Modified recombinant factor viii and von willebrand factor and methods of use
a technology of recombinant factor and modified recombinant factor, which is applied in the field of modified recombinant factor viii and von willebrand factor and methods of use, can solve the problems of limiting the molecular field as to the clearance mechanism of factor viii, and affecting the survival of hemophilic patients, so as to increase the survival of factor viii, inhibit the clearance receptor of coagulation protein,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
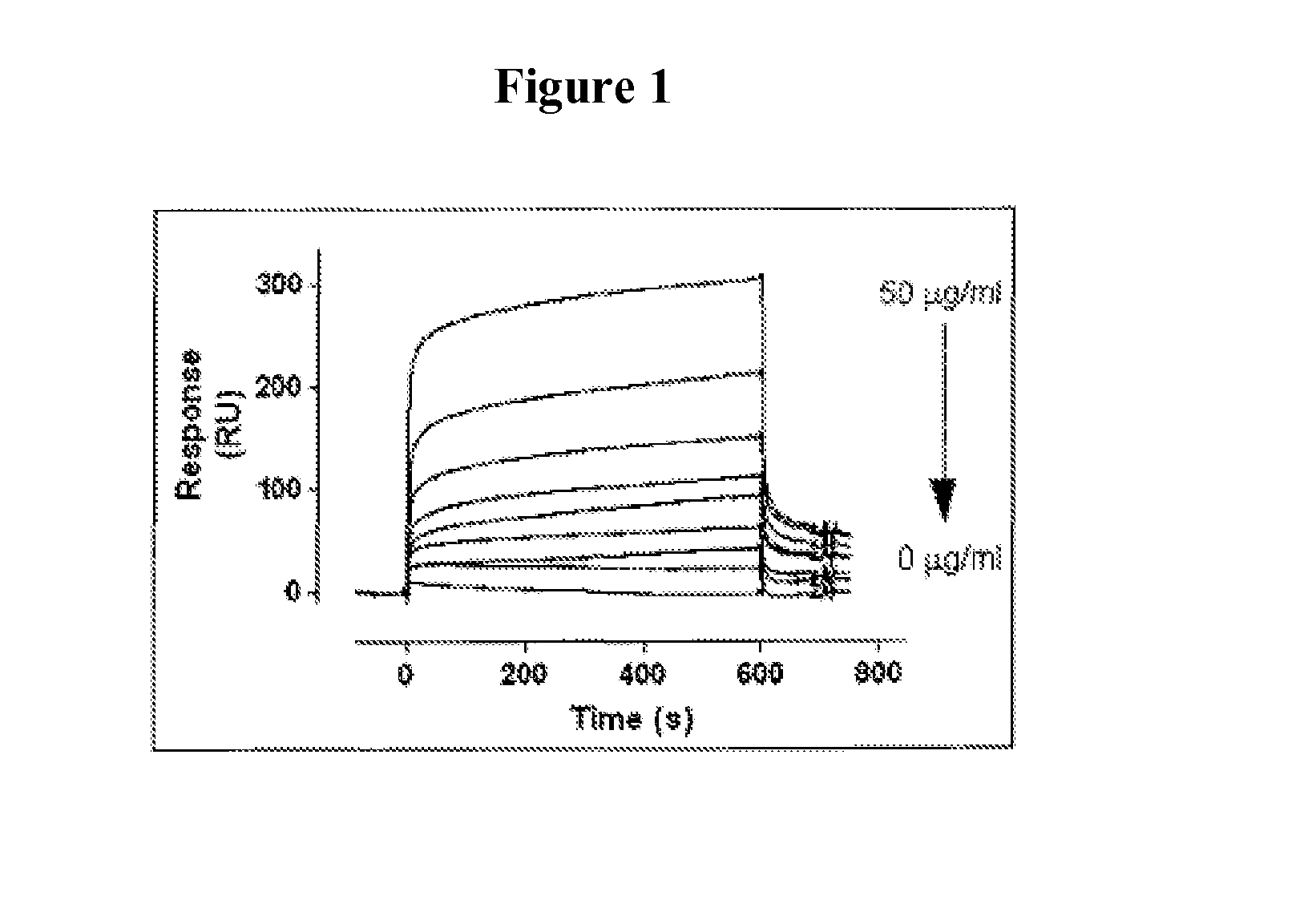
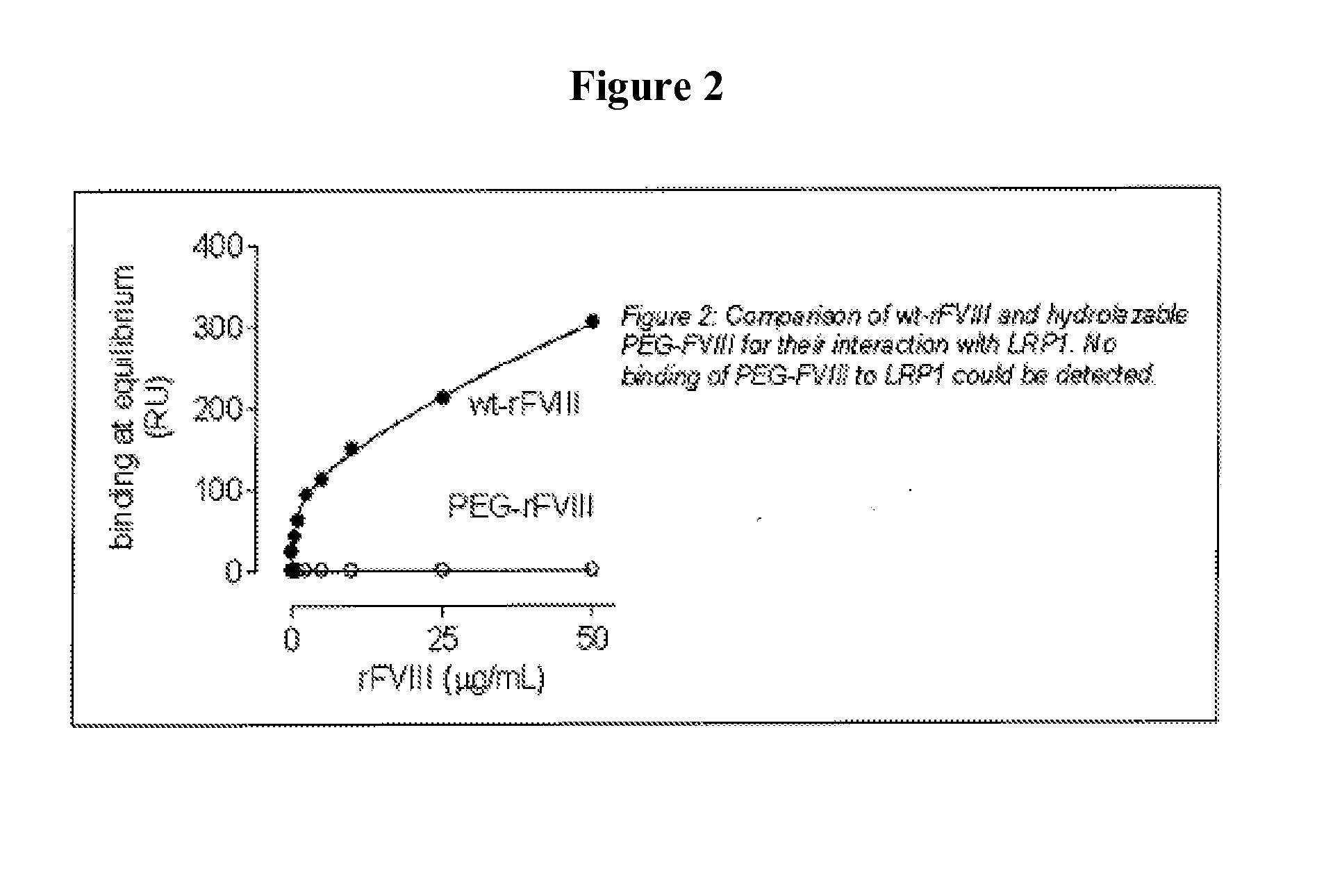
[0147]It has been shown that LRP1 contributes to the regulation of FVIII plasma levels. LRP1 is a cellular receptor that is able to bind and transport FVIII to intracellular degradation pathways. The present example, demonstrates that PEGylation or polysialylation of FVIII disrupts in vitro binding to LRP1.
[0148]Components: Purified recombinant wild-type FVIII (batch MOQ-Hepes-08E; 2.28 mg / ml; 12117 IU / ml); PEGylated FVIII (batch hydrolysable PEG-rFVIII ORHLUFB07001PHR; 1.76 mg / ml; 2498 IU / ml); polysialylated FVIII (batch PSA-rFVIII-11.0 KD NHS; 0.613 mg / ml; 268 IU / ml). Purified LRP1 was obtained from Biomac (Leipzig; Cat no. #04-03).
[0149]Experimental design: Binding of FVIII or its derivatives to LRP1 was assessed using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis using Biacore2000 equipment. Specifications: LRP1 was immobilized on a standard CM5-biosensorchip (Biacore). The flow rate was set at 20 μl / min to avoid potential rebinding due to mass-transfer limitations. Samples were run ...
example 2
[0151]Binding of FVIII to LRP1 is inhibited in the presence of VWF, because LRP1 interaction sites within the FVIII light chain are inaccessible when FVIII is bound to VWF. The present example demonstrates that PEGylation or polysialylation of vWF does not interfere with the vWF-mediated inhibition of LRP1 binding by FVIII.
