Privacy protection method, system and key transmission method for named data network
A named data network, privacy protection technology, applied in the field of system and key transmission, privacy protection, can solve the problems of ambiguity, high bit error rate, unfriendliness, etc., to improve satisfaction, strengthen security, and increase security. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
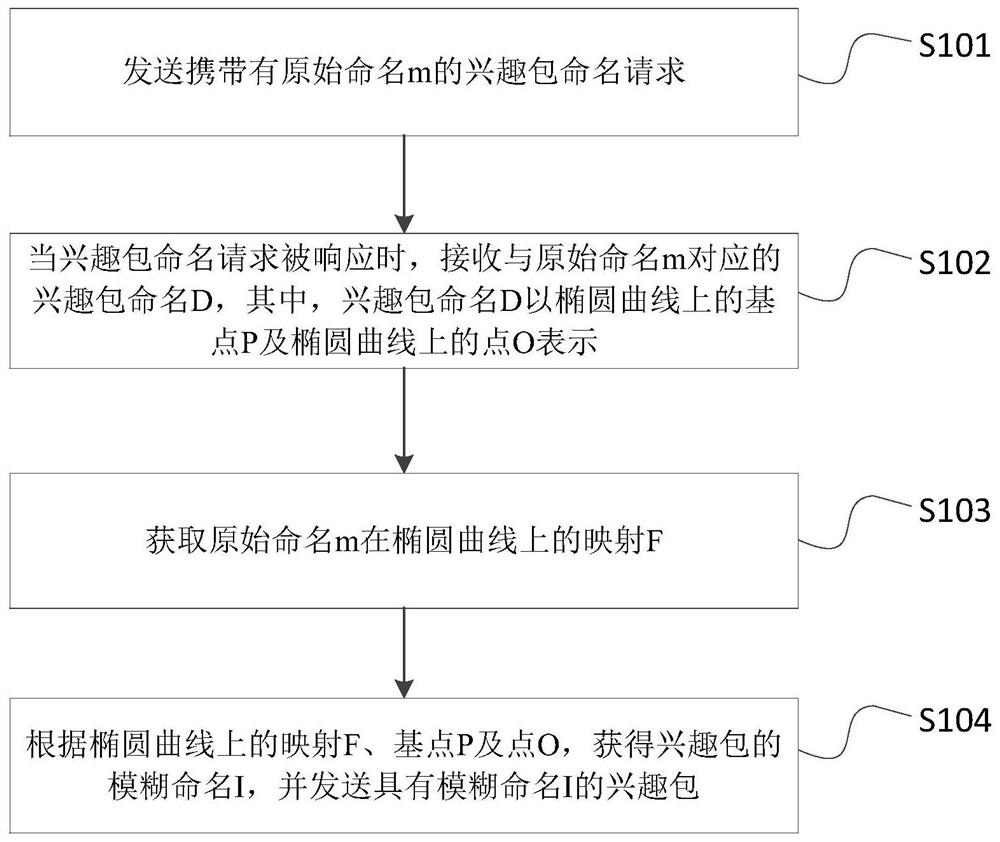
[0065] image 3 A flowchart of a privacy-preserving method for named data networks, such as image 3 As shown, the privacy protection method for a named data network in this embodiment is applied to a data requester, and the method includes the following steps:
[0066] S101: Send an interest packet naming request carrying the original name m;
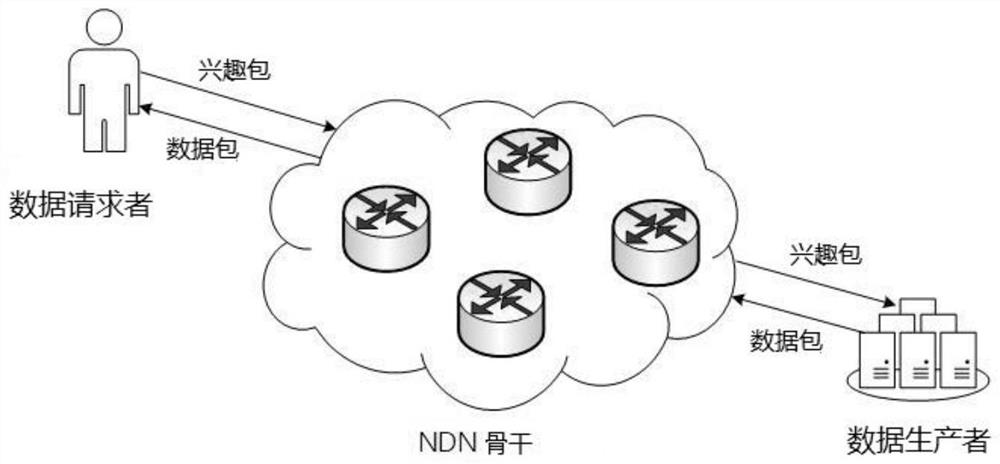
[0067] Specifically, since the named data network is a receiver-driven model, the data requester, as the receiver of the data, is the initiator of the communication. When the data requester needs to request the interest package name of the present invention, it needs to request the interest package name from the server. In the process of requesting the interest package name, the data requester needs to send the original name m of the interest package to the server. The original name m can be a string of indeterminate length. When the server receives the interest package name request information, the server identifies the data request...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Image 6 A flowchart of a privacy-preserving method for named data networks, such as Image 6 As shown, the privacy protection method for a named data network in this embodiment is applied to a router, and the method includes the following steps:
