Climbing-free navigation mark with cylindrical spring floating scaffold
A technology of buoys and buoys, which is applied to buoys, lighting and heating equipment, ships, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the operation of the waterway and the inability to reduce weight, so as to reduce direct economic losses, reduce the cost of daily maintenance of the waterway, and reduce daily maintenance workload effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
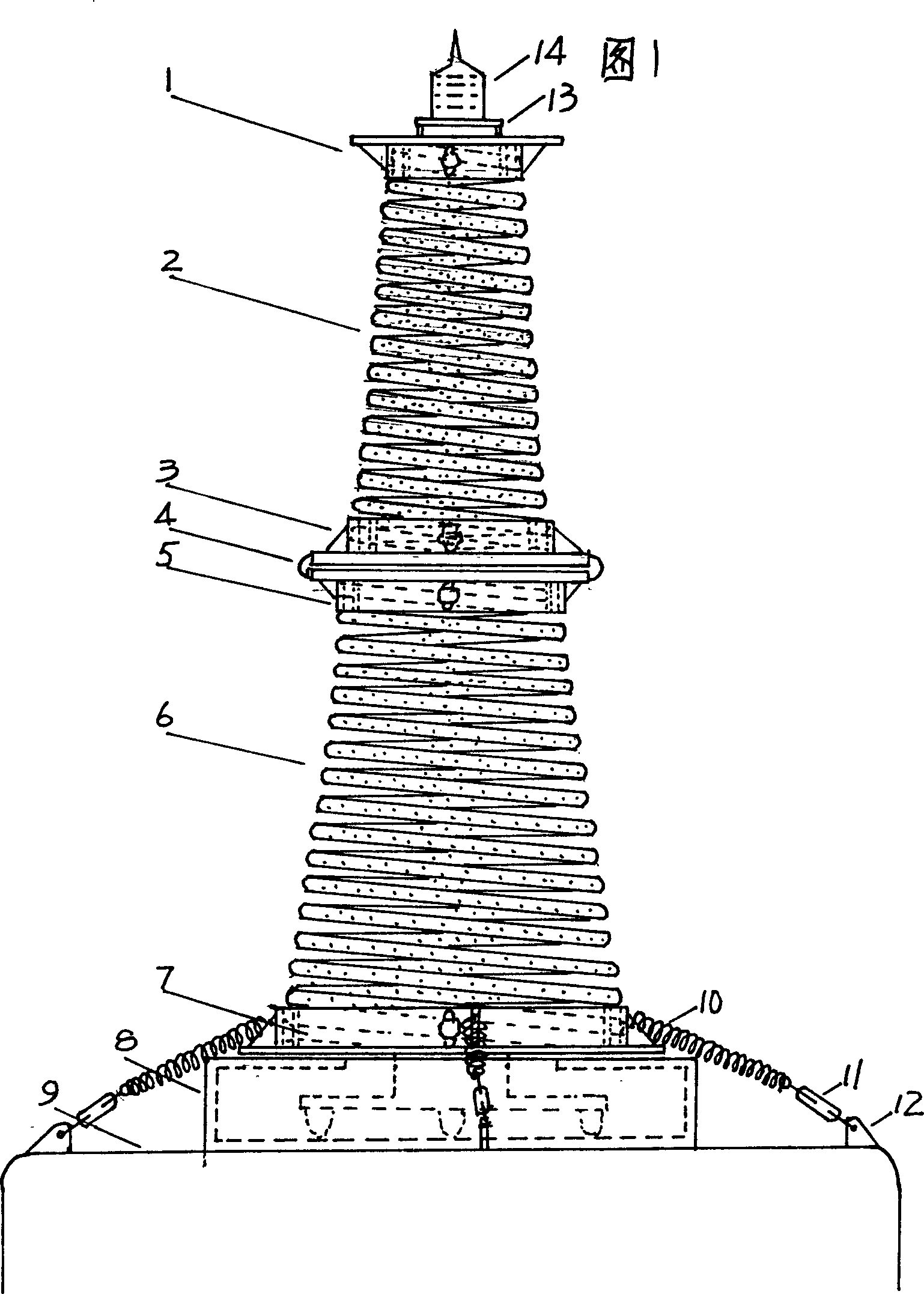
[0019] Embodiment 1, free-climbing column spring buoy buoy (QX) assembly: 1 and 3 in Fig. 1 are the special double-layer spring holders (QX) of the upper main frame, and 2 are the special conical springs of the upper main frame ( QX), 5 and 7 are the special double-layer spring holders (QX) of the lower main frame, 6 is the special conical spring (QX) of the lower main frame, 4 is the folding connector connecting the upper and lower main frames, and 8 is the passive Translation base, 9 is a floating drum, 10 is a fixed return spring of a passive translation base, 11 is a centering regulator of a passive translation base, 12 is a footing, 13 is a beacon light base, and 14 is a navigation light. The upper main frame (including a special conical spring (QX) and a pair of special double-layer spring holders (QX)) connected to the top seat of the folding connector, and the lower main frame connected to the bottom of the folding connector base ( Including a special conical spring (Q...
