Optical fiber
An optical fiber and fiber core technology, which can be used in polarized fibers, clad fibers, optics, etc., and can solve problems such as increased SSC loss.
Active Publication Date: 2019-04-16
FUJIKURA LTD
View PDF8 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
However, if the mode field diameter of the semiconductor optical waveguide is enlarged to the s
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mode field diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Login to View More
Abstract
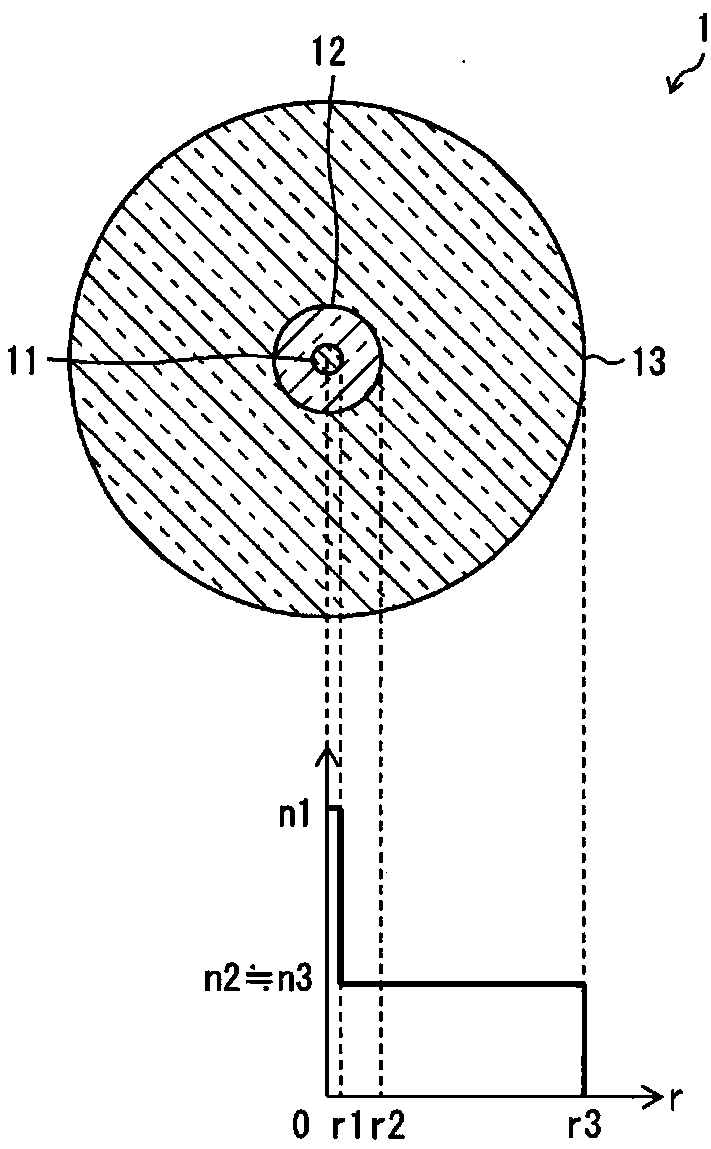
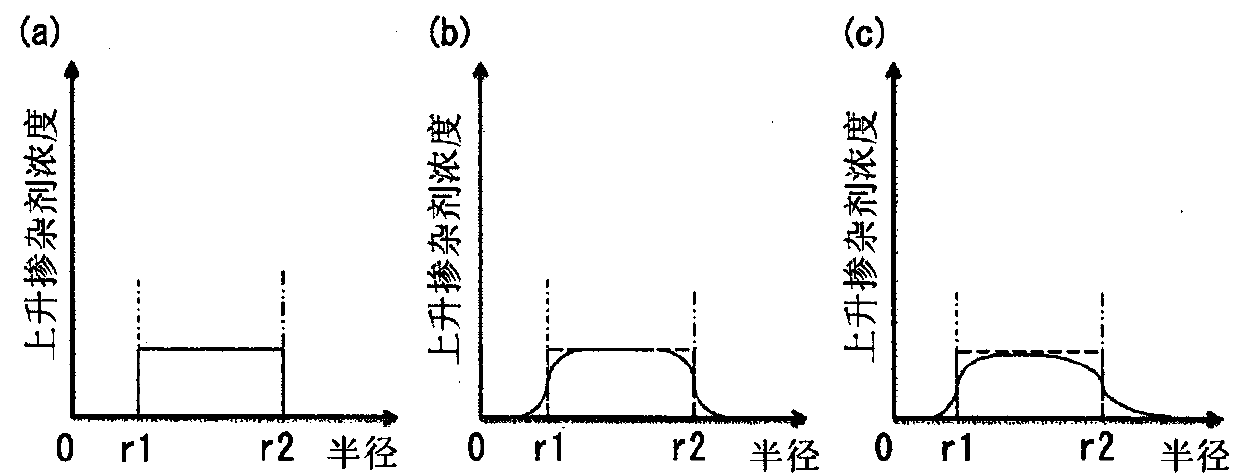
Provided is an optical fiber capable of sufficiently reducing the connection loss at a fusion splice point with a CSMF. The optical fiber is configured such that the refractive index of inner cladding(12) is substantially the same as the refractive index of outer cladding (13) while the concentration of the up-dopant in the inner cladding (12) is set so that the rate of increase of the refractiveindex due to the up-dopant is between 0.25% and 0.5%, inclusive.
