Sensor node positioning method
A technology of sensor nodes and positioning methods, applied in electrical components, wireless communication, network topology, etc., can solve the problems of high computing resource consumption of nodes to be positioned, algorithms falling into local optimal solutions, and low node positioning accuracy, so as to reduce computing costs. Effects of resource consumption, speed improvement, and burden reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
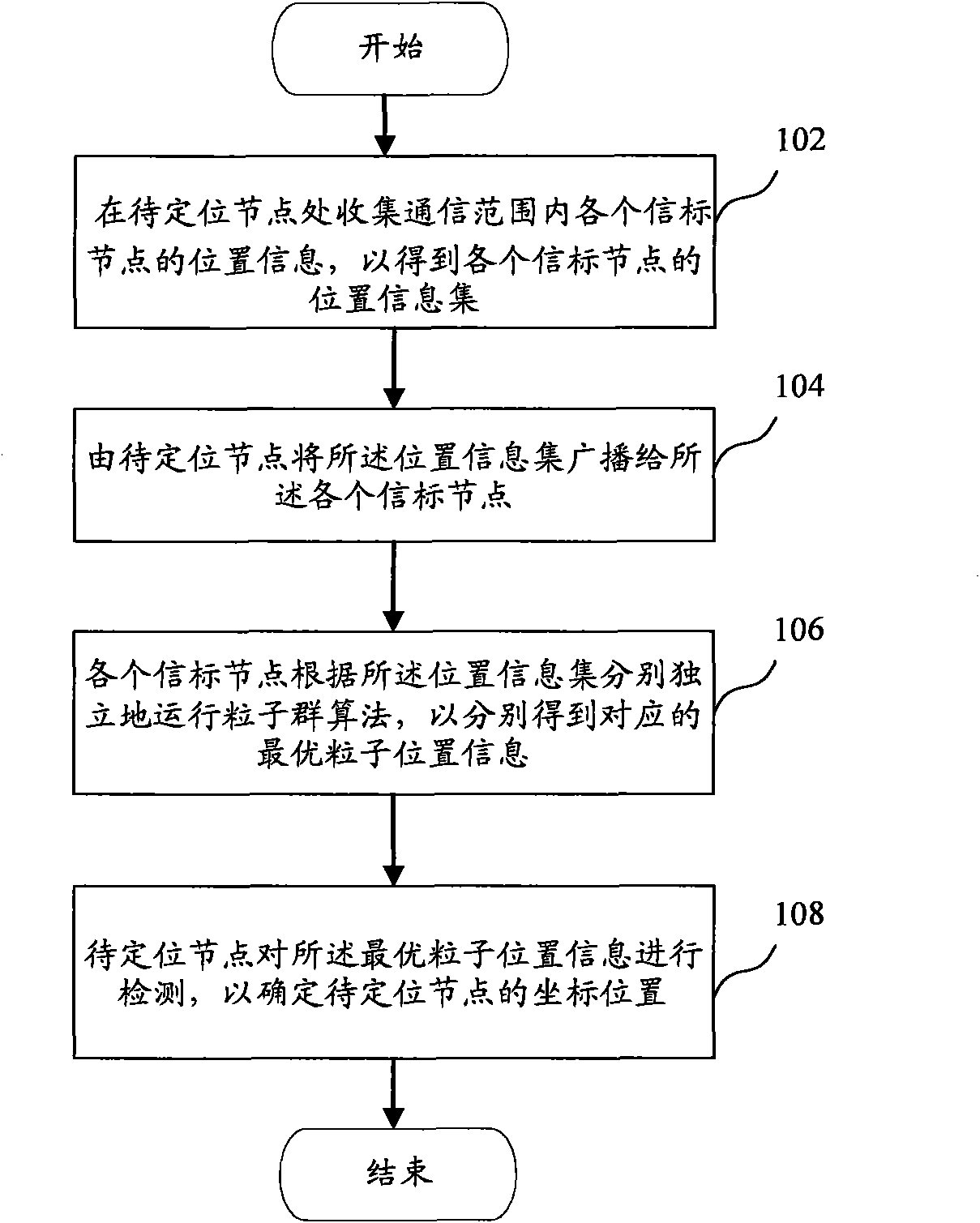
[0043] Embodiment 1: After receiving the coordinates of the optimal particles of all beacon nodes, the node to be positioned calculates the corresponding optimal particle position information of each beacon node according to the optimal particle position information and the evaluation function F. F value.
[0044] Then, find out all the particles satisfying F<ε. The threshold ε can be selected according to actual conditions, such as experimental results, and the threshold ε is generally selected to be between 10 and 30.
