Data processing apparatus with shadow register and method thereof
A data processing device and data processing technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, register devices, machine execution devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
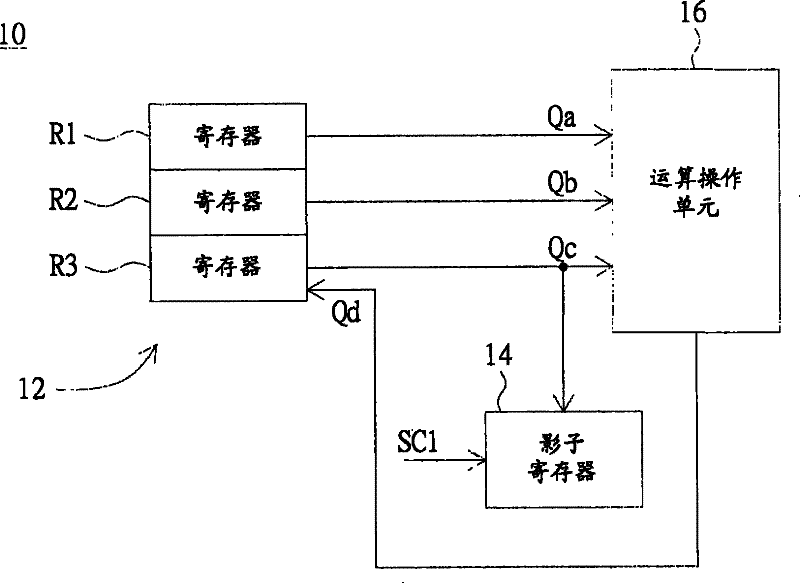
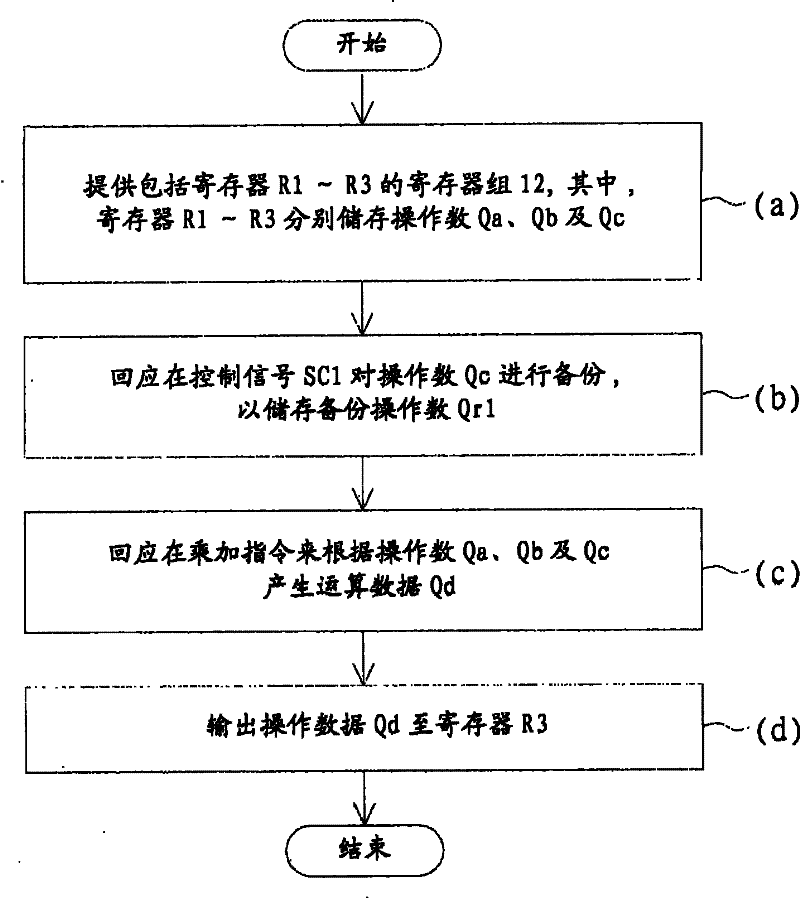
[0029] Please refer to figure 2 , which is a block diagram of a data processing device according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The data processing device 10 includes a register bank (Register Bank) 12 , a shadow register (ShadowRegister) 14 and an operation unit 16 . The register group 12 includes a plurality of registers, and these registers are respectively used to store a plurality of operands. The shadow register 14 is used for backing up the first operand among the operands in response to the first control signal, and storing the first backed up operand. The first operand is stored in a first of these registers. The arithmetic operation unit 16 is used for performing at least one arithmetic operation on the operands in the registers in response to the arithmetic operation instruction to obtain the operational data Qd, and store the operational data Qd in the first register. Next, a case where the data processing device 10 is a multiply-accumulate (ML...
no. 2 example
[0036] Please refer to Figure 4 , which is a block diagram of a data processing device according to a second embodiment of the present invention. The difference between the data processing device 10' of this embodiment and the data processing device in the first embodiment is that the data processing device 10' further includes a logic unit 18 to generate operands Qa', Qb according to operands Qa, Qb and Qc ' and Qc'. In addition, the calculation operation unit 16' in the data processing device 10' performs the calculation: Qd'=Qa'×Qb'+Qc', and outputs the calculation data Qd'.
[0037] The logic unit 18 is further used for receiving operation data Qd', selection signals SS1-SS3 and control signal SC2. The logic unit 18 is used to select one of the operands Qa, Qb, and Qc as the operand Qa' in response to the selection signal SS1, and select the other of the operands Qa, Qb, and Qc as the operand in response to the selection signal SS2. Qb' selects yet another one of the o...
no. 3 example
[0042] Please refer to Figure 5 , which shows a block diagram of a data processing device that fails at the third stage according to the present invention. The difference between the data processing device 20 of the third embodiment and the data processing device 10' of the second embodiment is that the register set 12' additionally includes registers R4 to Rm, wherein m is a natural number greater than 3. Another difference is that the logic unit 18' of the third embodiment transmits the operation data Qd' to one of the registers R4 to Rm when the data processing device 20 intends to perform an operation that needs to refer to the operand Qc.
[0043] For example, the logic unit 18' transmits the operation data Qd' previously stored in the register R3 to the register R4 before transmitting the backup operand Qr1' stored in the shadow register 14' to the register R3. As mentioned above, backup operand Qr1' is substantially equal to the operand previously stored in register R...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap