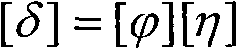Modal modeling method of kinematic system with spatial six degrees of freedom
A technology of motion system and modeling method, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as structural mode leakage, inability to optimize design, and high performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: A modal modeling method for a space six-degree-of-freedom motion system of the present invention, the steps are as follows: firstly, the complex space six-degree-of-freedom parallel motion system is discretized into several substructures, and the substructure Riccati transfer matrix method is used to calculate its front The low-order modal characteristics of the substructure are obtained, and its modal matrix is constructed, and then the physical coordinates are converted into modal coordinates by modal coordinate transformation, and the second-order differential equations of the modal motion of each substructure are established, and then Use the force balance conditions and coordination conditions between substructures to remove redundant degrees of freedom, and carry out modal synthesis on each substructure, so as to establish the overall modal motion equation of the space six-degree-of-freedom parallel kinematic system, and obtain a space-connected six-...
Embodiment 2
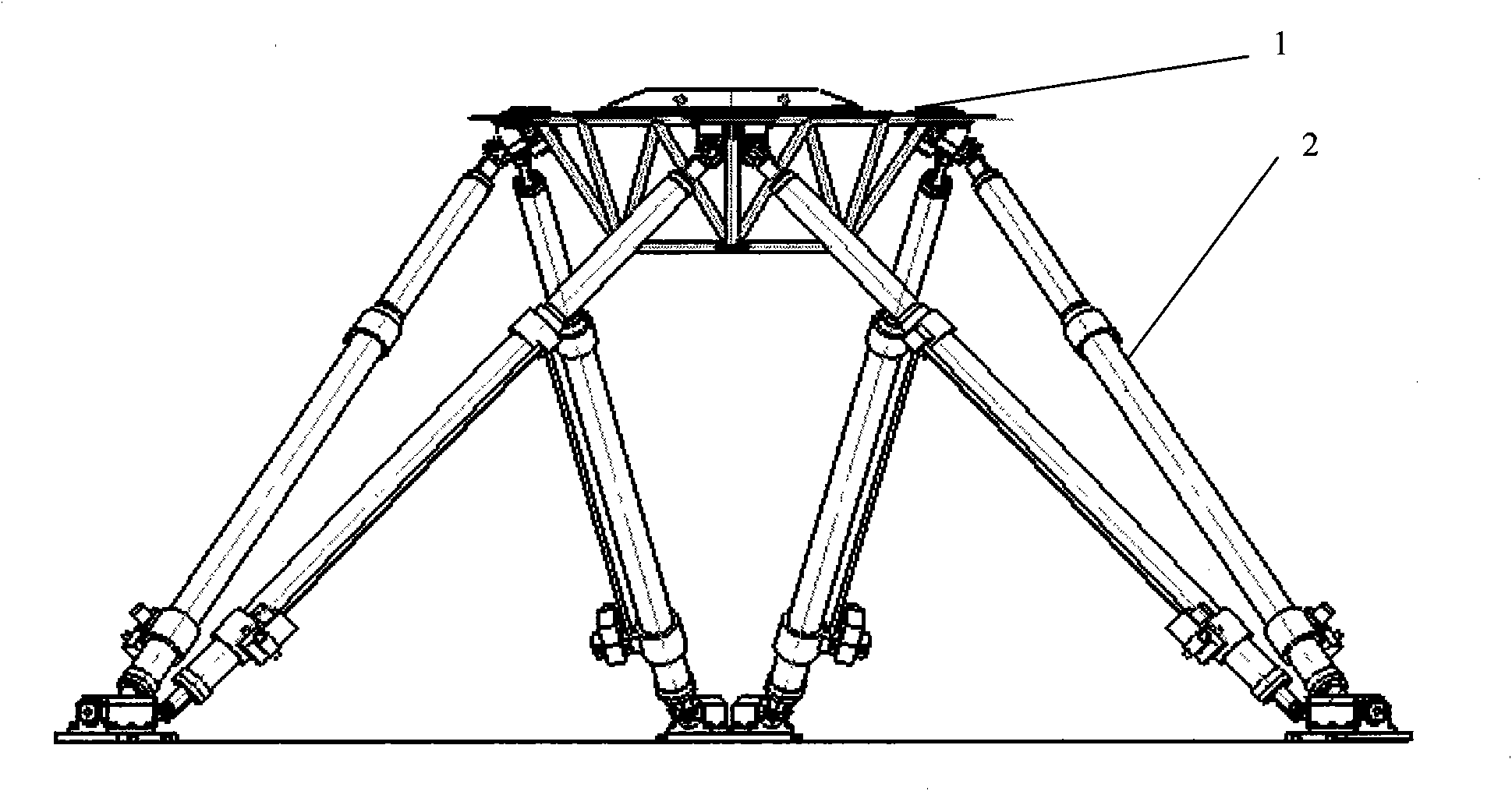
[0080] Example 2: Combining figure 1 , figure 1 It is a composition diagram of a super-large parallel kinematic system for space docking. In the figure: (1): docking platform of the kinematic system of the docking mechanism, (2): driving outriggers.
