Method and device for coordinating neighbor network interference
An interference coordination and network technology, applied in network planning, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as network resource waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
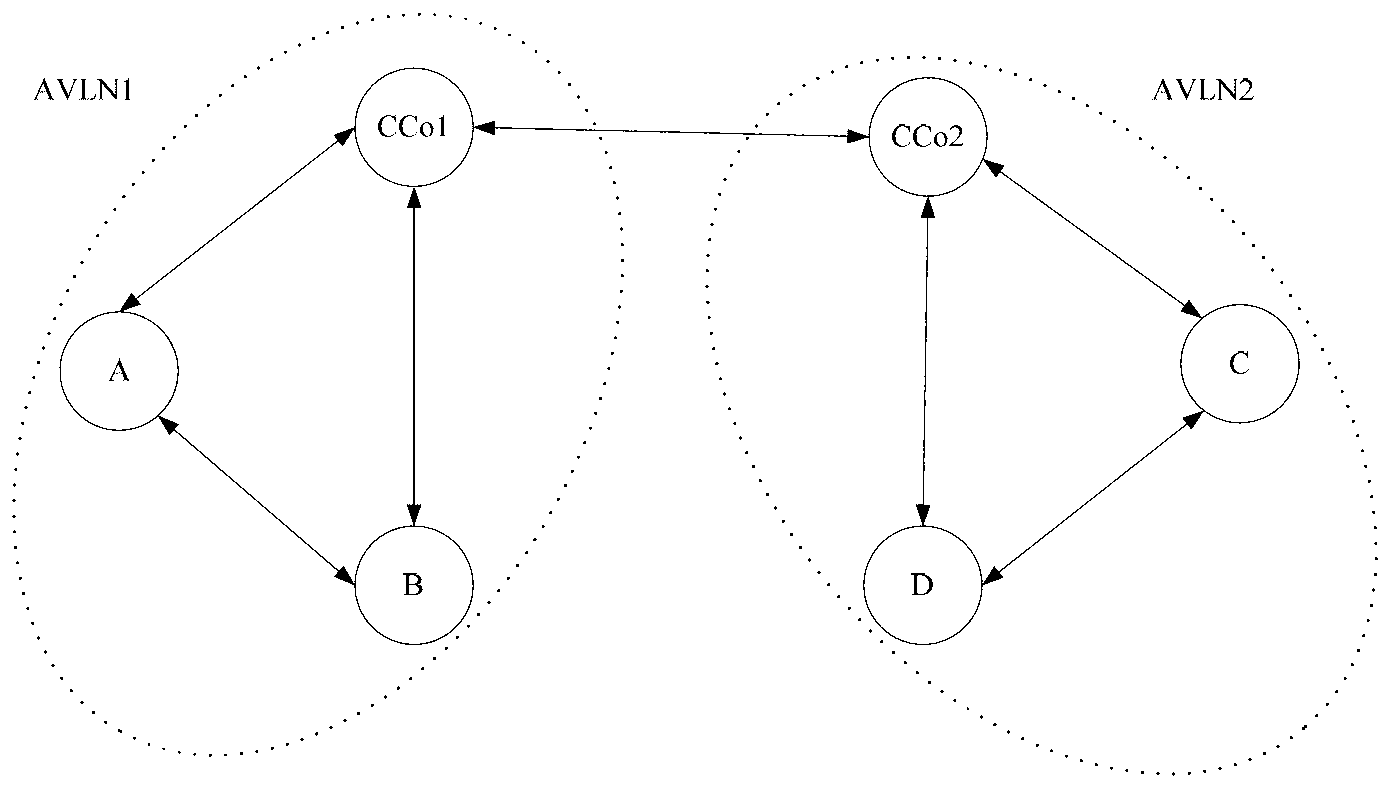
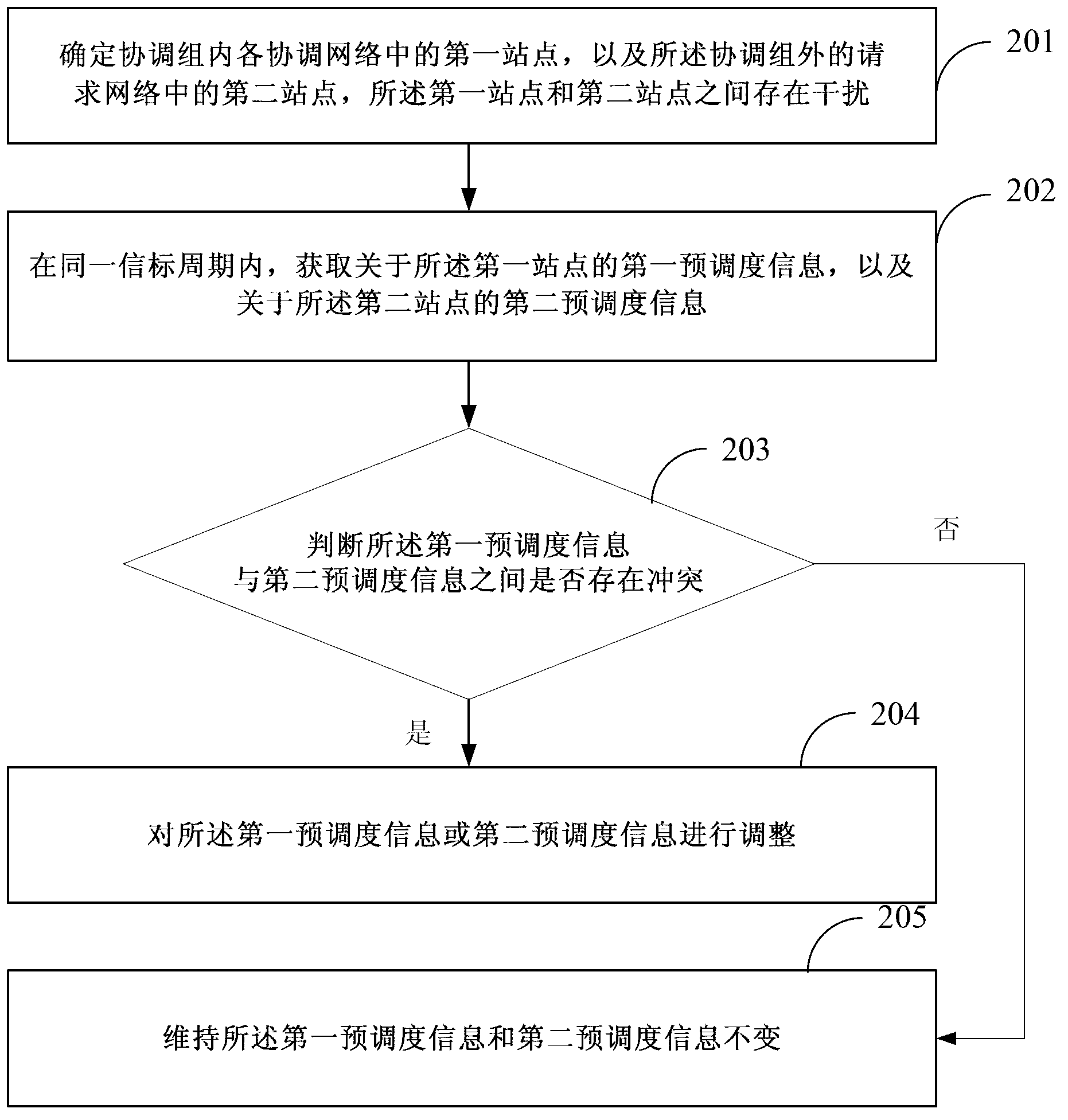
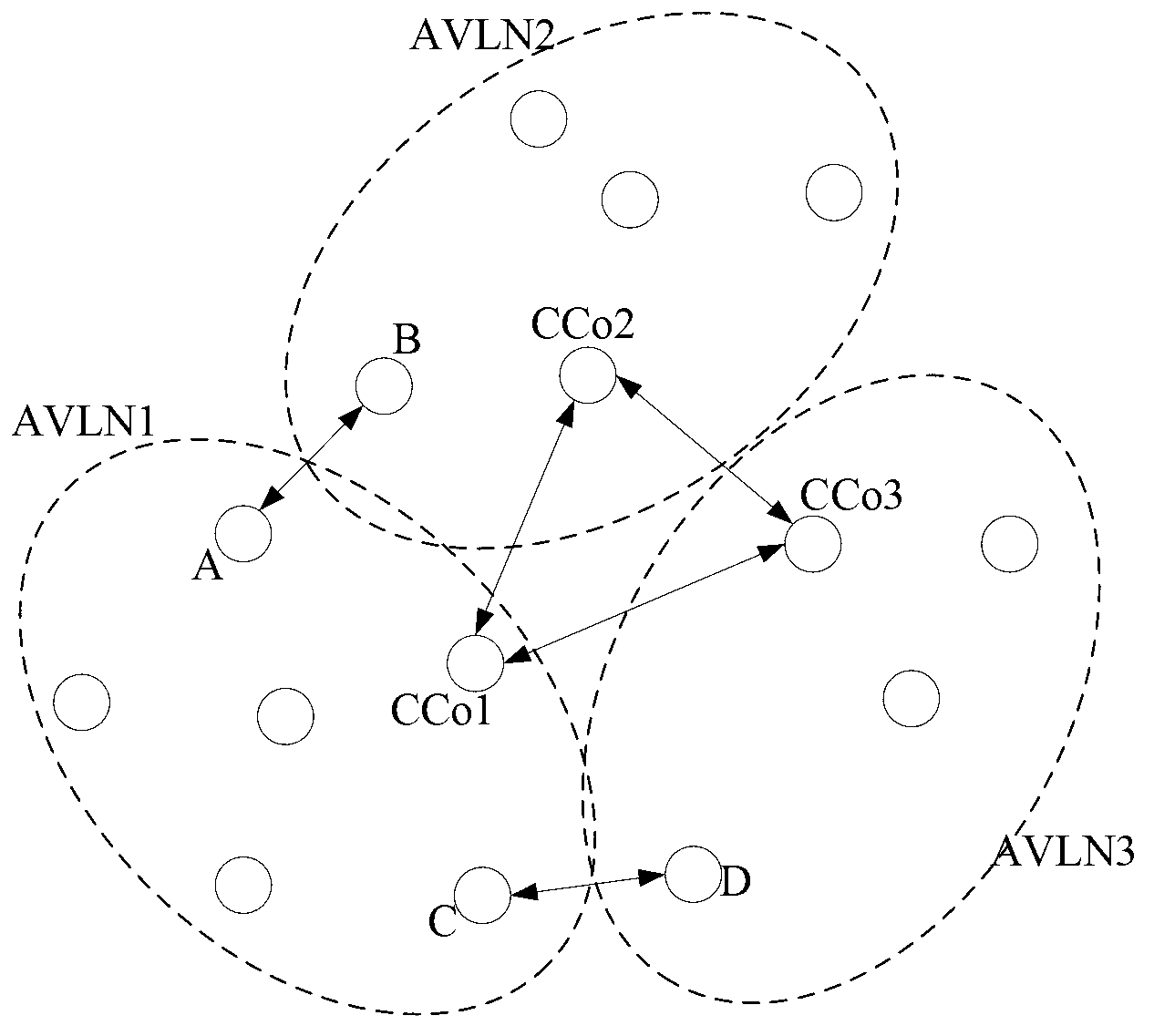
[0141] Such as image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram of a scene for network coordination. Among them, the coordination networks AVLN1 and AVLN2 form a coordination group in coordination mode, CCo1 is the coordinator in AVLN1, CCo2 is the coordinator in AVLN2, and the coordinators CCo1 and CCo2 in the group can hear the central beacon sent by each other. Site A in AVLN1 and site B in AVLN2 interfere with each other, and they are both an interference site and a victim site. The request network AVLN3 was initially in non-coordination mode and did not coordinate with the network in the coordination group. When CCo3 receives the central beacon from the coordination group, it requests to join the coordination group and conduct interference coordination with the coordination group, such as Figure 4 As shown, the specific process of interference coordination is as follows:
