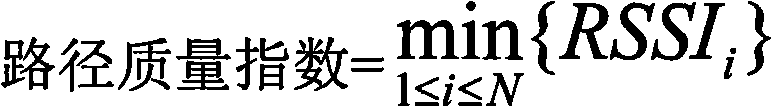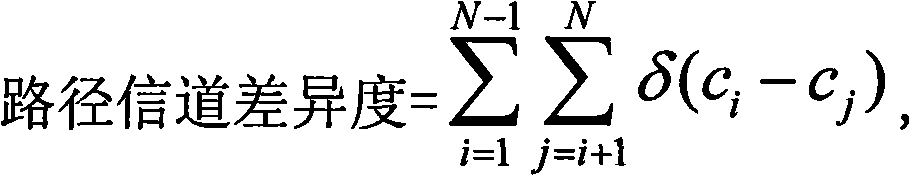Route comparing method for 802.11 multi-interface wireless mesh network router
A multi-interface and path technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of inaccessibility, single factor to be considered, low feasibility, etc., achieve simple path comparison method, improve end-to-end speed, easy-to-get effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] In the following, the present invention will be further described in conjunction with the drawings and specific embodiments.
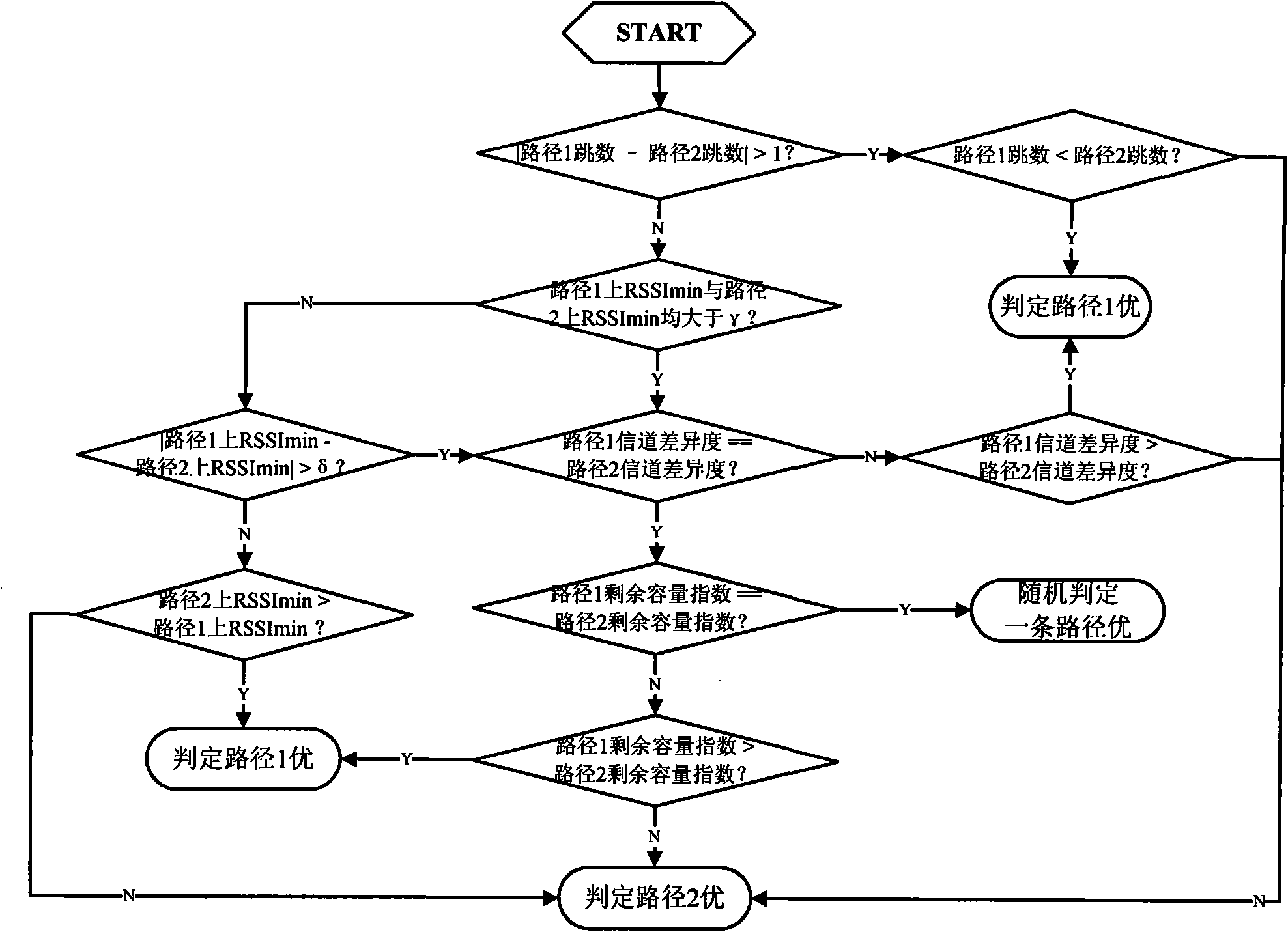
[0029] figure 1 The process of the path comparison method of the present invention is shown: 1) If the hop count difference between the two paths is greater than 1, then it is directly determined that the path with the smaller hop count is the best; otherwise, step 2 is performed; 2) If the path quality index of one of the paths Or the path quality indexes on the two paths are less than a preset first threshold γ, and the difference between the path quality indexes of the two paths is greater than another preset second threshold δ, then the path quality index is directly determined The larger path is the best, otherwise go to step 3; 3) If the channel difference of the two paths is not equal, directly determine the path with the larger channel difference is the best, otherwise go to step 4; 4) If the remaining capacity indexes of the two paths are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com