[0085] S201: Obtain the mapping F of the original name m on the elliptic curve, wherein the base point on the elliptic curve is represented as P;
[0086] In this embodiment, similar to the first embodiment, the mapping F can be obtained from the data production end. The data production end stores all the mappings F corresponding to the original name m on the elliptic curve. All original names m and their mappings F on the elliptic curve can also be stored locally on the server. Of course, the mapping F of the original name m on the elliptic curve can also be obtained through calculation every time. For the specific acquisition process, please refer to Figure 4 .
[0087] S202: Create a data table containing the verifi...
Embodiment 3
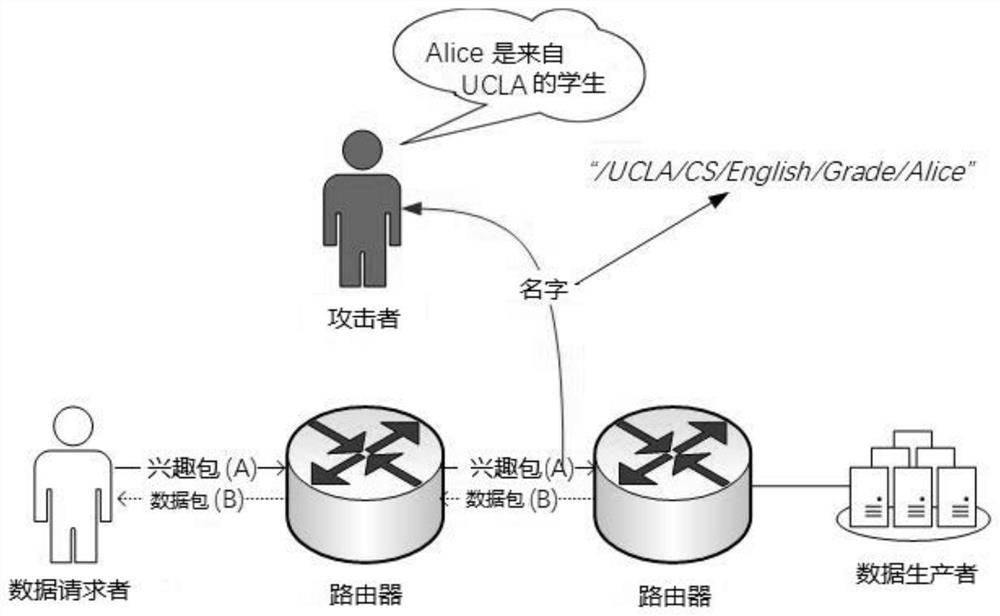
[0110] For a legitimate data requester, in addition to obtaining D from the server to construct the interest packet in the named data network, it also needs to know the decryption key of the data content value to decrypt the data packets that may be obtained later. . To this end, embodiments of the present invention provide a key transmission method. The core of this method is that when a legitimate data requester needs to request a decryption key, it needs to combine the I obtained in the previous paragraph to construct an interest packet named I:key and send it to the network. The routers in the network send this Interest packet to the data producer according to the forwarding principle. The data production end constructs a data packet, the data packet is named I:key, and the content value part is the encryption key of the real data corresponding to I. The encryption key is encrypted by an attribute-based encryption method, and is packaged into a data packet and sent to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com