Comprehensive assessment method for student lecture attending level based on attention and concentration degree
A technology of comprehensive evaluation and concentration, applied in the field of educational informatization, can solve the problems of neglecting the influence of seated classroom attention, not clearly defining the boundary between attention and concentration, and failing to achieve classroom quality, etc., to achieve easy management. improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
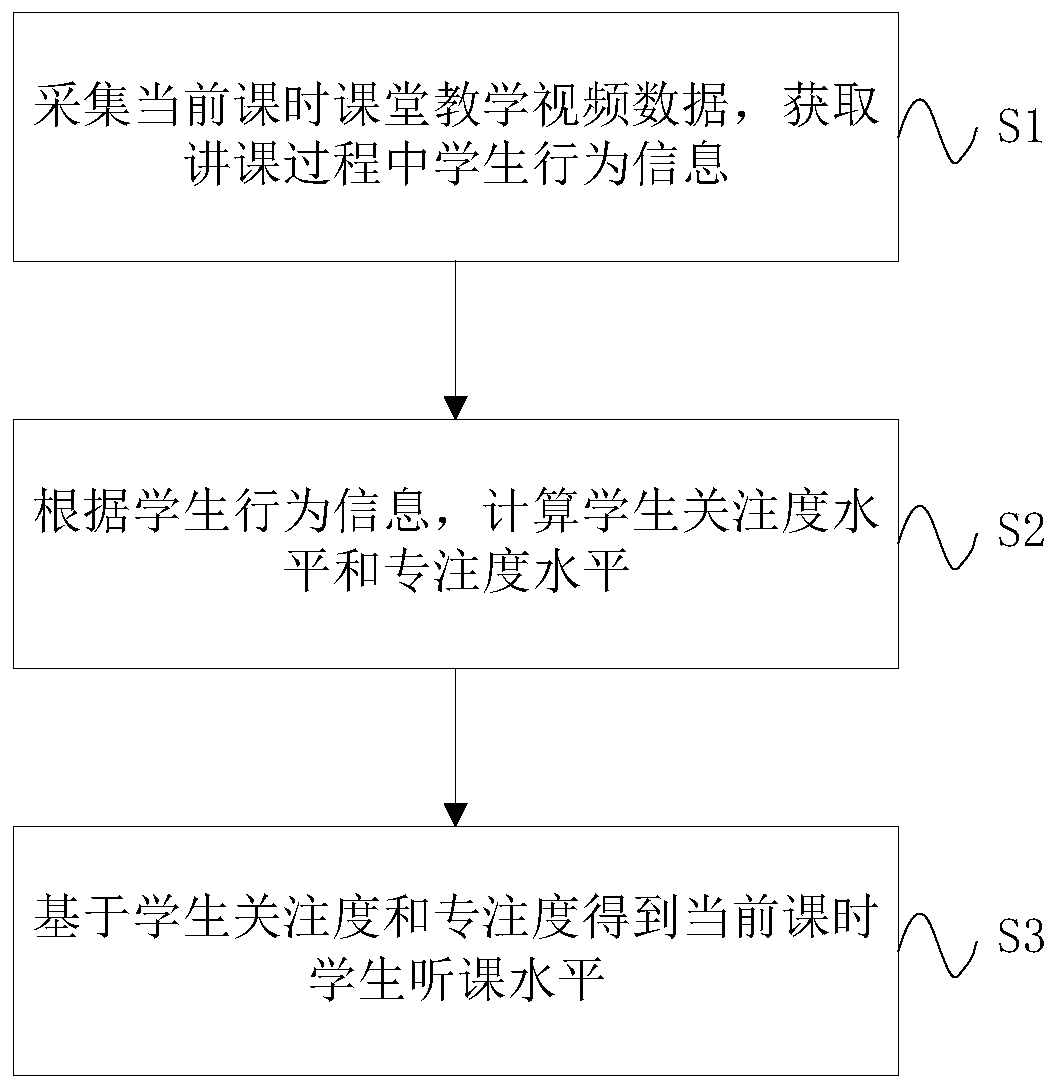
[0068] This embodiment provides a method for comprehensive evaluation of students' listening level based on attention and concentration, such as figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0069] S1: Collect classroom teaching video data during the current class, and obtain student behavior information during the lecture process;
[0070] S2: According to the student behavior information, calculate the student's attention level and concentration level;
[0071] S3: Obtain the student's listening level during the current class based on the student's attention and concentration.