Description
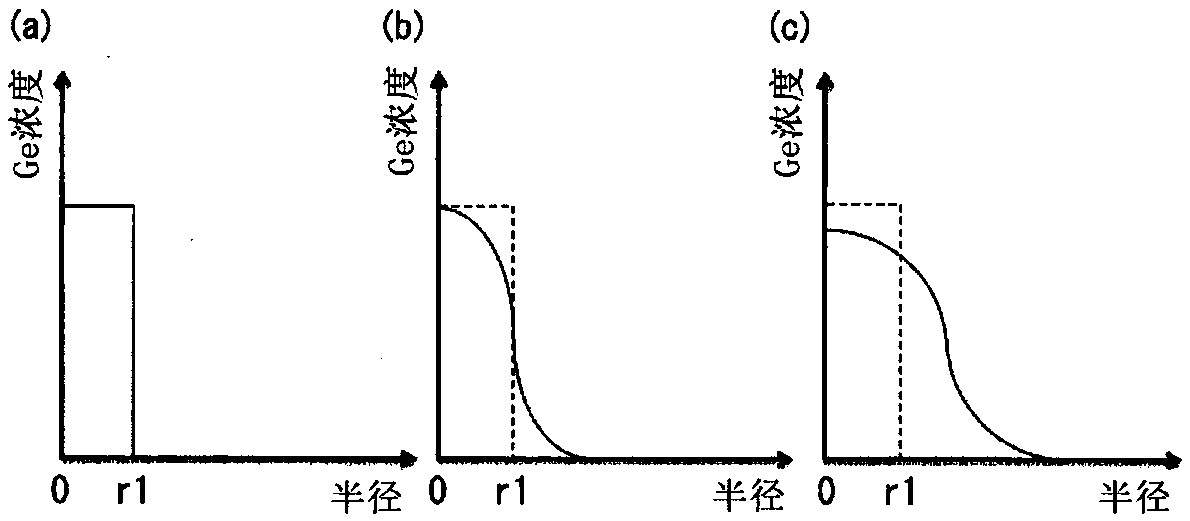
technical field [0001] The present invention relates to an optical fiber capable of expanding the core by thermal diffusion. Background technique [0002] Semiconductor optical waveguides typified by silicon optical waveguides are highly expected as technologies that contribute to the integration of optical communication devices. For example, silicon waveguides with functions such as optical modulators, optical detectors, and optical switches have been realized, and the utilization of optical communication has begun. [0003] In order to propagate light input to or output from the semiconductor optical waveguide, the semiconductor optical waveguide is often connected to a CSMF (Conventional Single Mode Fiber: Conventional Single Mode Fiber). However, while the mode field diameter of a semiconductor optical waveguide is about 1 μm, the mode field diameter of CSMF is about 10 μm. Therefore, if the CSMF is butt-connected to the semiconductor optical waveguide, the connection ...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G02B6/036G02B6/024G02B6/30
CPCG02B6/024G02B6/036G02B6/30G02B6/03694G02B6/03622G02B6/02004G02B6/2551G02B6/305G02B6/0286C03C3/06C03C2201/12C03C2201/31C03C13/045C03C2201/28C03C2201/10G02B6/255
Inventor 平川圭祐市井健太郎林和幸
Owner FUJIKURA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com