[0152]Components: Purified recombinant wild-type FVIII (batch MOQ-Hepes-08E; 2.28 mg / ml; 12117 IU / ml); recombinant-wt-vWF (batch ORWSEC06006F1HL; 0.464 mg / ml; 72.1 IU Ag / ml; 20.6 IU RCo / ml), stable PEG-vWF (batch NTT-VWF-600-S2 I; 1.021 mg / ml; 61.4 IU Ag / ml; 41.9 IU RCo / ml); and stable PSA-vWF (batch PSA-RVWF-19.3 KD CAO batch2 (Jun. 10, 2006); 0.0087 mg / ml; 11.3 IU Ag / ml; 0.2 IU RCo / ml).
[0153]Wild-type recombinant FVIII (40 nM) was pre-incubated with various concentrations of vWF (0-400 nM for wt-vWF and PEG-vWF and 0-200 nM for PSA-vWF). Concentrations of vWF were based on protein concentrations and a molecular weight of 250 kDa per vWF monomer. Again, since the...
example 3
[0159]The relationship between the half-life survival rate of FVIII in the presence and absence of VWF was studied in patients with Haemophilia A and Von Willebrand Disease type 3. Haemophilia A patients have a deficiency in FVIII levels, but typically display normal VWF expression. Conversely, patients with Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) type 3 are homozygous for deficient VWF, but show normal FVIII expression. However, despite the normal expression of FVIII in patients with Von Willebrand Disease type 3, plasma levels of the clotting factor are greatly reduced, presumably due to a lack of protection normally provided by stable binding of VWF to FVIII. Thus, it is predicted that administration of a FVIII concentrate to Haemophilia A patients will result in a longer half life of the clotting factor than will administration to patients with Von Willebrand Disease type 3.
[0160]The hypothesis presented above was tested by determining the survival rate of administered FVIII in Haemophilia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com