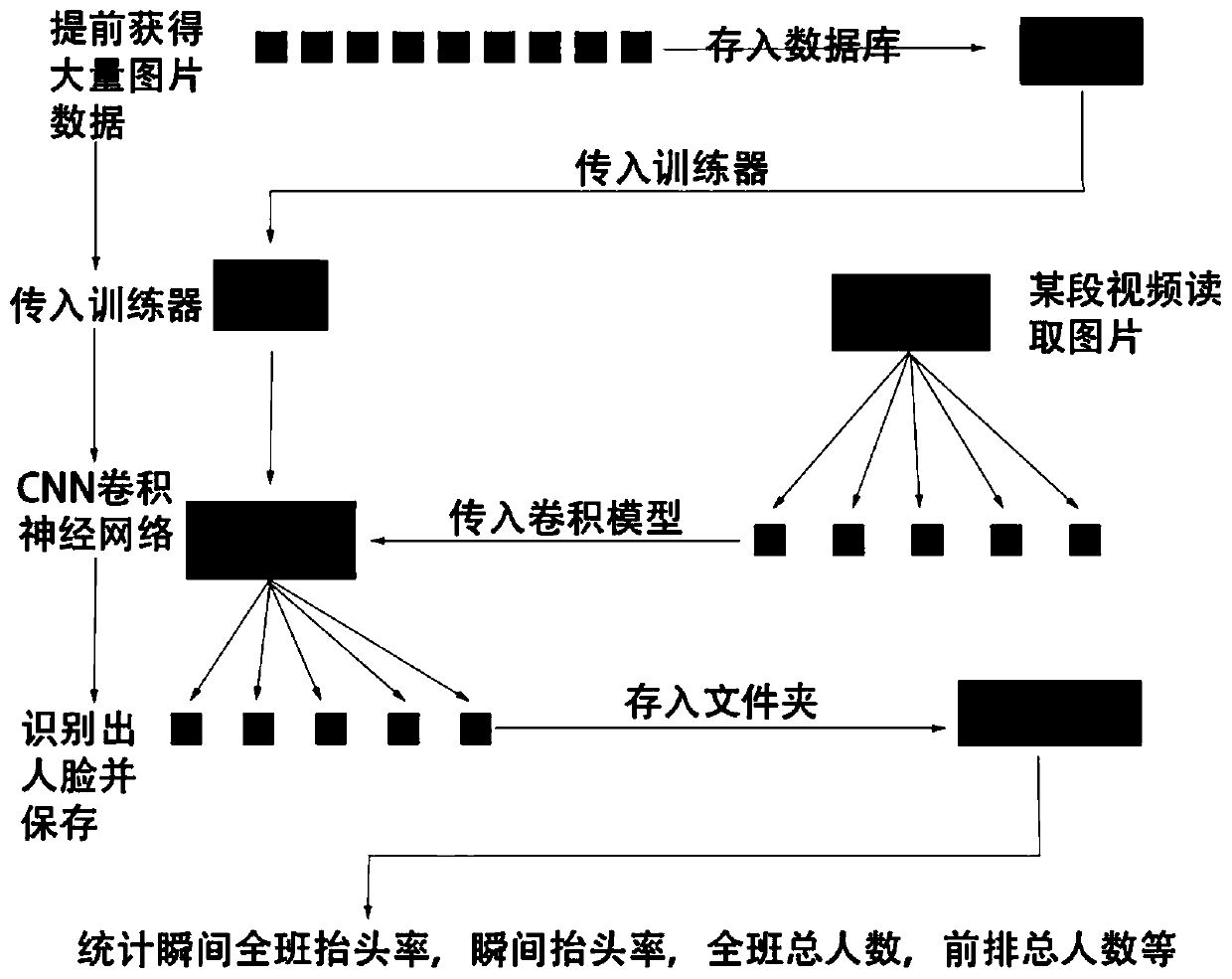
[0072] In step S1, the classroom teaching video data of the current class is collected, and the student behavior information during the lecture is obtained, such as figure 2 , including the following steps:
[0073] S1.1: Collect the classroom teaching video of the current class, extract the image at the set frame interval, store the read frame as a picture and store it as a picture set in the orde...
