Method for monitoring PDCCH, terminal and network equipment
A technology for network equipment and terminals, which is applied in the field of communication and can solve problems such as inability to configure UE
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
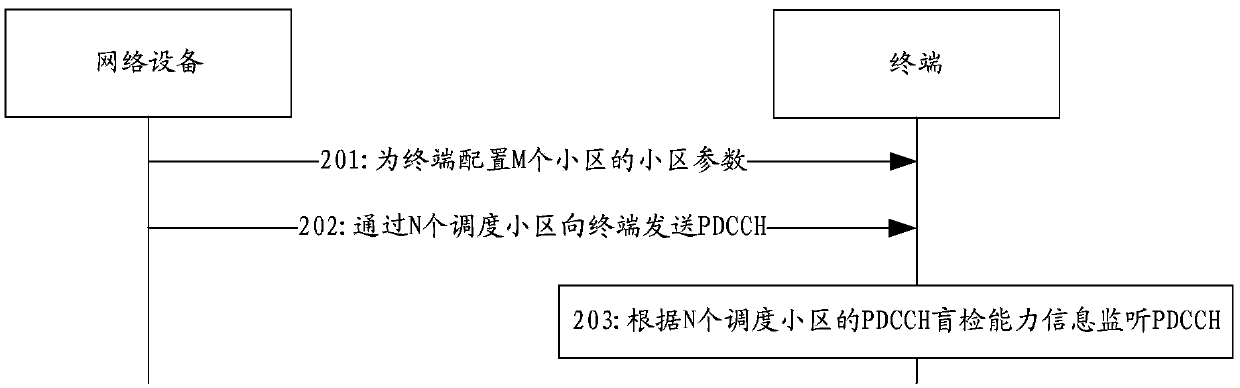
[0061] figure 2 It shows a schematic flowchart of a method for monitoring a PDCCH provided by an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in figure 2 As shown, the method for monitoring the PDCCH may include:
[0062] Step 201: The network device configures cell parameters of M cells for the terminal.
[0063] Correspondingly, the peer terminal receives the cell parameters sent by the network device to the terminal. Among them, the above-mentioned network equipment can be figure 1 A network device in the communication system shown, for example, a base station; the above-mentioned first terminal may be figure 1 Terminal equipment in the communication system shown.
[0064] Step 202: the network device sends the PDCCH to the terminal through the N scheduling cells.
[0065] Step 203: The terminal monitors the PDCCH according to the PDCCH blind detection capability information of the N scheduling cells.
[0066] In the embodiment of the present invention, the above-m...
Embodiment 2
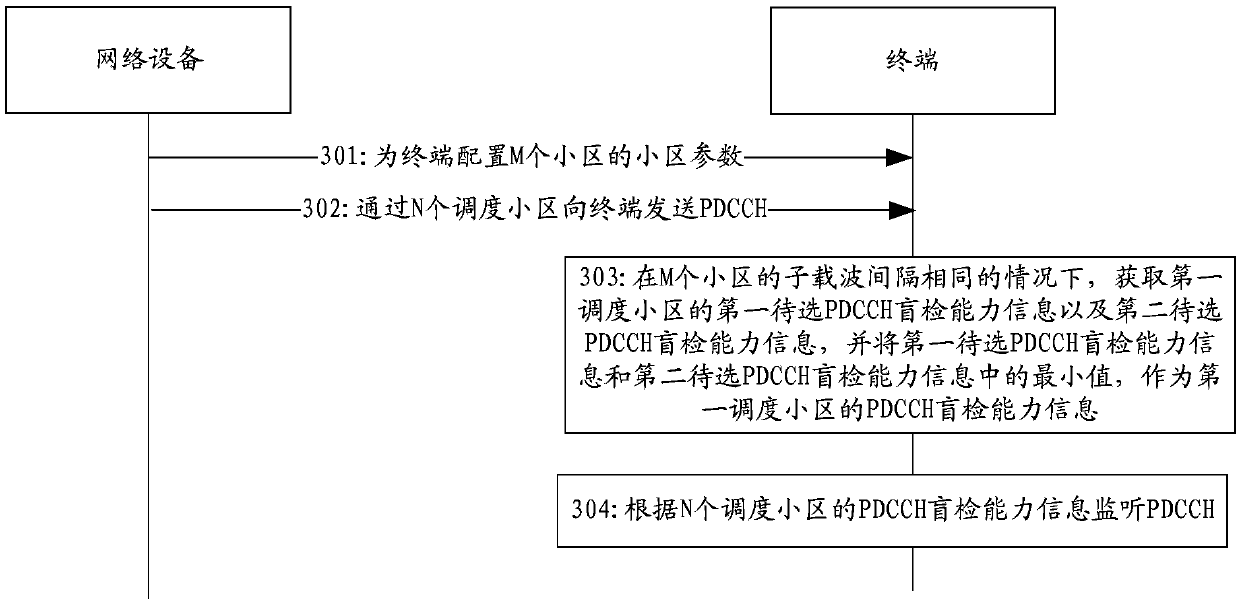
[0076] image 3 It shows a schematic flowchart of another method for monitoring a PDCCH provided by an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in image 3 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention is mainly aimed at the scenario where the subcarrier spacing of M cells is the same. In this scenario, the method for monitoring the PDCCH may include:
[0077] Step 301: The network device configures cell parameters of M cells for the terminal.
[0078] Step 302: the network device sends the PDCCH to the terminal through the N scheduling cells.
[0079] Step 303: When the subcarrier spacing of the M cells is the same, the terminal obtains the first candidate PDCCH blind detection capability information and the second candidate PDCCH blind detection capability information of the first scheduling cell, and stores the first candidate PDCCH The minimum value of the blind detection capability information and the second candidate PDCCH blind detection capability informatio...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Figure 4 It shows a schematic flow chart of another method for monitoring PDCCH provided by the embodiment of the present invention. The embodiment of the present invention can be applied to any cross-carrier scheduling scenario (that is, not only applicable to the scenario where the subcarrier spacing of M cells is the same , is also applicable to the scenario where the subcarrier spacing of the M cells is not the same). Such as Figure 4 As shown, the method for monitoring the PDCCH may include:
[0104] Step 401: The network device configures cell parameters of M cells for the terminal.
[0105] In the embodiment of the present invention, the above cell parameters further include: first priority information of N scheduling cells and / or second priority information of M cells.
[0106] Step 402: The network device sends the PDCCH to the terminal through the N scheduling cells.
[0107] Step 403: According to the first priority information / or the second priority in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com