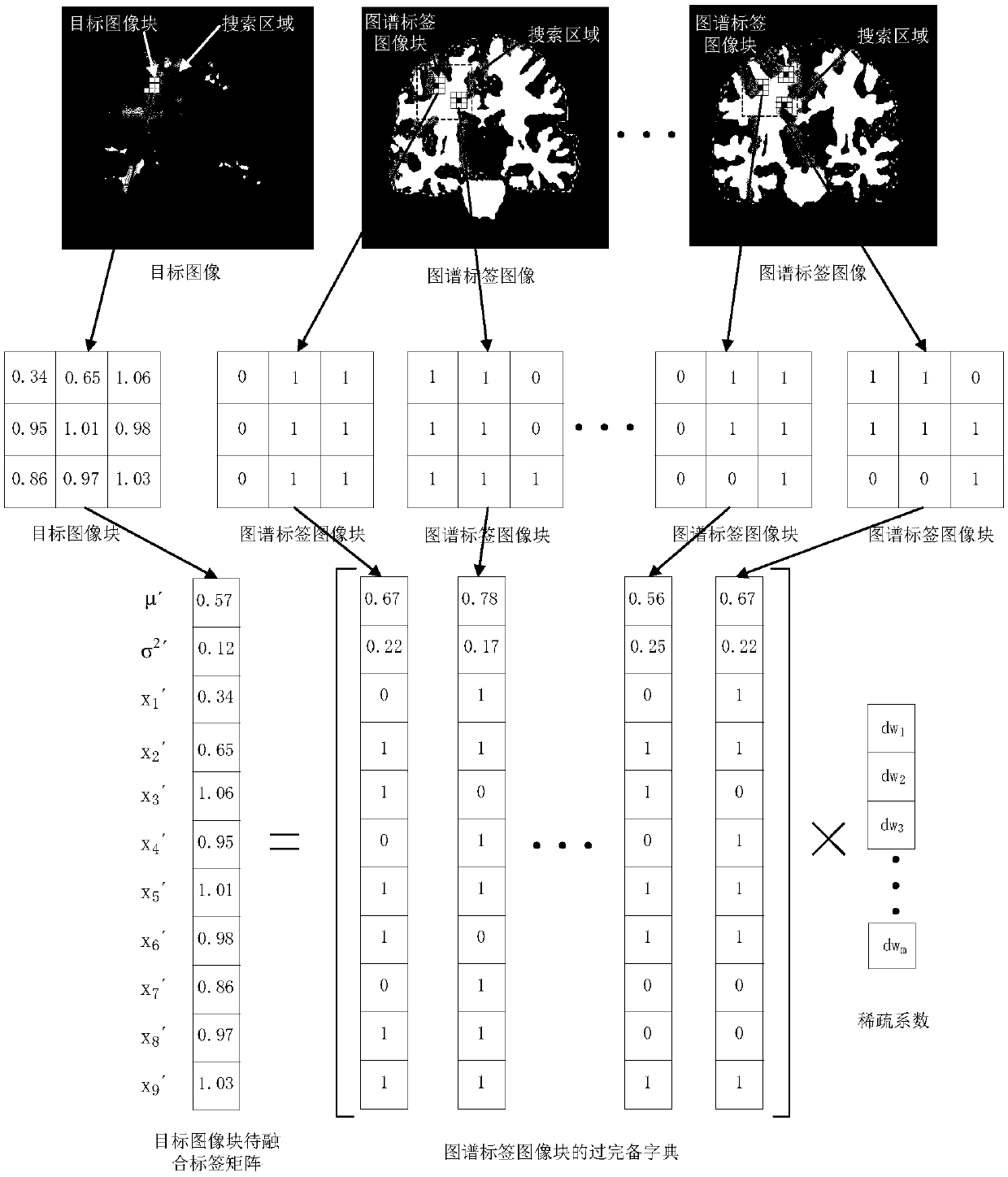
[0056] Given a human brain atlas containing white matter and gray matter markers, the atlas contains N grayscale images F i (i=1,2...N) and the spectrum grayscale image F i The corresponding atlas label image L i (i=1,2…N), the L i for manual from F i The image of the target tissue is marked in , and the target image T is compared with each F i for registration.
[0057] The specific process of map registration is as follows:
[0058] First to T and F i (i=1,2...N) to normalize the pixel values to reduce the error caused by t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com