Debonding a glass substrate from carrier using ultrasonic wave
An ultrasonic and substrate technology, which is used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, electric solid state devices, and semiconductor/solid state devices.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
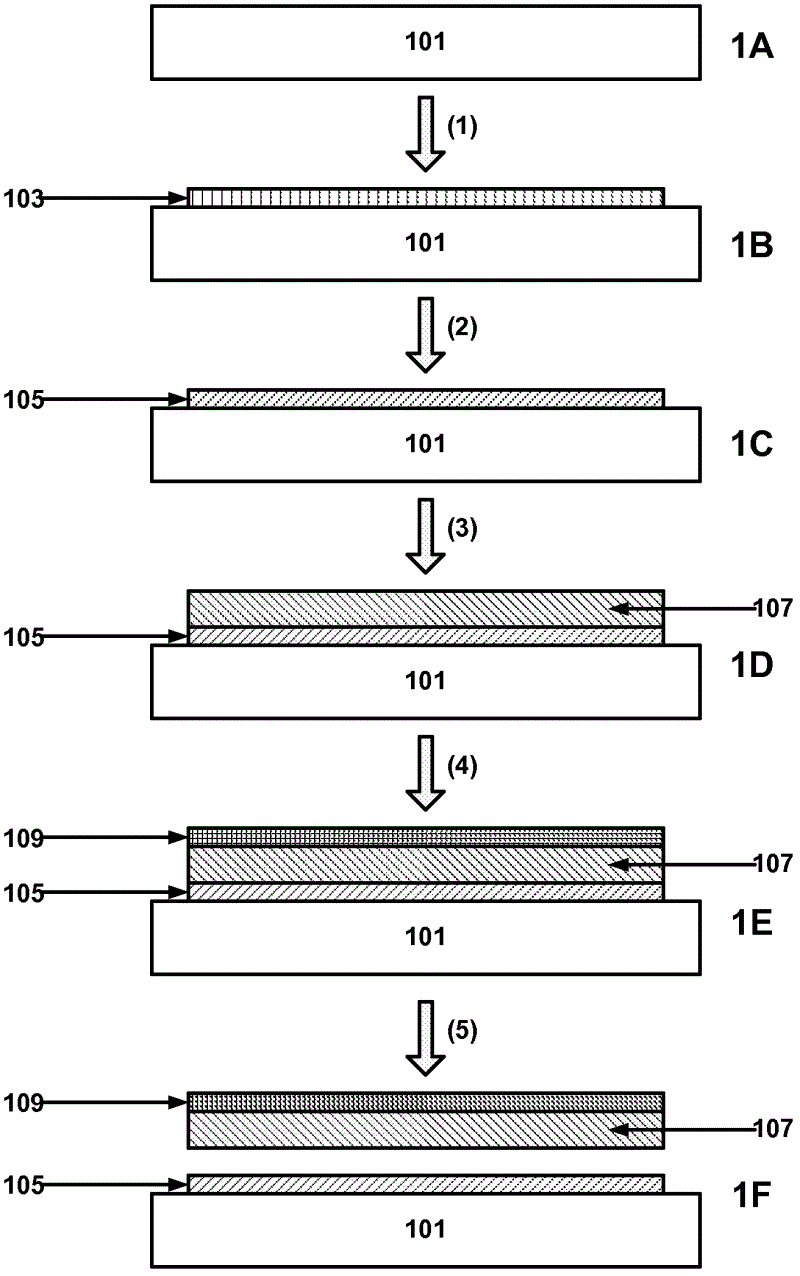
[0105] The functional substrate, temporarily bonded to a carrier substrate using a friable silica inorganic adhesive, was exposed to an aggressive ultrasonic bath. Small cracks and liquid penetration into the bondline were observed. This demonstrates that exposure to ultrasound can weaken the bond between the adhesive and the functional substrate and assist in separation.
Embodiment 2
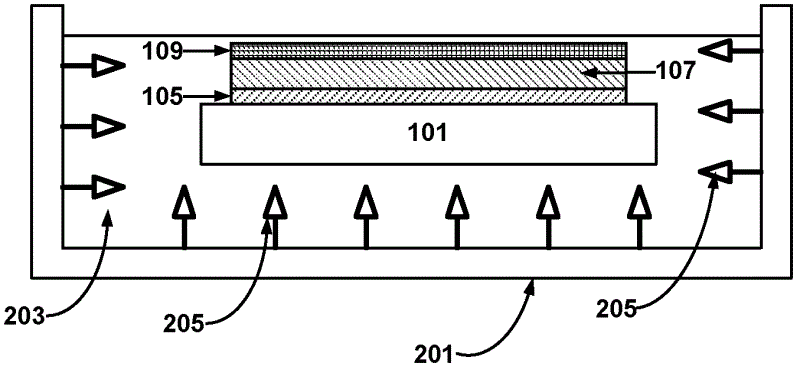
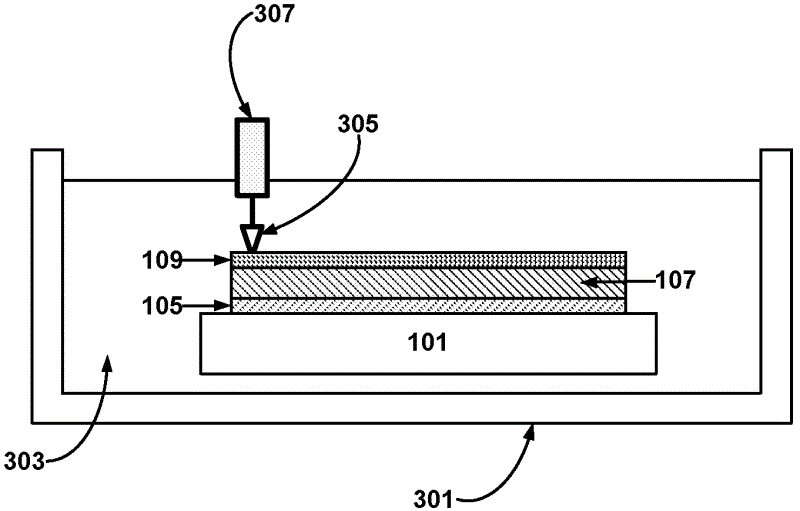
[0107] Use elastic adhesive (surface tension γS=17mJ / m 2 ) The adhesive strength for temporarily bonding the functional substrate to the carrier substrate follows figure 1 The method shown in the water (surface tension γ L =72mJ / m 2 ) in ultrasonic tanks were fabricated and tested without failure. The same equipment was tested in propanol (which has a lower surface tension compared to water (γ L =23mJ / m 2 ) was tested in liquid) and stratification was observed.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com