Prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal infection in mammals
A technology for mammals and gastrointestinal diseases, which can be used in drug combinations, medical raw materials derived from bacteria, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as animal harm.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0022] Higher doses of lactic acid producing bacteria are known to reduce the number of pathogens such as E. coli O157:H7 or Salmonella in cattle. Reducing pathogenic bacteria in cattle can in turn enhance the food safety of meat or milk produced from such cattle. In a preferred embodiment, the dose of lactic acid producing bacteria may be increased to 5 x 10 per mammal per day later in the animal's life, for example about 40 days before said animal is slaughtered. 8 up to 5×10 9 between CFUs. In another embodiment, the at least one probiotic suitable for use in the method of the invention may include Lactobacillus strain NP51 and Propionibacterium strain PF24.
[0023] Brief description of the drawings
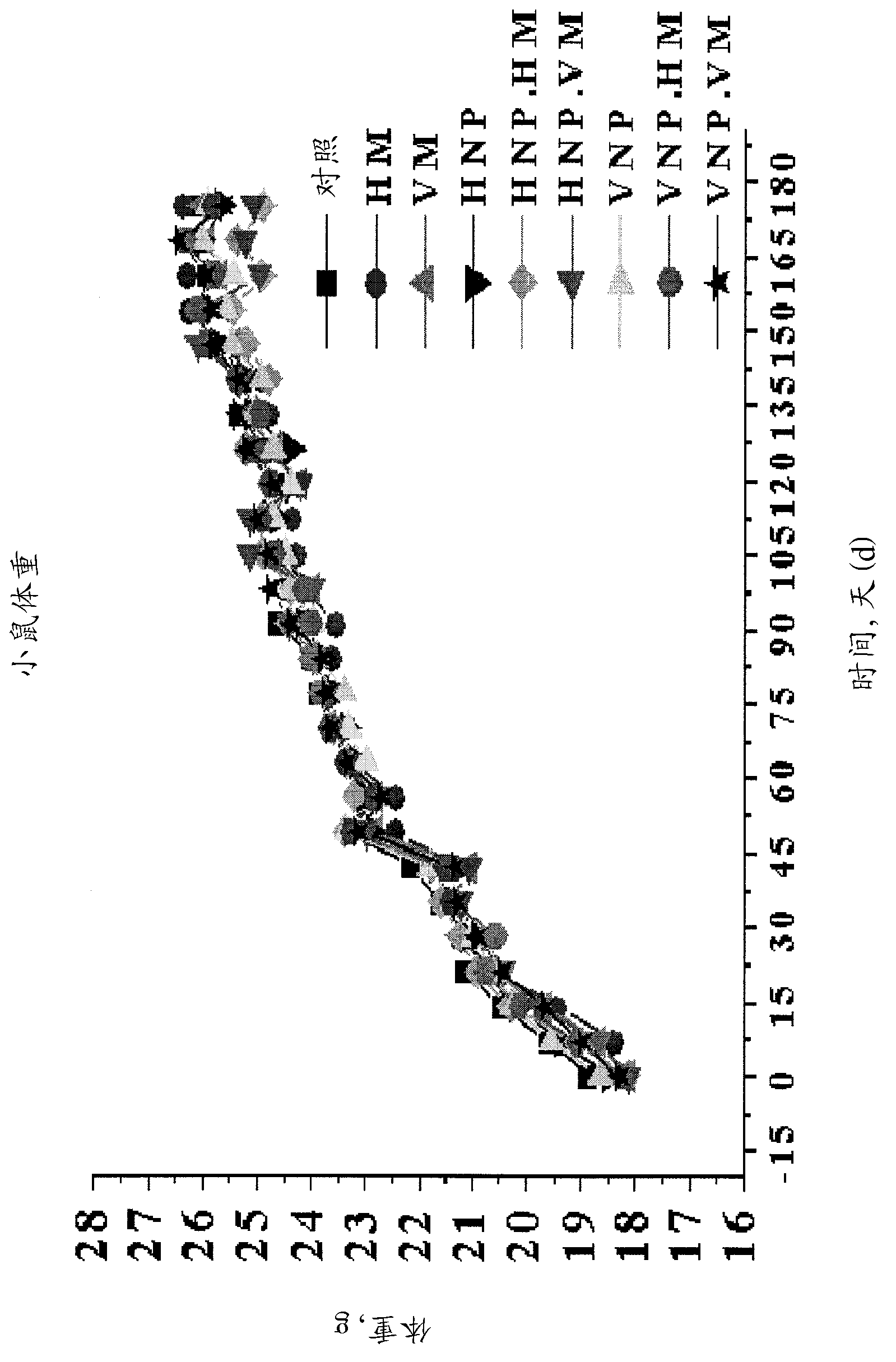
[0024] figure 1 Mouse body weights measured at 15-day intervals from day 1 to day 180 are shown.
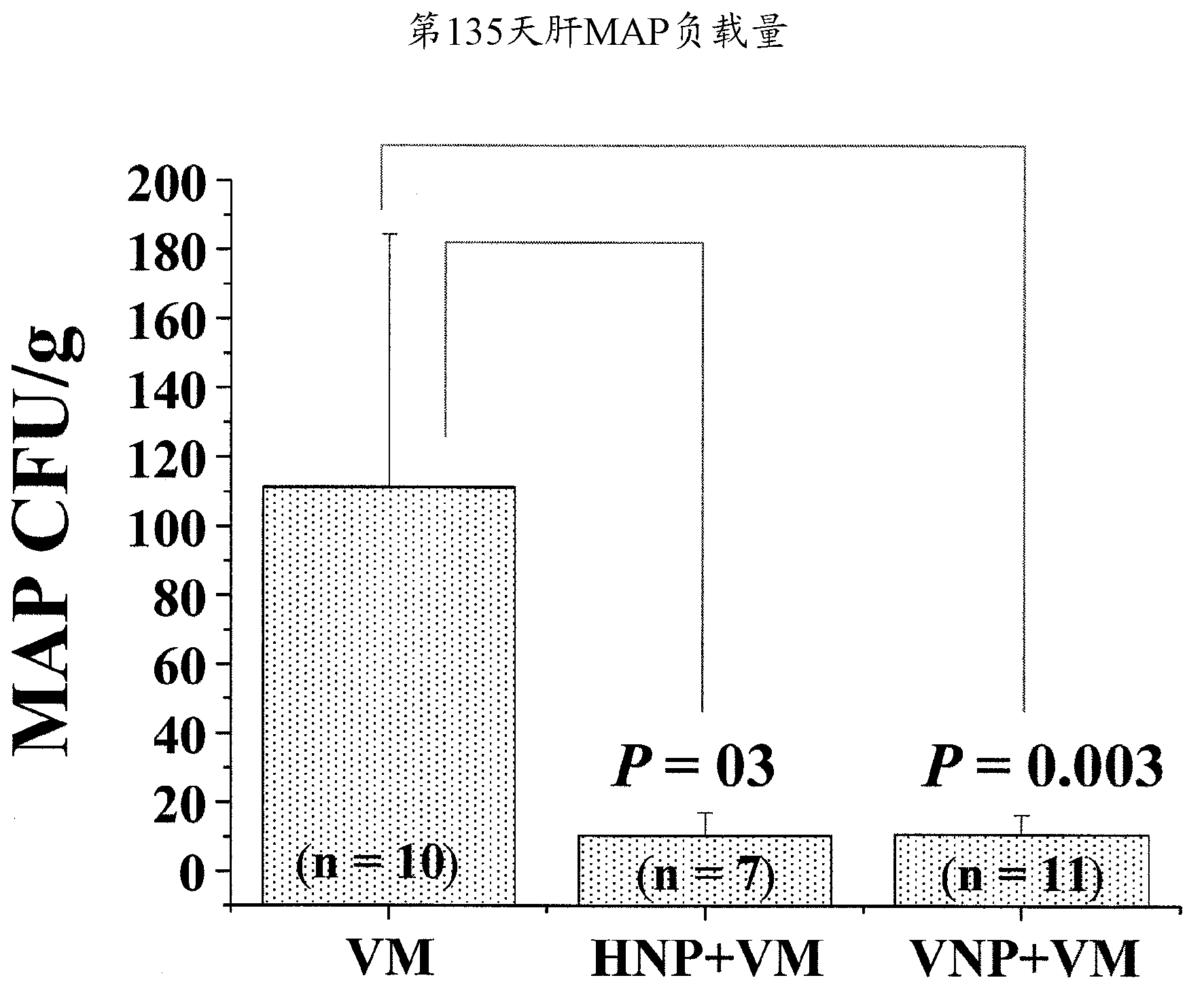
[0025] figure 2 MAP load in the liver of mice treated with VM (live MAP), VM+HNP (heat-inactivated NP51 ) or VM+VNP (live NP51 ) at day 135 is shown.
