Space crowdsourcing method based on block chain and deep reinforcement learning and terminal
A reinforcement learning and blockchain technology, applied in the space crowdsourcing method and terminal field based on blockchain and deep reinforcement learning, can solve the problems of spatial crowdsourcing data privacy and security, not considering the task assignment requester, stealing data, etc. , to achieve the effect of overcoming data privacy leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
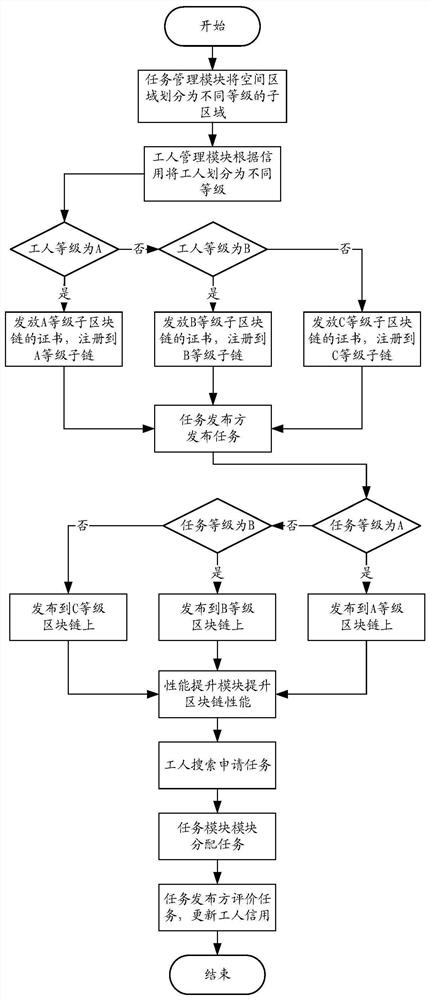
[0096] Please refer to figure 1 , Embodiment 1 of the present invention is:
[0097] A spatial crowdsourcing method based on blockchain and deep reinforcement learning, including steps:
[0098] S1. Obtain a registration request sent by the requesting end, where the registration request includes a requester ID and a requester level;
[0099] S2. Obtain blockchain information, where the blockchain information includes a blockchain level;
[0100] S3. Determine the corresponding block chain level according to the requester level, and register the requester identification on the block chain corresponding to the block chain level corresponding to the requester level, so that the request The requester corresponding to the identifier can query the blocks on the blockchain;
[0101] S4. Obtain the task release information sent by the issuer, where the task release information includes location information, task completion time limit, estimated remuneration, and task identification...
Embodiment 2
[0117] A spatial crowdsourcing method based on blockchain and deep reinforcement learning, which differs from Embodiment 1 in that:
[0118] The S5 is specifically:
[0119] S51. Obtain the set of computing capabilities of the block generation nodes on the block chain corresponding to the block chain level corresponding to the task level and the set of transaction sizes up to the first moment, according to the set of transaction sizes and the set The block chain node computing capability set determines the first state space of the first DQN algorithm:
[0120] S 1 (t1) =[TSize t1 ,N c ] (t1) ;
[0121] Among them, S 1 (t1) represents the first state space, t1 represents the first moment, TSize t1 Indicates the set of transaction sizes up to the first time t1, N c Indicates the set of computing power of the block generation node;
[0122] Specifically, the transaction size set represents a set of the sizes of all tasks in the blockchain determined up to the first mom...
Embodiment 3
[0160] A spatial crowdsourcing method based on blockchain and deep reinforcement learning, which differs from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that:
[0161] After said S53, it is specifically:
[0162] S54. Determine the deployment mode of the block according to the alternative action space, and publish the task release information to the blockchain corresponding to the blockchain level corresponding to the task level according to the deployment mode ;
[0163] S55. Calculate and execute the candidate action space A 1 (t1) ′ after the reward R 1 (t1) And get the updated first state space S 1 (t1+1) ;
[0164]
[0165] S55, will S 1 (t1) 、A 1 (t1) ', R 1 (t1) and S 1 (t1+1) Stored in the experience library of the first DQN algorithm as a piece of test information at t1 time;
[0166] S56. Randomly take out mini-batch from the experience library 1 pieces of quiz information, mini-batch 1 Indicates the number of iterations of the first DQN algorithm;
[0167...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com