Embodiment 2
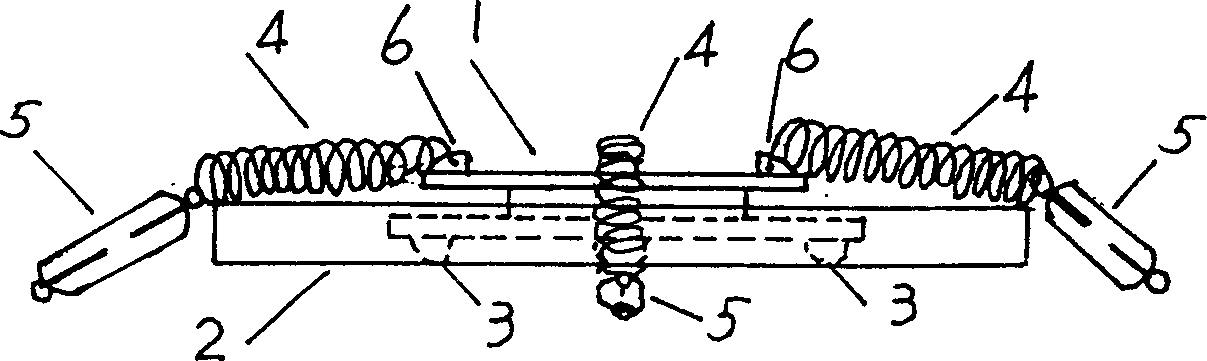
[0020] Embodiment 2, component passive translation base (patent application number: 200410068086.8 and 200420109773.5): including: figure 2 The top seat 1 in the middle, the base 2, the base helps to move the convex 3 (at least 4 pieces), the fixed return spring 4 (4 pieces) and the center regulator 5 (4 pieces). It is characterized in that: the lower circle of the passive translation top seat 1 at the upper end is embedded in the concave body of the passive translation base 2 . The diameter of the lower circle of the passive translation top seat 1 is smaller than the outer diameter of the passive translation base 2. The diameter of the lower circle of the passive translation top seat 1 is greater than the hollow circle diameter of the passive translation base 2. The shape of the lower circle can also be A small-angle conical body that is concave downward, the bottom surface profile of the base 6 may also be a small-angle conical body that is concave downward. When a ship col...
Embodiment 3
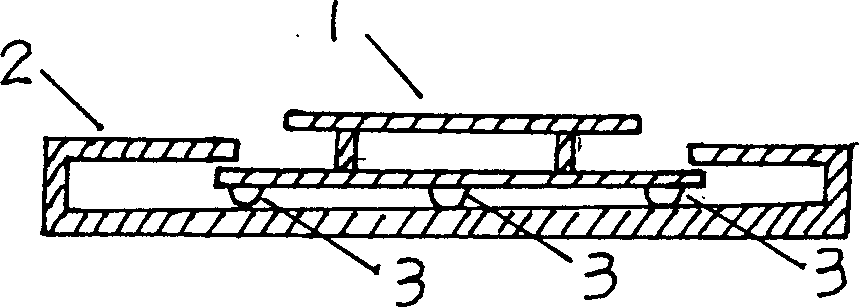
[0021] Embodiment 3, component-specific conical spring (QX): Figure 5 The special conical spring (QX) of the middle main frame includes three parts of upper 1, middle 2 and lower 3 connected as a whole. It is better designed to be closely connected with the double-layer spring holder (QX). Shake left and right and take off; the middle part of the main part is conical, and the length is longer than that of the upper part and the lower part respectively. The stability of the center of gravity plays a key role, ensuring that the entire navigation mark remains balanced and stable in the violent ups and downs of the wind and waves. The diameter of the spring steel for making the spring is between 5-30 mm, the length of the spring is between 10-300 cm, and the diameter of the circle at the bottom is between 5-200 cm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com