Document printed with graphical symbols which encode information
a technology of graphical symbols and documents, applied in the field of documents printed with graphical symbols, can solve the problems of inability to obtain or reproduce the actual materials from which they are made, the inability to integrate documents, and the threat of fraud is ever presen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
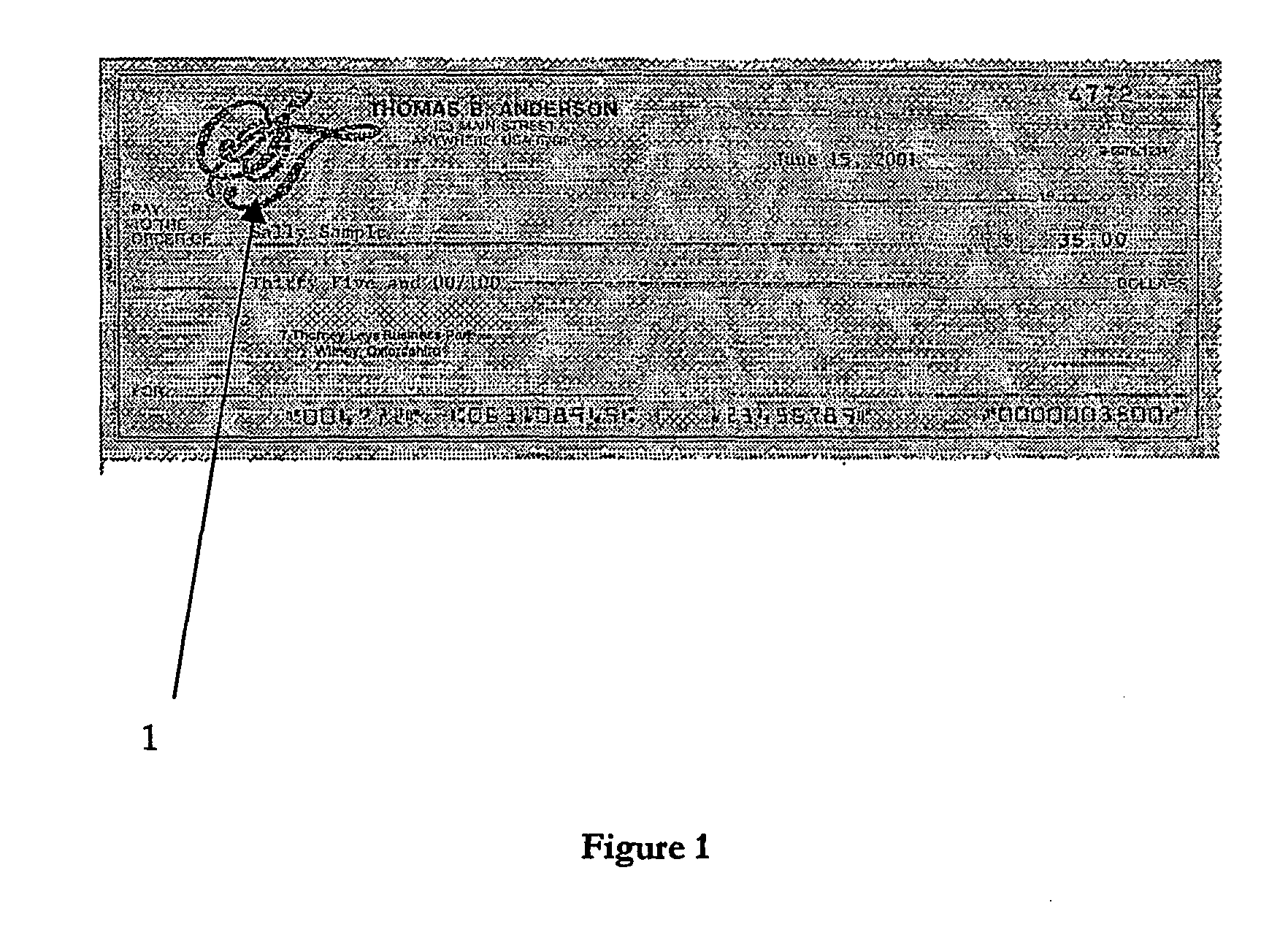
[0051] A description of the preferred implementation is given below. This implementation is called Bitmorph.TM. Seal Encoding.TM. from EnSeal Systems Limited of the United Kingdom. Bitmorph Seal Encoding provides a new method of embedding information into a seal or logo in contexts where neither a 2D bar code nor a digital watermark provide the required characteristics.
[0052] Bitmorph Seal Encoding provides a means of embedding a large amount of information into a compact symbol where the appearance of a conventional 2D bar code is unacceptable. The 2D bar code requirement for a set of predetermined characters (e.g. the industry-standard pdf417 bar code) is replaced by any form of printed logo, picture, seal, word etc. in which individual pixels are subtly varied according to the key used for encoding and the data to be encoded.
[0053] In essence, the Seal Encoding method comprises a process of scrambling the information to be added, followed by aggregation of the scrambled informati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com