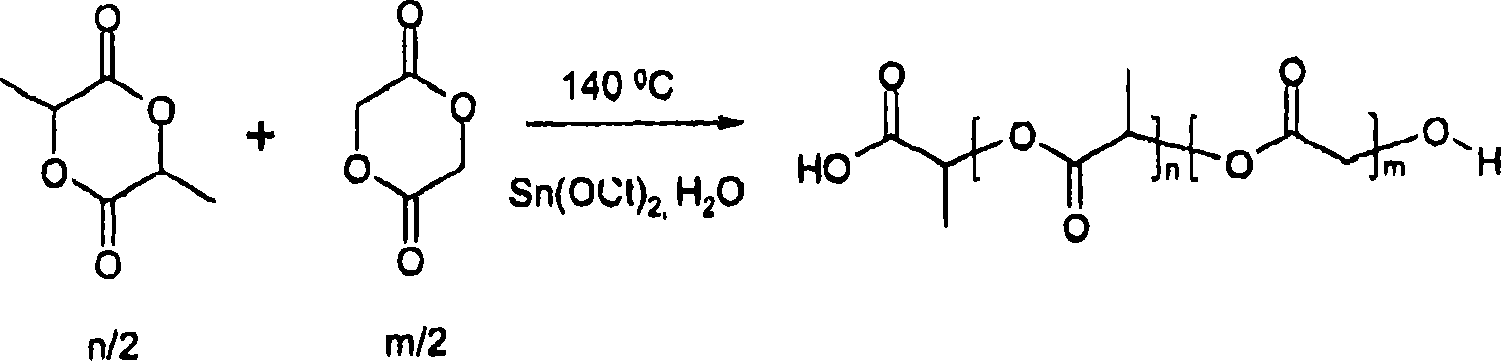A coating for a medical device having an anti-thrombotic conjugate
A conjugate and antithrombotic technology, applied in the field of preparing heparin-bioabsorbable polymer conjugates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Preparation of bioabsorbable polymers with carboxyl-terminated polymers
[0047] A predetermined amount of d,l-lactide (from Purac USA) was transferred to a dry round bottom glass reactor equipped with a magnetic stir bar. A predetermined amount of water and a toluene solution containing stannous octoate were added to the glass reactor. The glass reactor was then sealed with a stopper and cycled between argon and vacuum three times to remove air and oxygen from the reactor. The sealed reactor was then gradually heated to 140°C under vacuum and kept stirring with a magnetic stir bar. Until the reaction was complete, the polymer was dissolved in dichloromethane and precipitated in ethanol and dried under vacuum and low temperature heating. The process is figure 1 Illustrated with a schematic diagram.
Embodiment 2
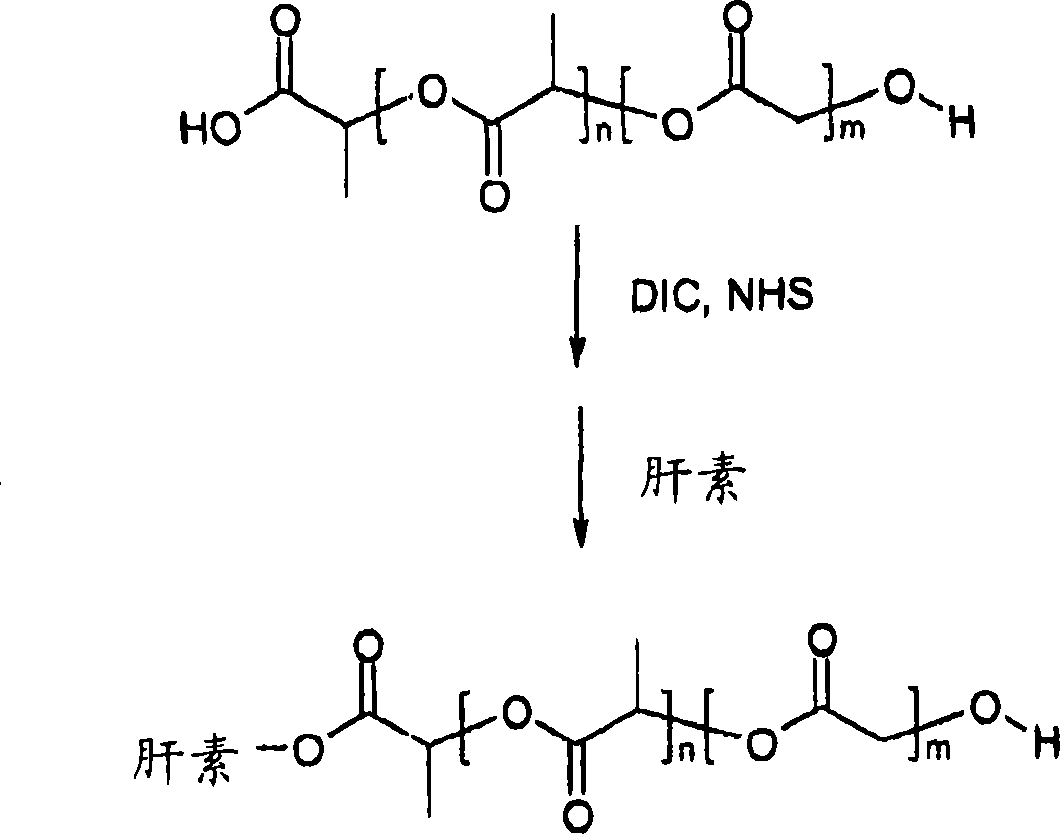
[0049] Preparation of Antithrombotic Heparin-Bioabsorbable Polymer Conjugates
[0050] The bioabsorbable polymer prepared in Example 1 was dissolved in dimethylformamide (DMF), followed by N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC). The molar ratio of PLA, NHS and DCC was 1:1.6:1.6. The resulting solution was kept under vacuum at room temperature for 5 hours. By-product dicyclohexylurea (DCU) and unreacted DCC and NHS were removed by filtration and extraction with water. Then, the activated bioabsorbable polymer was dissolved in DMF and reacted with heparin at room temperature for 4 hours. The final heparin-PLGA conjugate was then precipitated and lyophilized. The process is figure 2 Illustrated with a schematic diagram.
