Gas compressor
A technology of gas compressor and driving gas, which is applied in the field of gas compressors, can solve the problems of low compression efficiency and achieve the effect of improving compression efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention.
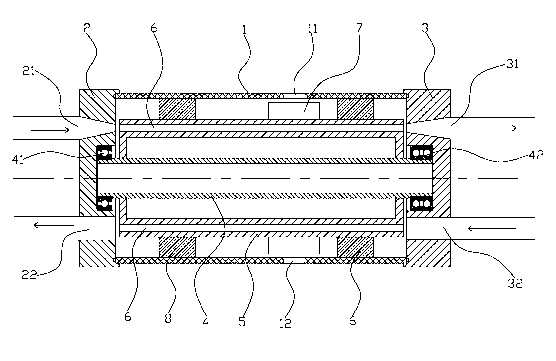
[0018] like figure 1 As shown, a gas compressor provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes a casing 1 with openings at both ends, one end of the casing 1 is in sealing connection with the first end cover 2, and the other end of the casing 1 is connected with the second end cover 3 sealed connection;
[0019] The first end cover 2 and the second end cover 3 are pierced with a rotating shaft 4 located in the casing, the first end cover 2 is fixed with a first bearing 41, and the second end cover 3 is fixed with a second bearing 41. Bearing 42, the two ends of the rotating shaft 4 are respectively connected with the first bearing 41 and the second bearing 42, so as to achieve the purpose of rotationally connecting the two ends of the rotating shaft 4 with the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com