Embodiment 2
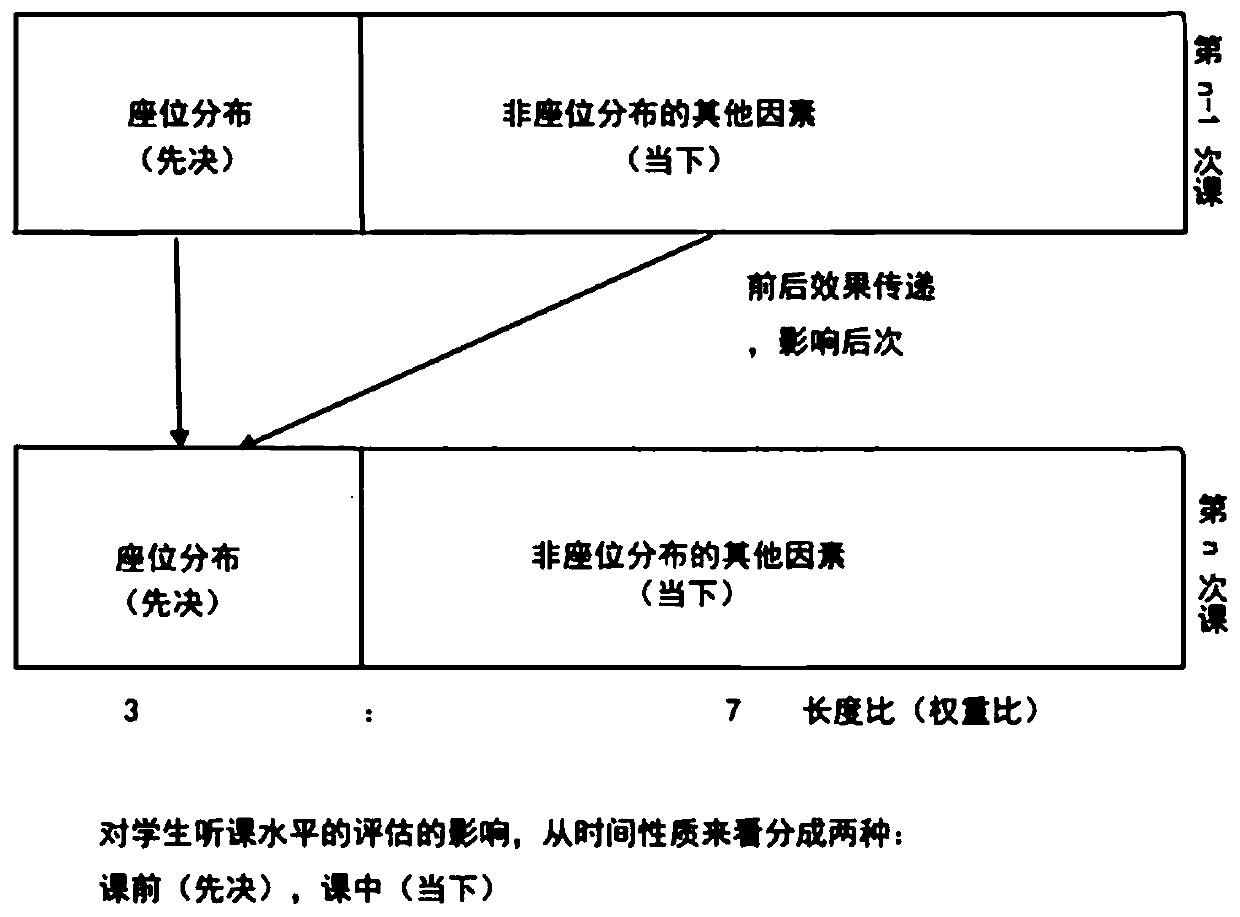
[0117] This embodiment has the same steps as Embodiment 1. In the specific implementation process, the course quality evaluation of the semester is carried out based on the 16 class hours of the student's listening level W of the course:
[0118] TCQ=γ D / 2 ·Z α / 2 ·Σ (α+D+2) / 2 ·exp[-0.5(Tr[Z·Σ -1 ]+γ(μ-V) T Σ -1 (μ-V)γ D / 2 )]+b
[0119] Among them, γ and α are parameters, Z is a C×D-dimensional matrix, D is the number of semester-divided modules, C is the number of class hours divided into different semester sub-modules by the total class hours; V is D×D for different semester sub-modules 1-dimensional weight matrix; Σ is C×D covariance matrix; Tr[Z] is the rank of matrix Z; μ is D×1 weight mean matrix, such as weight matrix V is [a,b,c,d] T , set e=(a+b+c+d) / 4, then the matrix μ is [e,e,e,e] T . b is a constant.
[0120] This course has a total of 16 class hours. If D is set to 4, it is 4 semester sub-modules, which are: the beginning of the semester, before the mid-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com