A lane-changing decision-making method for multi-vehicle interaction considering driving benefit increment
A decision-making method and technology of interest, applied in the field of active prevention and control of road traffic safety, can solve problems such as low accuracy and poor safety, and achieve the effect of ensuring stability, reducing possibility, and improving accuracy and safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0027] Specific implementation mode 1: In this implementation mode, a multi-vehicle interactive lane-changing decision-making method that considers the driving benefit increment. The specific process is as follows:
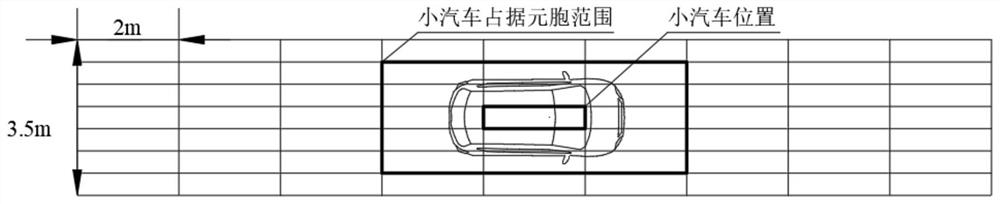
[0028] Step 1: as attached figure 1 As shown, the traffic module is constructed using the cellular automata model. Divide the road into a grid with cells with a width of 0.5m and a length of 2m, where each car occupies 15 cells, and the middle cell represents the position of the car;
[0029] Step 2: Determine the interacting vehicles in the lane changing process. Let car i be the target vehicle, car i-1 be the car in front of the current lane of car i, car i+1 be the car behind the current lane of car i, car j-1 be the car in front of the target lane of car i, and car j be The following car on the target lane of car i;
[0030] When the distance between vehicles is greater than the critical gap (safety distance) d of interaction safe When the interaction betw...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the interactive critical gap d in the step 2 safe The expression is:
[0042] d safe =min(v i +a i ,v max )-min(v j +a j ,v max ) (1)
[0043] where: v j is the speed of car j at time t, in m / s; T is the step length of lane change, v i is the longitudinal velocity of the target vehicle i at time t, in m / s; v max is the maximum speed of car i, in m / s; a i is the acceleration of i car, the unit is m / s 2 ;aj is the acceleration of j car, the unit is m / s 2 .
[0044] Car j is the following car on the target lane.
[0045] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
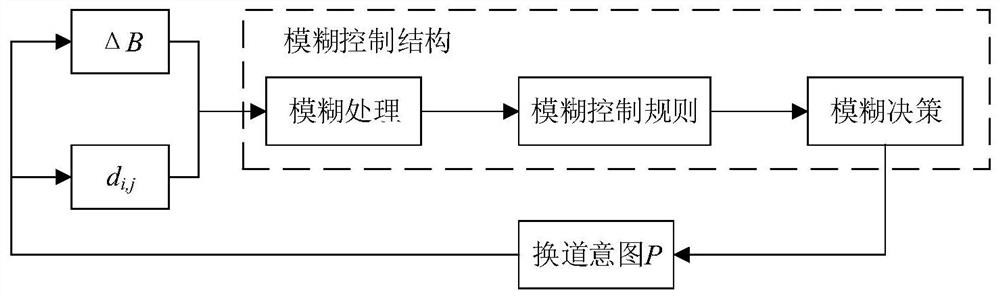
[0046] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in the step 3, the driving benefit increment ΔB and the distance d before and after the lane change of the target car i are determined i,j The generation of lane-changing intention is often caused by the difference in driving interests between the current lane and the target lane. The greater the increase in driving interest after lane-changing, the more obvious the driver's lane-changing intention. The specific process is:
[0047] According to the distance and speed difference between the target car and the front car, define the driving benefits of the current lane;
[0048] According to the distance and speed difference between the target vehicle and the vehicle behind the target lane, define the driving benefits of the target lane;
[0049] Define the driving benefit increment ΔB according to the driving benefit difference between the target lane and the current lane;
[0050] The d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com