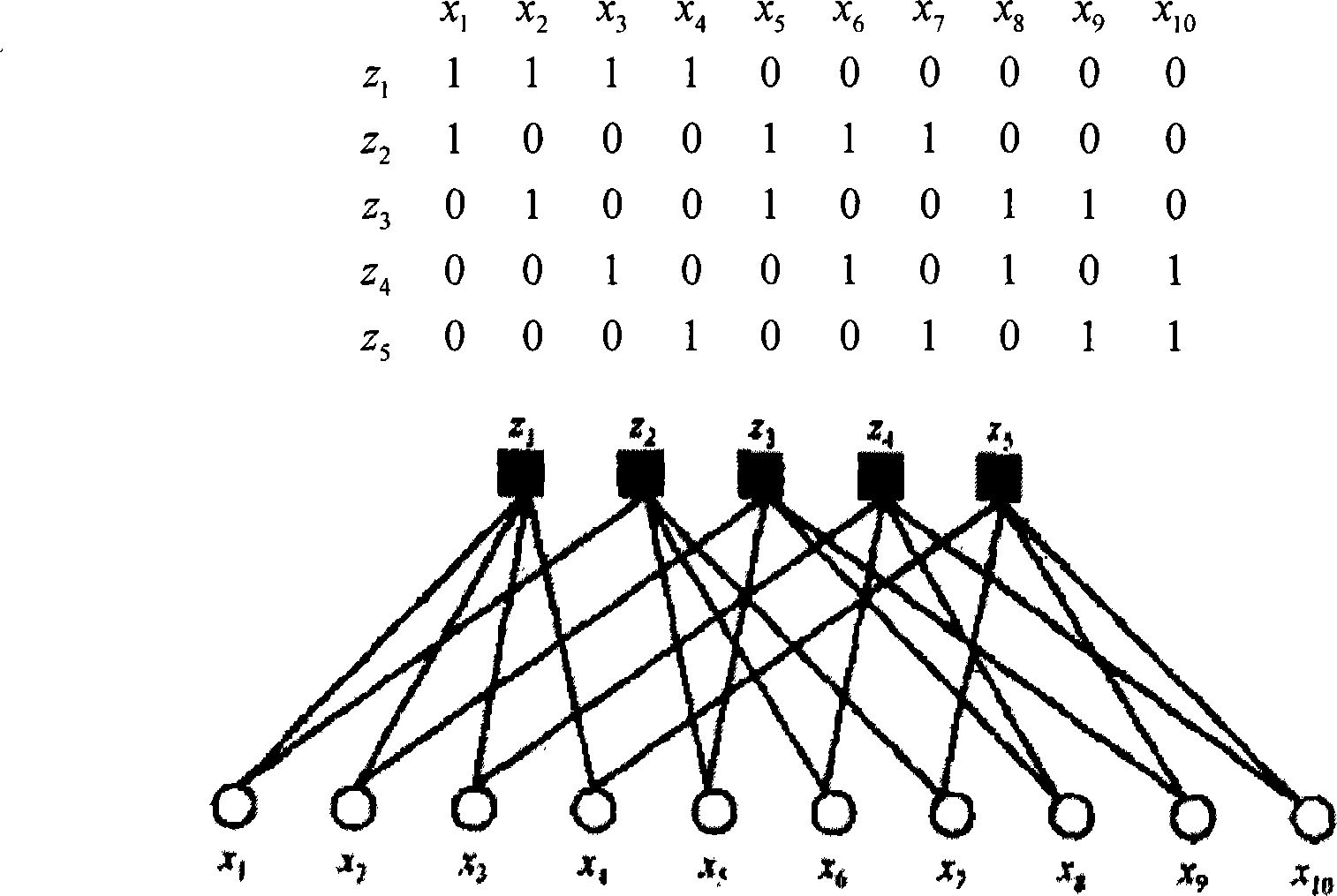
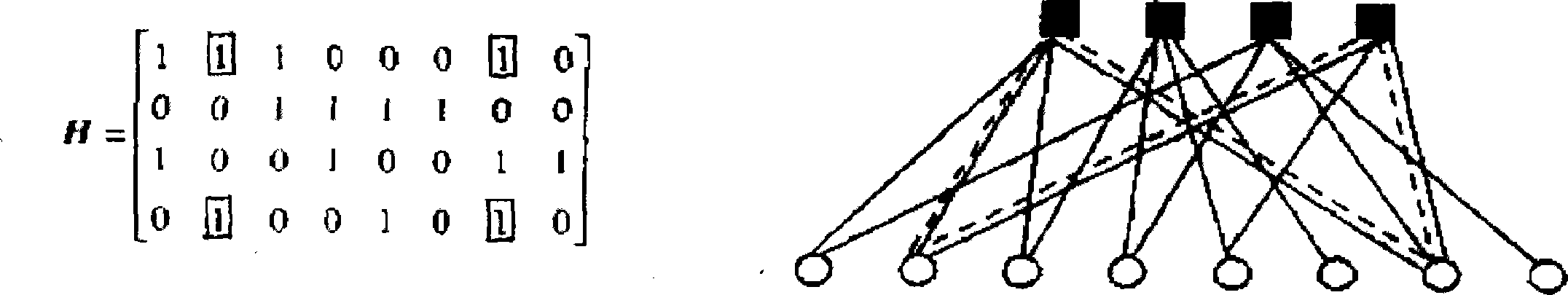
Structured constitution method of high enclose long low code rate multi-scale LDPC code
A technology of LDPC codes and construction methods, which is applied in the field of communication channel coding and decoding, and can solve problems such as inability to reflect superiority
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0033] The first step select m=3, s=2, then q=2 6 = 64;
[0034] The second step is to construct the set B={1, α, α 2 , 1+α+α 2};
[0035] The third step is to construct GF(2 6 ) on the basis matrix of 256×4;
[0036] The fourth step replaces each element in the base matrix with its address vector, and the non-zero elements of the address vector use the original elements in the base matrix to obtain GF(2 6 ) on the final check matrix of 256×252. Although the parity check matrix has more rows than columns, its rank is only 175, so the LDPC code corresponding to this parity check matrix is a 64-ary (252, 77) code, the code rate is 0.3056, and the column weight is 4. And the minimum ring length is 8.
