An antenna calibration method and device in a time-division duplex coordinated multi-point system
An antenna calibration and time-division duplexing technology, which is applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, space transmit diversity, transmitter monitoring, etc., can solve the problems of destroying the uplink and downlink reciprocity of cells, and realize difficulties, so as to improve channel reciprocity Performance, easy to promote, simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0168] The antenna calibration method in this embodiment is specifically described as follows:
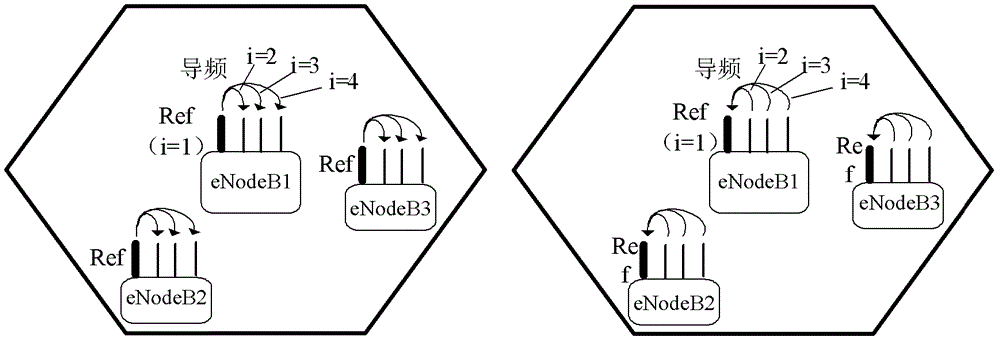
[0169] Step 101: The reference antenna n1 of eNB1 and the reference antenna w1 of eNB2 send pilot signals to the antenna m1 of the CoMP user through the air interface, and the user estimates the channel from the reference antenna n1 of eNB1 to the user reference antenna m1 after receiving the pilot signal information and channel information from the reference antenna w1 of eNB2 to the user reference antenna m1, and feed it back to eNB1.
[0170] Step 102: The antenna m1 of the CoMP user sends a pilot signal to eNB1 and eNB2, and eNB1 and eNB2 only use antenna n1 and antenna w1 to receive the pilot signal, and eNB1 estimates the channel information from user antenna m1 to eNB1 after receiving the pilot signal , eNB2 estimates channel information from user antenna m1 to eNB2 after receiving the pilot signal.
[0171] Step 103: eNB1 obtains correction coefficients on antenna n1 of eN...
Embodiment 2
[0176] The antenna calibration method in this embodiment is specifically described as follows:
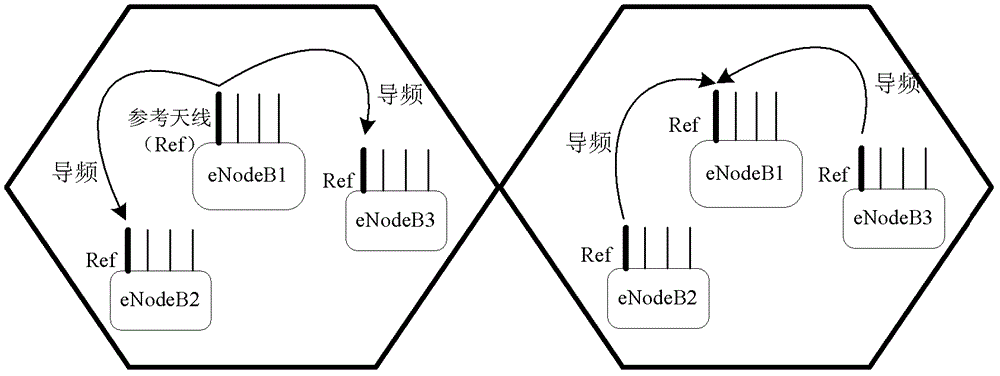
[0177] Step 201: The reference antenna n1 of eNB1 sends a pilot signal to the reference antenna w1 of eNB2 through the air interface. After receiving the pilot signal, eNB2 estimates the channel information from antenna n1 of eNB1 to antenna w1 of eNB2, and feeds it back to eNB1.
[0178] Step 202: The reference antenna w1 of eNB2 sends a pilot signal to the reference antenna n1 of eNB1 through the air interface. After receiving the pilot signal, eNB1 estimates the channel information between the antenna w1 of eNB2 and the antenna n1 of eNB1.
[0179] Step 203: eNB1 obtains correction coefficients on antenna n1 of eNB1 and antenna w1 of eNB2 based on the obtained round-trip channel information between eNB1 and eNB2.
[0180] Step 204: eNB1 notifies eNB2 of the correction coefficient on antenna w1 of eNB2.
[0181] Step 205: eNB1 calibrates other antennas on eNB1 based on antenna ...
Embodiment 3
[0184] The antenna calibration method in this embodiment is specifically described as follows:
[0185] Step 301: The reference antenna n1 of eNB1 sends a pilot signal to the reference antenna w1 of eNB2 through a feeder or a dedicated correction circuit. After receiving the pilot signal, eNB2 estimates the channel information from antenna n1 of eNB1 to antenna w1 of eNB2, And feed it back to eNB1.
[0186] Step 302: The reference antenna w1 of eNB2 sends a pilot signal to the reference antenna n1 of eNB1 through a feeder or a dedicated correction circuit. After receiving the pilot signal, eNB1 estimates the channel between antenna w1 of eNB2 and antenna n1 of eNB1 information.
[0187] Step 303: eNB1 obtains correction coefficients on antenna n1 of eNB1 and antenna w1 of eNB2 based on the obtained round-trip channel information between eNB1 and eNB2.
[0188] Step 304: eNB1 notifies eNB2 of the correction coefficient on antenna w1 of eNB2.
[0189] Step 305: eNB1 calibrate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com