A recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica strain and its construction method and application
A yeast strain, the technology of Yarrowia lipolysis, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of large by-products and pollution, long plant extraction cycle, etc., and achieve the effect of high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
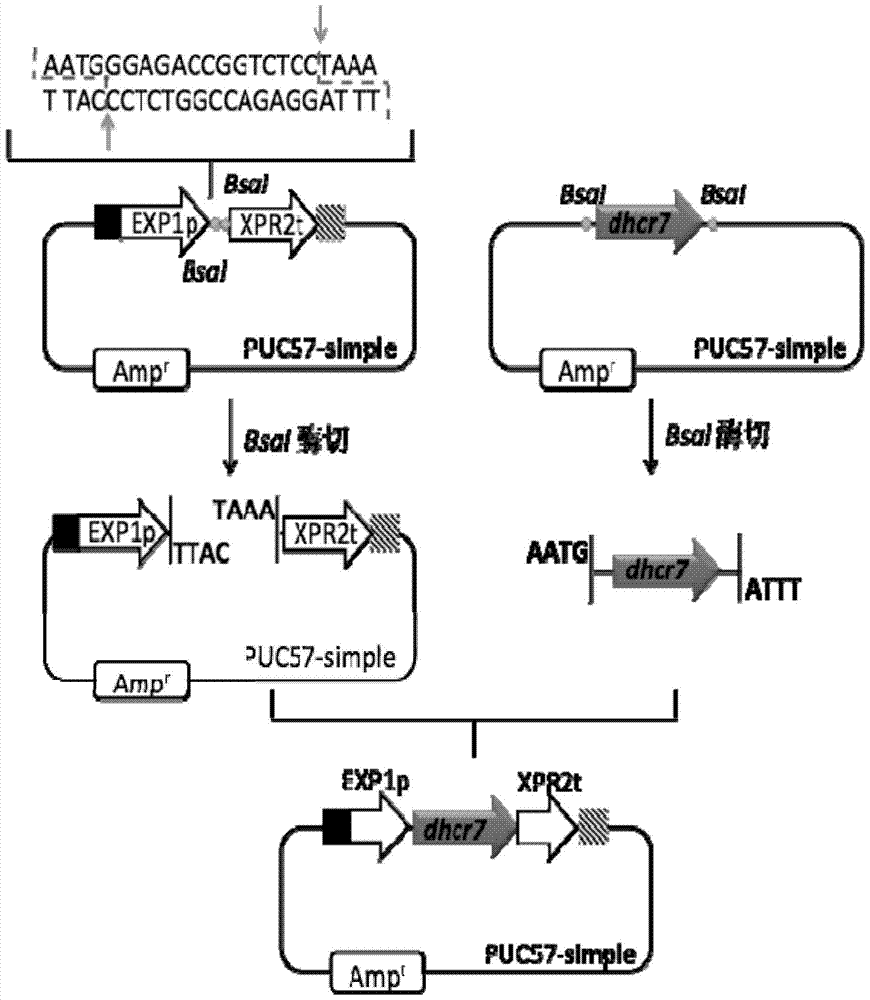
[0050] Embodiment 1: Construction of single gene expression cassette
[0051] Shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 (optimized Rattus norvegicus-derived dhcr7 gene), shown in SEQ ID NO: 5 (optimized rice-derived dhcr7 gene) and SEQ ID NO: 6 (optimized toad-derived Add BsaI restriction sites to both ends of the nucleotide sequence of the dhcr7 gene) to obtain the exogenous target gene, and connect it to the pUC57-simple plasmid;
[0052] The endogenous promoter EXP1 (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 27) and the terminator XPR2 (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 28) of Yarrowia lipolytica were selected, and a pair of reverse BsaI restriction sites were constructed between the two To form an expression cassette, add NotI restriction sites at both ends of the expression cassette, and connect it to the pUC57-simple plasmid;
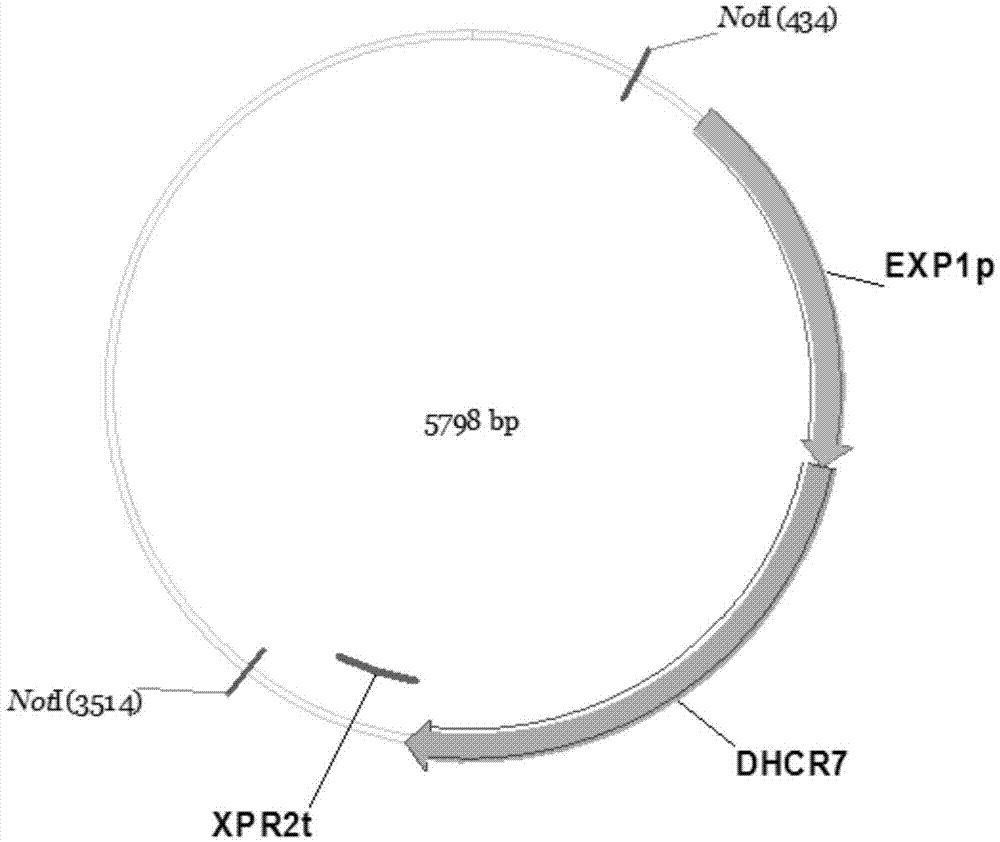
[0053] The pUC57-simple plasmid connected with the exogenous target gene and the pUC57-simple plasmid connected with the expression cassette were digested with BsaI, and the exogenou...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2: Obtaining of fragment 1 (gene fragment upstream of erg5 site) and fragment 2 (gene fragment downstream of erg5 site)
[0056] Using the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NOs: 15-20 as primers, the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NOs: 7-9 were connected by OE-PCR to obtain fragments containing NotI restriction sites at both ends, Connected into the pEASY-Blunt plasmid, and carried out NotI digestion to obtain Fragment 1, as shown in SEQ ID NO:21.