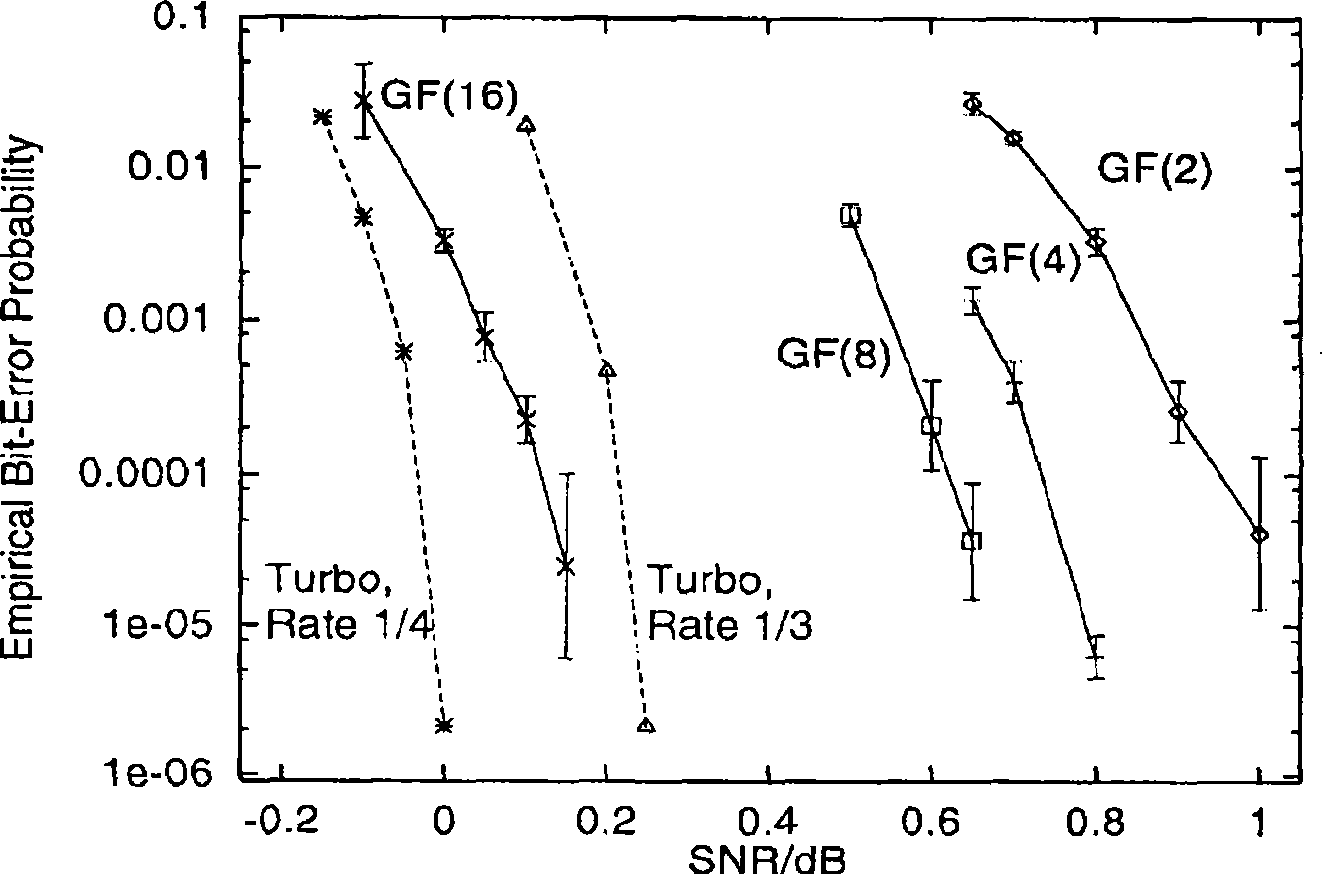
[0037] Figure 4 The performance simulation results of this code are given in , for comparison, in Figure 4 The performance simulation of Mackay random LDPC codes with the same code rate, code length, base number and column weight is also given in . It can be seen from...
example 2
[0039] The first step select m=4, s=2, then q=2 8 =256
[0040] The second step is to construct the set B={1, α, α 2 , 1+α+α 2 , 1+α+α 2 +α 3}
[0041] The third step is to construct GF(2 8 1280×4 basis matrix on )
[0042] The fourth step replaces each element in the base matrix with its address vector, and the non-zero elements of the address vector use GF(2 4 )={γ -∞ , gamma 0 , gamma 1 ,...,γ 14} in non-zero elements. The specific replacement method is as follows: the first position in the address vector corresponds to γ 0 (That is, if the non-zero element in the address vector is in the first position, set this non-zero element to γ 0 , similar to the following), the second position corresponds to γ 1 ,..., the 15th position corresponds to γ 14 , the 16th position corresponds again to γ 0 ……So on and so forth. After replacing the elements in the basis matrix with the address vector, we get GF(2 4 ) on the final parity check matrix of 1280×1024. Although...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com