Embodiment 3
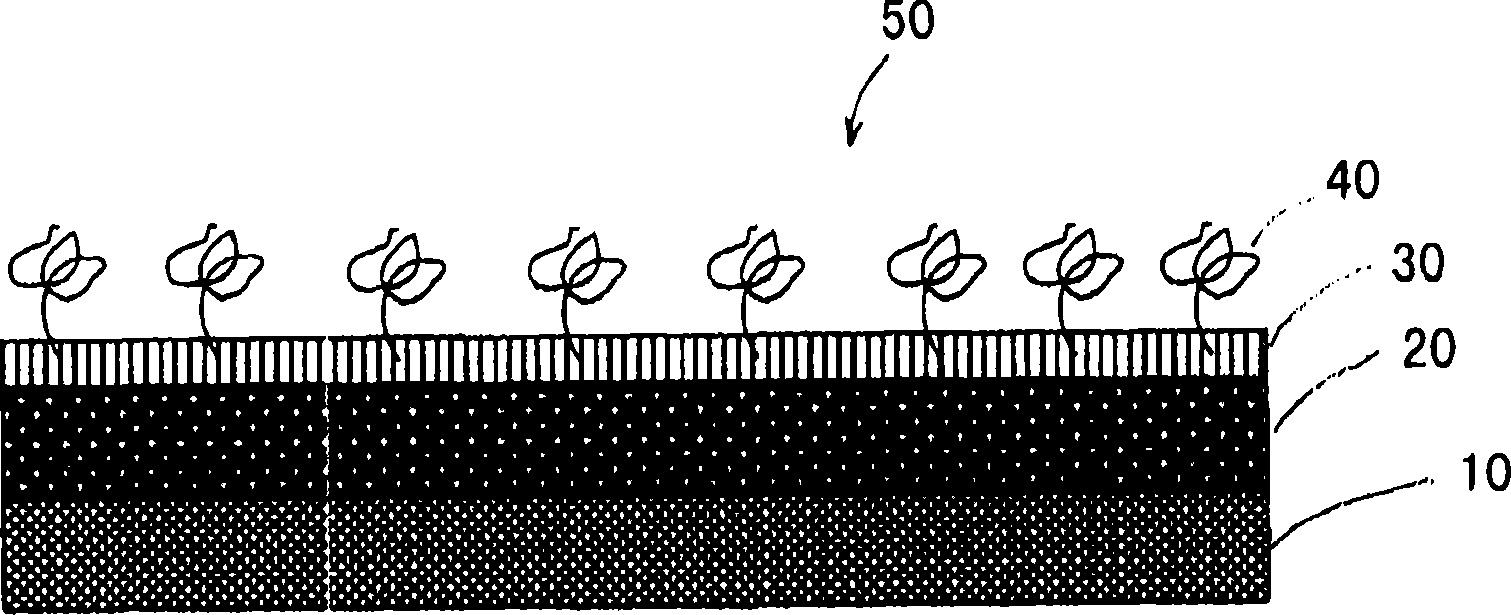
[0052] Coating of a drug-eluting stent having an outermost layer comprising a heparin bioabsorbable polymer conjugate
[0053] A medical device 50 coated in accordance with the present invention is attached image 3 Illustrated with a schematic diagram. The surface 10 of the cobalt chromium stent is sprayed with a drug-containing polymeric solution 20 which may include, for example, ethyl acetate (EA) containing PLGA and rapamycin. The weight ratio of PLGA and rapamycin was 2:1. After the drug-containing layer 20 is dried, a coating solution 30 containing a heparin absorbable polymer conjugate is sprayed on the first drug-containing layer 20 . After drying of the coating solution 30, a thin film with heparin 40 substantially on the outermost surface is obtained. While the invention has been described above with particularly preferred embodiments, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that many modifications and variations can be made without departing from the spi...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap