Computer vision stereo matching method
A computer vision and stereo matching technology, which is applied in the field of stereo matching of computer vision, can solve the problems of inability to process three-dimensional images and poor image effects, and achieve the effects of good processing, improved visual effects, and improved effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
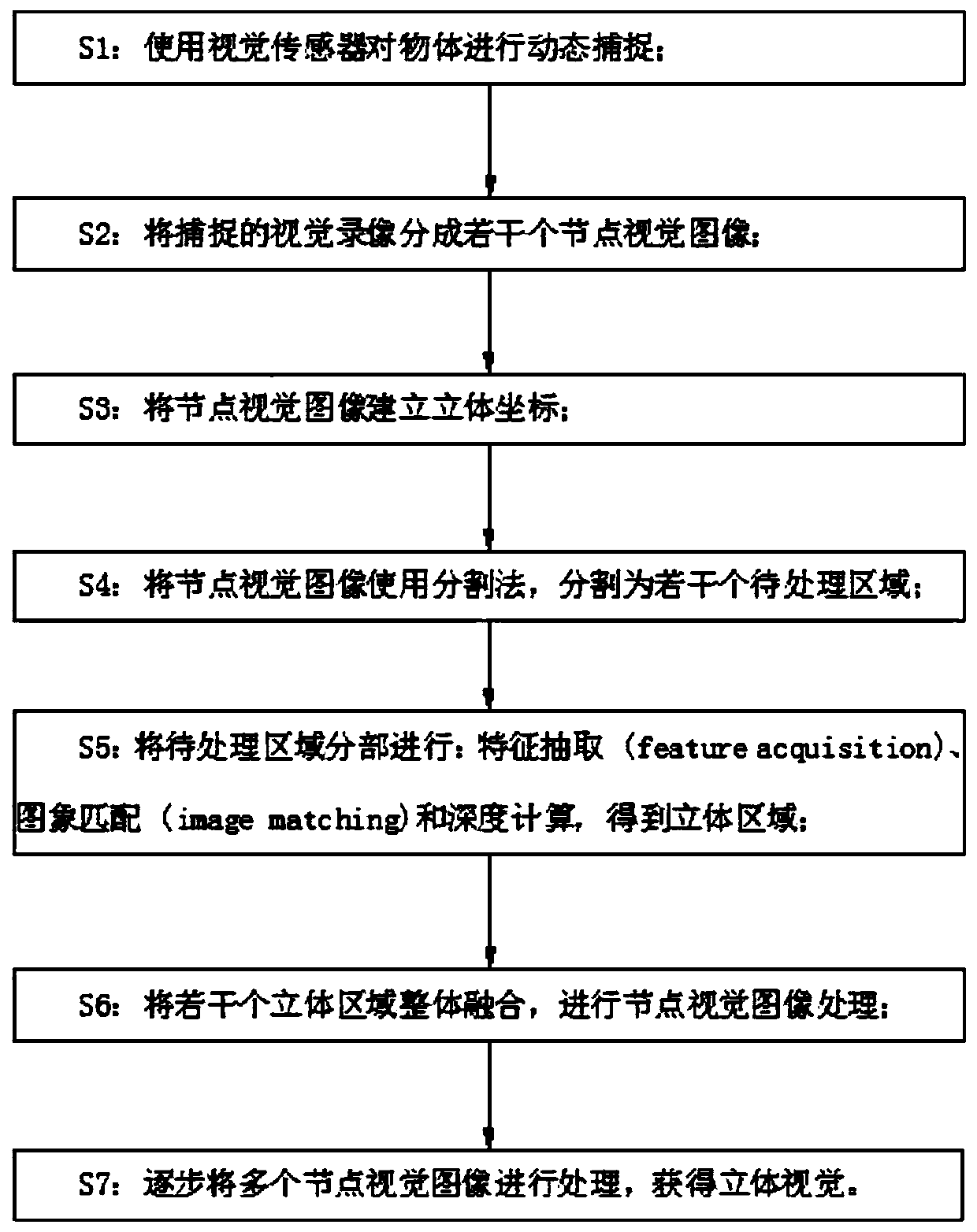
[0029] Embodiment one: refer to figure 1 , a stereo matching method for computer vision, comprising the following steps:
[0030] S1: Use visual sensors to dynamically capture objects;
[0031] S2: dividing the captured visual video into several node visual images;
[0032] S3: establish the stereoscopic coordinates of the node visual image;
[0033] S4: Divide the visual image of the node into several regions to be processed using the segmentation method;
[0034] S5: Divide the area to be processed into: feature acquisition, image matching and depth calculation to obtain a three-dimensional area;
[0035] S6: integrate several three-dimensional areas as a whole, and perform node visual image processing;
[0036] S7: Process multiple node visual images step by step to obtain stereoscopic vision.
[0037] In this embodiment, the visual sensor in S1 is a left and right binocular visual sensor, which can simulate the way human eyes perceive stereoscopic images, and the visu...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment two: a kind of stereo matching method of computer vision, comprises the following steps:
[0048] S1: Use the visual sensor to dynamically capture the object, and the visual sensor can be moved according to the usage;
[0049] S2: Divide the captured visual video into several node visual images, and the conversion of the node visual images is to convert the moving picture into a static picture;
[0050] S3: Generate two-dimensional coordinates from the visual image of the node;
[0051] S4: Use the segmentation method to divide the visual image of the node into several regions to be processed, which can be easily processed by dividing into regions;
[0052] S5: Divide the area to be processed into parts: feature acquisition, image matching and depth calculation to obtain a two-dimensional area;
[0053] S6: Combine several two-dimensional areas as a whole, process the node visual image, build a three-dimensional model of the node visual image, and perform t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com