[0142] Step 400: CCo3 analyzes which stations in AVLN3 will be interfered by AVLN1 and ANLN2 and / or which statio...
Embodiment 2
[0168] Still with image 3 Take the application scenario shown as an example, a certain GLID may correspond to CSMA allocation. In CSMA allocation, each station accesses the channel through competition, and the coordinator cannot determine in advance which station has access to the channel, and thus cannot determine whether it will conflict with the interfering station in the neighbor network.
[0169] In one case, the GLID2 allocated by CCo3 corresponds to the time period (t3, t4), and this time period is used for contention-free transmission of site D. And CCo3 knows from the NN_GLID_MAC.IND message sent by CCo1 that GLID1 corresponds to competing transmission. Since all nodes compete to win transmission resources, it is impossible to know in advance which site will win in the end, so it is impossible to know in advance which site (or which) will transmit during the period (t1, t2). Therefore, CCo3 cannot know whether site C will transmit during the period (t3, t2), and will c...
Embodiment 3
[0175] In this embodiment, the coordinator will assign a GLID to a certain station, instructing the station to send a discovery beacon in the reserved area. Since the discovery beacon is sent by broadcast, when a site in the network broadcasts the discovery beacon, all other sites (including the victim site in the network) need to receive the discovery beacon. Therefore, if the interference site in the neighboring network also performs Data transmission will cause interference to stations in this network receiving discovery beacons.
[0176] Still with image 3 For example, CCo3 judges whether there is a conflict between AVLN1 and AVLN3. Assuming that CCo1 in AVLN1 is allocated GLID1, the corresponding time period is (t1, t2), which is used for site A to broadcast discovery beacons. CCo3 in AVLN3 is allocated GLID3, and the corresponding time period is (t3, t4), which is used for site D for contention-free transmission, and t1
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com