Dynamic addressing in transient networks
A network address and network technology, applied in the field of computer networks, can solve the problems of unmanageable P2P systems, not very suitable for large-capacity commerce, and not very suitable for secure transactions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
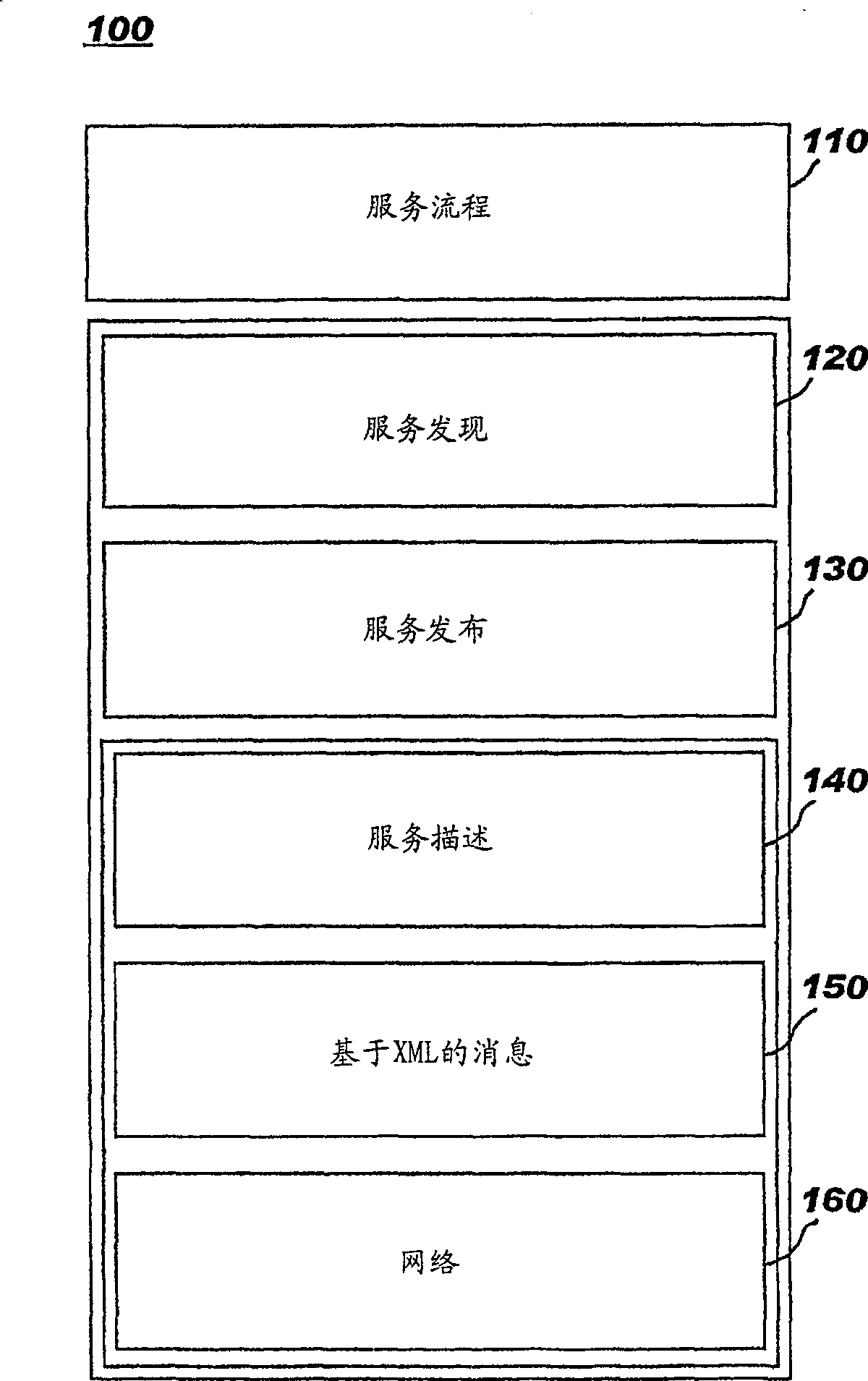
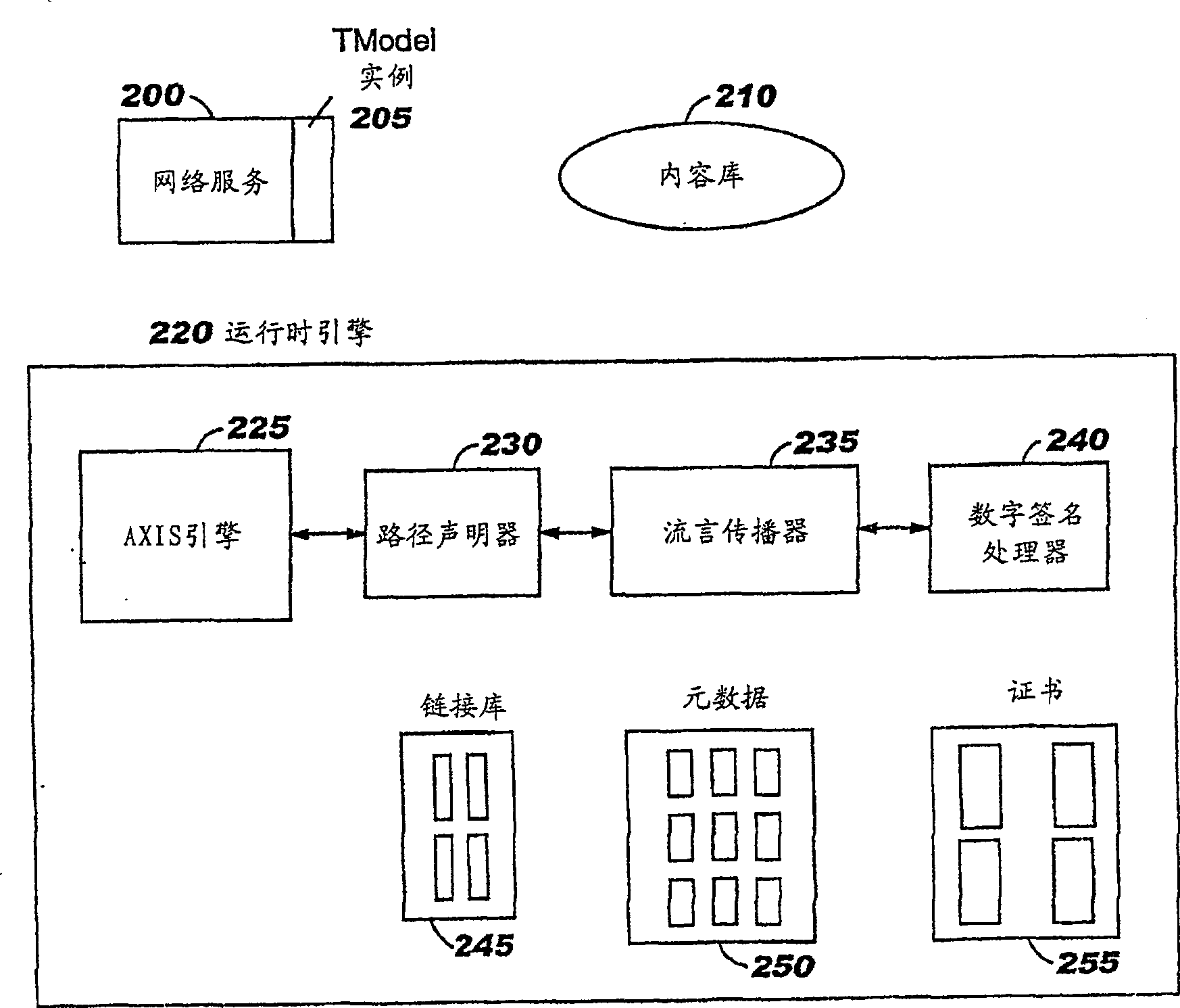
[0031]The implementation(s) described below define techniques to improve the operation of P2P networks. Each network participant (i.e. node) is assigned a permanent identifier such that it can be identified after the node leaves and re-enters the network. The paths taken by content traversing the network are tracked and are persistent. Persisting content path and context node information, as disclosed herein, will enable peer-to-peer relationships to be maintained across launches. Thus, the disclosed technology overcomes the shortcomings of the prior art, enabling relationships between peer devices to persist beyond a single session, even if the community in which participants communicate is a strictly defined transient network.
[0032] The disclosed technology supports the inherent dynamic network addressing characteristic of the P2P network, and provides support for heterogeneous network nodes at the same time. Persistent information can be used to support business enterp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com