[0045] Finally, take the coordinate average of the selected optimal particle position information as the coordinate position of the node to be located. In one embodiment, the position of the node to be positioned is obtained by the following formula:
[0046] x = Σ i = ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2: After receiving the coordinates of the optimal particles of all beacon nodes, the node to be positioned calculates the corresponding optimal particle position information of each beacon node according to the optimal particle position information and the evaluation function F. F value. Then, select the minimum value of F value corresponding to each optimal particle position information as the coordinate position of the node to be located. That is, use the particle coordinates with the smallest F value as the coordinates of the nodes to be located.
[0049] From the experimental data, it can be concluded that compared to using the particle coordinate position with the smallest F value as the position of the node to be located in the embodiment 2, the average value of these particle coordinate positions used in the embodiment 1 will be more accurate.
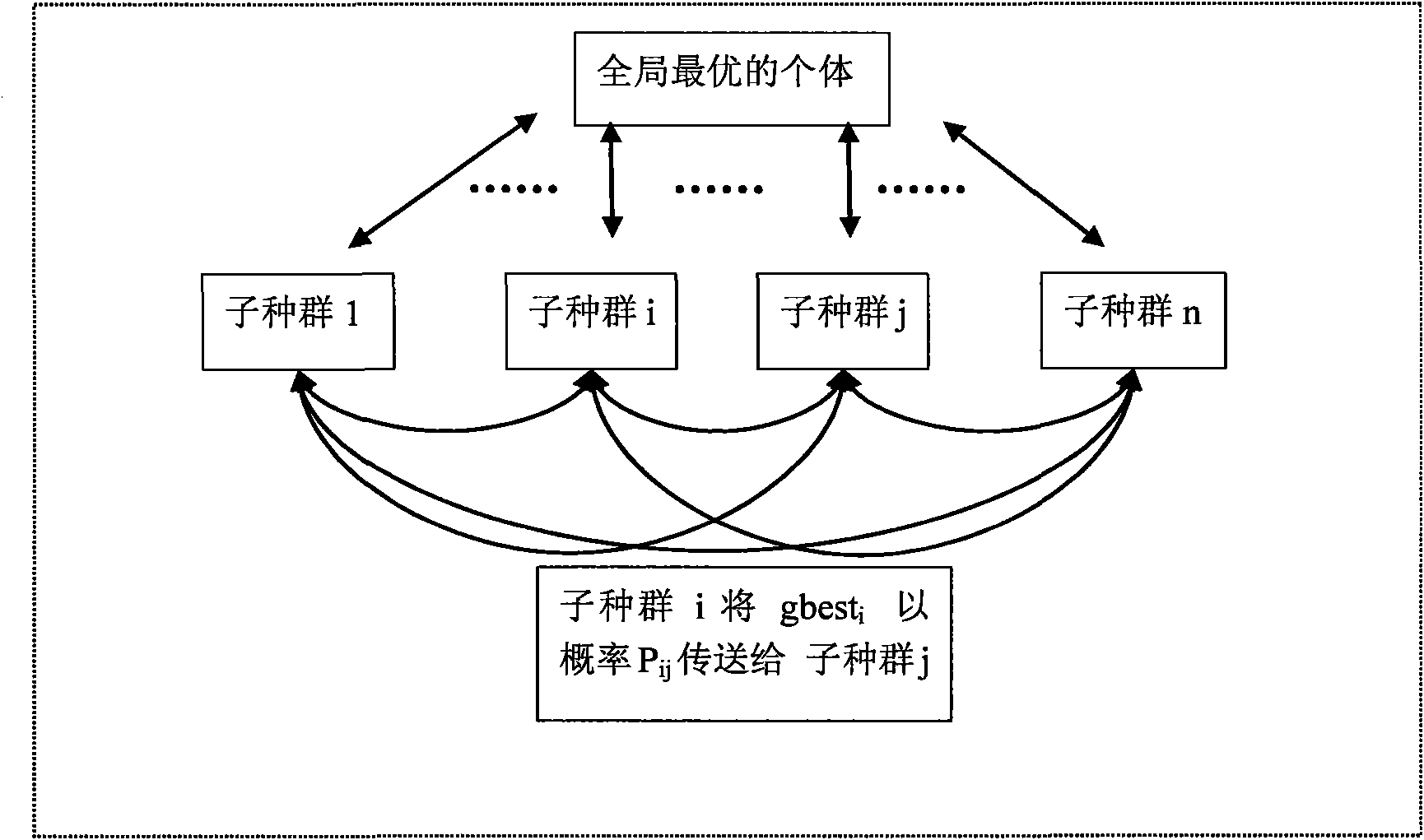
[0050] In step 106, each beacon node corresponds to the obtained phased global optimal particles, and there...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com