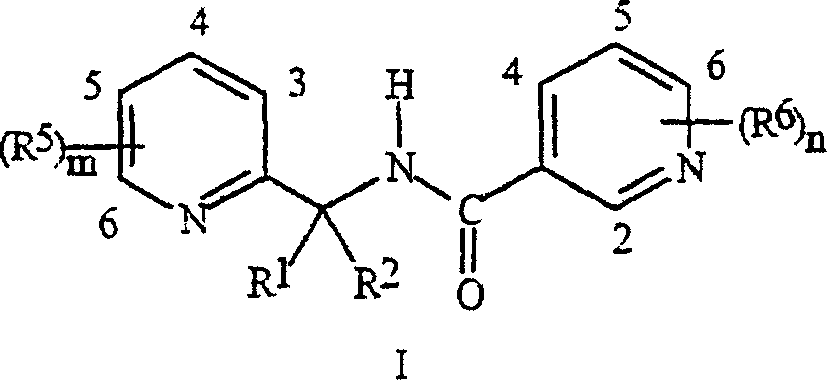
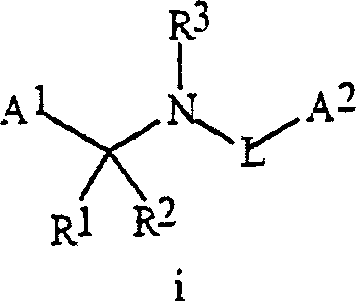
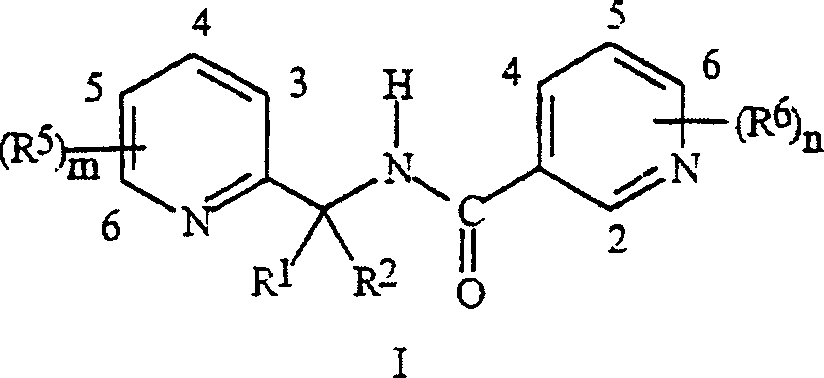
Synergistic fungicide compositions containing at least one N-(2-pyridinyl) 1-3-pyridinecarboxamide derivative and one or more further fungicides useful for controlling fungal plant diseases
A plant disease and composition technology, applied in the field of pyridyl amides, can solve problems such as increased consumer costs and reduced yields
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] 2,4-Dichloro- N- [[3-Chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]methyl]-6-methyl-3-
[0083] Preparation of pyridinecarboxamide
[0084] Step A: 2,4-Dichloro- N- [[3-Chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]methyl]-6-methyl-3-pyridine Preparation of pyridine carboxamide
[0085] To a solution of 2,4-dichloro-6-methyl-3-pyridinecarbonyl chloride (0.65 g) in 2 mL of dichloromethane was added 2-aminomethyl-3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl - A solution of pyridine hydrochloride (prepared as described in WO99 / 42447) (0.79 g) and triethylamine (0.68 g) in 10 mL of dichloromethane. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. The reaction mixture was then poured onto a 1 inch plug of silica gel, eluted with 30 mL of dichloromethane, and the eluate was concentrated to give 0.69 g of the title compound, a compound of the present invention.
[0086] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 )δ2.57(s, 3H), 4.96(m, 2H), 7.22(s, LH), 7.48(bs, 1H), 8.00(s, LH), 8.71(s, 1H).
Embodiment 2
[0088] 2,4-Dichloro- N- Preparation of [[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]methyl]-3-pyridinecarboxamide
[0089] Step A: Preparation of 2,4-dichloropyridine
[0090] 6.7g 4-nitropyridine N-oxide in POCl 3 The solution in was refluxed for 3 hours and then cooled to room temperature. The solvent was removed in vacuo to leave an oily residue. Saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (200 mL) was added carefully, followed by extraction with dichloromethane (2X). The dichloromethane was then removed in vacuo to give an oil which was filtered through a plug of silica gel eluting with 20% ethyl acetate in hexanes. The solvent was removed in vacuo to leave 1.6 g of an oil.
[0091] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ) δ 7.25 (dd, 1H, J=1.7 and 5.4Hz), 7.38 (d, 1H, J=1.7Hz), 8.31 (d, 1H, J=5.4HZ).
[0092] Step B: Preparation of 2,4-dichloro-3-pyridinecarboxaldehyde
[0093] To a solution of 1.6 g of 2,4-dichloropyridine (the product of Step A) in 5 mL of dry THF was added a solution of...
Embodiment 3
[0101] 2,4-Dichloro- N- [1-[3-Chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]ethyl]-3-pyridine
[0102] Preparation of carboxamides
[0103] Step A: Preparation of 3-chloro-α-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinemethanamine
[0104] Add N-(diphenylmethylene)glycine ethyl ester (2.25 g) to a suspension of sodium hydride (0.74 g of a 60% oil dispersion) in 20 mL of dry N,N-dimethylformamide at room temperature During, gas was evolved violently. After stirring at room temperature for 5 minutes, 2 g of 2,3-dichloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridine was added, followed by stirring at room temperature for 1 hour. Then 0.80 mL of methyl iodide was added, followed by stirring overnight at room temperature. The reaction mixture was poured into ice water, extracted with diethyl ether (2X), and the solvent was distilled off in vacuo to give an oil. The oil was then refluxed overnight in 6N HCl. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, made basic with solid sodium carbonate, and ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com