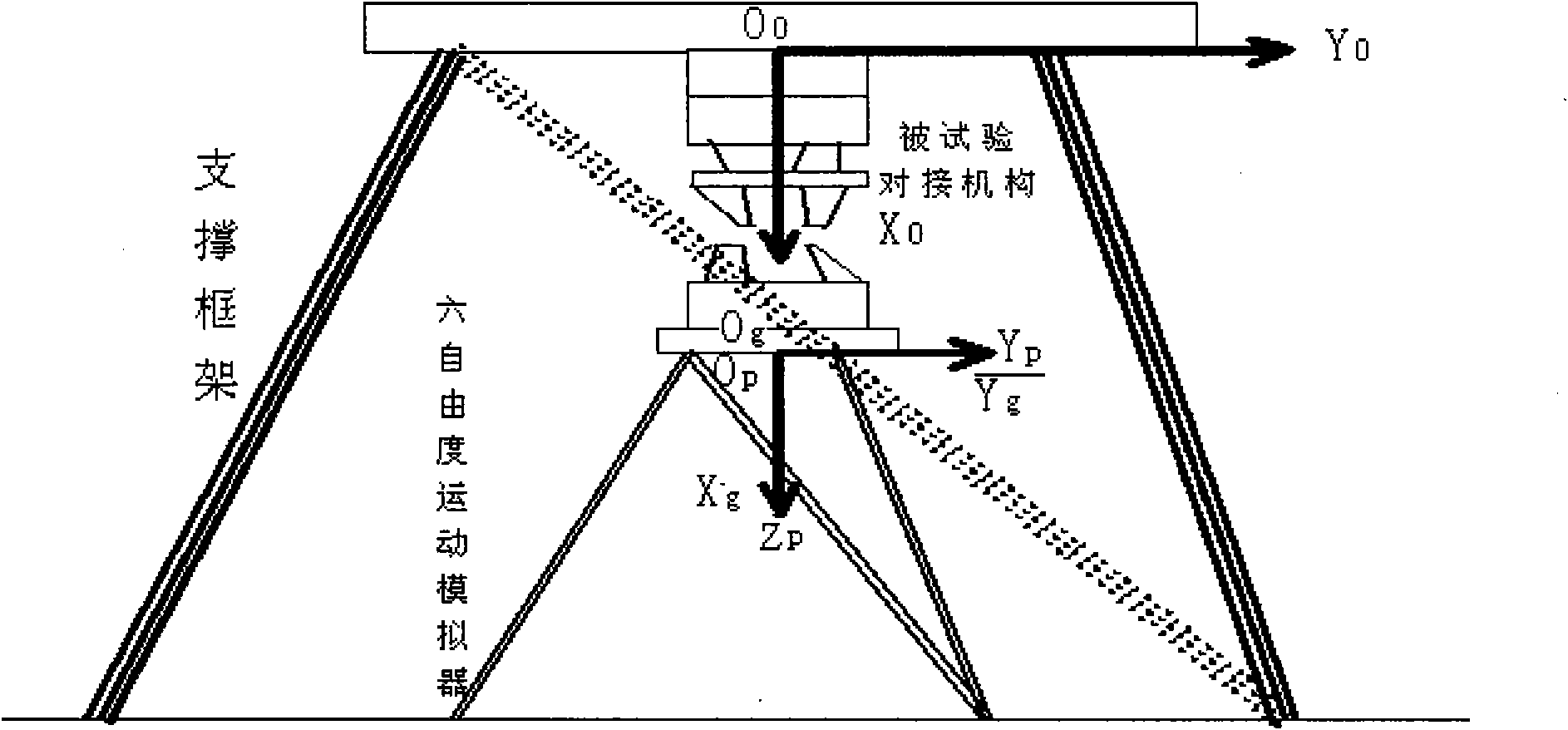
[0081] The super-large motion system of the space docking mechanism is discretely divided into a motion platform with load and 6 super-long outriggers. When performing modal modeling, the physical body coordinates of the kinematic system of the space docking mechanism are established at the combined center of mass of the platform and the load, and the system coincides with the inertial system (earth coordinate system) at the initial position. According to the geometric principle, it can be calculated that the upper hinge point of the kinematic system is in the lower coordinate matrix A of the system and the lower hinge point is in the lower coordinate matrix B of the inertial system. When the kinematic system of the space dockin...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap