Manufacture of edible fiber starch and usefulness of same as dressing/liquid food
A condiment and fiber technology, which is applied in the manufacture of dietary fiber starch and its use as a condiment/liquid food, and can solve the problems of easy separation and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
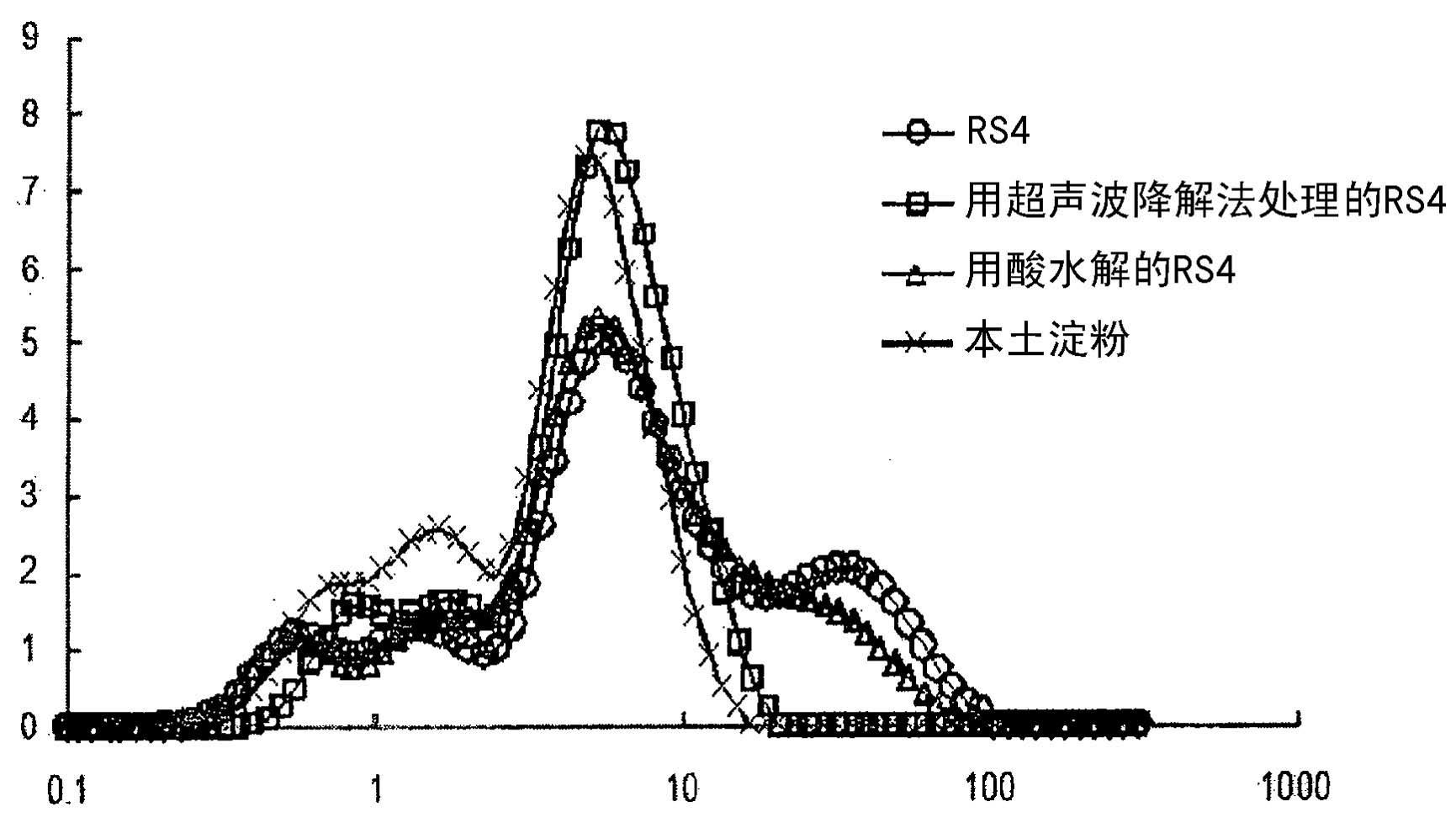
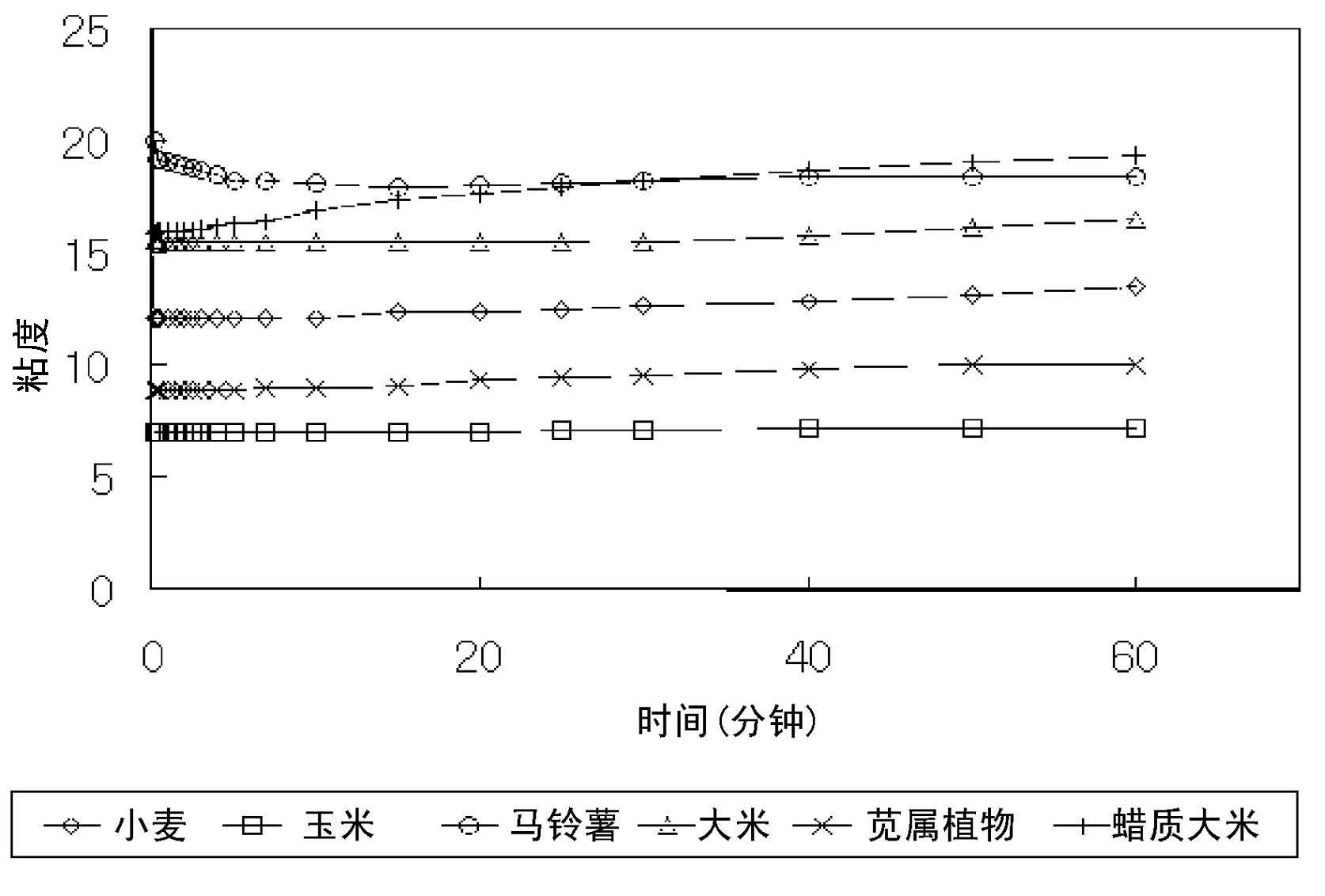
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Separation of starch for the production of fibrous fibers of rice
[0037] (1) Materials
[0038] Local rice, Dongjin No. 1, from KUMSUNG Nong Hyup rice processing plant in Dam-Yang Gun, Jeollanam-Do, Korea, and imported rice from Thailand were used as starch for making fibrous fibers. Starch was isolated from Dongjin No. 1 and Thai rice using alkali soaking or distilled water soaking.
[0039] (2) Analysis of general components in isolated starch
[0040] The water, protein, lipid and ash contents in the rice starch isolated from the above steps were measured. Water content was measured using Misture determination balances (HA-300, Precisa Instruments AG, Switzerland), protein content was measured using the microKelvin method, and lipid content was measured using a Soxhlet apparatus The ash content was measured in a muffle furnace at 550°C using the dry ash method.
[0041] The general compositional results measured in the isolated rice starch are shown i...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2: Stability of starch particles by high temperature heat treatment before crosslinking
[0067] The rice starch solution was prepared at a concentration of 40% (w / w) and heated in a 95°C water bath for 2 minutes. Water was added to make the starch concentration 35% for uniform stirring in the heated starch solution. Due to the partial gelation of starch particles, heat treatment at high temperature and short time stabilized the structure of starch particles, thereby increasing the total dietary fiber content (Table 3).
[0068] table 3
[0069] Dietary fiber content of rice starch heat-treated at high temperature before cross-linking
[0070] .
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3 Manufacture of fibrous fibers by sonication during crosslinking
[0072] Add 10% Na to a 35% rice starch suspension 2 SO 4 , 12% STMP and STPP, adjusted to pH 11.8 with 1N NaOH, and then sonicated for 30 min to control the size of fibrous fibers.
[0073] The starch mixture was reacted at 45°C for 3 hours, its pH value was neutralized at 6.0 using 1N HCl, and the starch mixture was centrifuged after washing four times with distilled water. Then, the starch mixture was dried at 40°C, ground and passed through a 100-mesh sieve to finally obtain fibrous fibers.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com