[0057] Using the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NOs: 22-25 as primers, the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NOs: 10-11 were connected by OE-PCR to obtain fragments containing NotI restriction sites at both ends, Connected into the pEASY-Blunt plasmid, carried out NotI digestion, and obtained fragment 2, as shown in SEQ ID NO:26.
[0058] Table 1 OE-PCR primers
[0059]
[0060]
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3: Construction of recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica strain
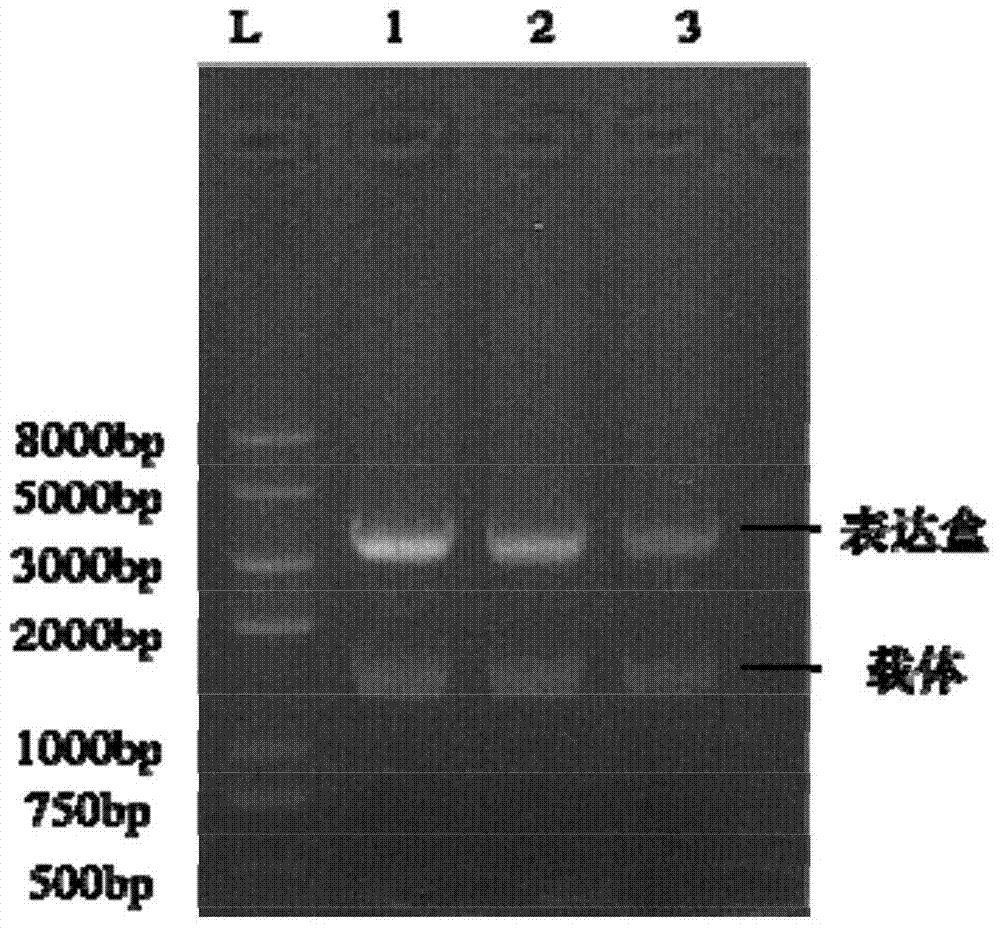
[0062] The single gene expression cassette in Example 1, fragment 1 and fragment 2 in Example 2 were transformed into lipolytic yeast by the lithium acetate method, and the above-mentioned fragments were transformed by homologous recombination between the fragments using the principle of homologous recombination of the yeast itself. The source sequences were joined and integrated into the genome by recombination with homologous sequences at the erg5 locus on the yeast genome. After transformation, the yeast was screened using SC-drop solid medium (synthetic yeast nitrogen source YNB6.7g / L, glucose 20g / L, mixed amino acid powder 2g / L, solid supplemented with 2% agar powder), and the obtained transformants were After separation and purification by streaking, transfer to liquid medium and culture for 24 hours, extract the yeast genome as a template, carry out PCR verification, confirm the correct recomb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com