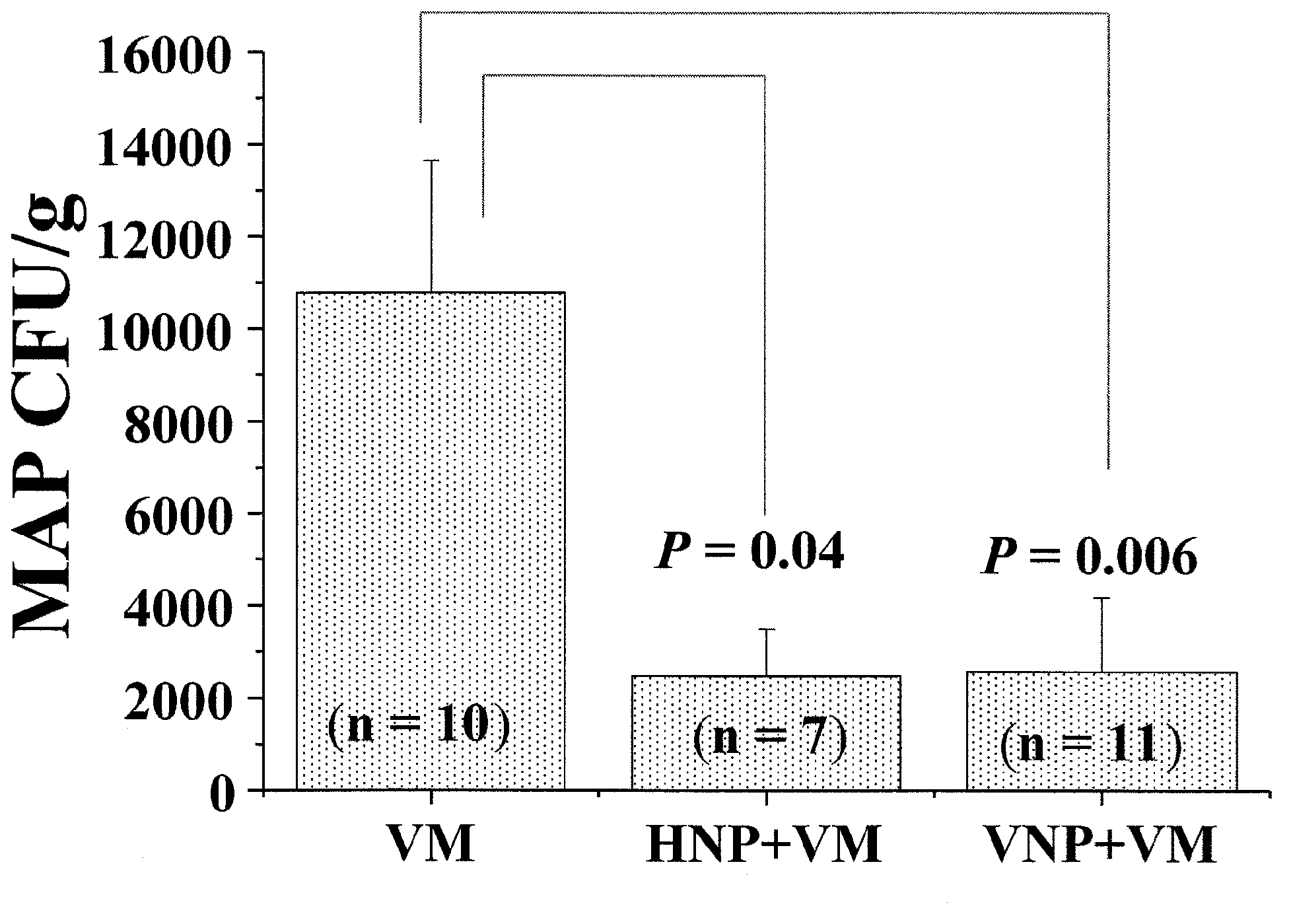
[0026] image 3 MA...
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1. Prevention of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) infection in mice by oral administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus NP51
[0048] Three hundred and seventy (370) Balb / c mice, 185 females and 185 males, were maintained in standard mouse cages with raised wire floors in a pathogen-free environment. From 6 weeks of age, these mice were fed 3-5 grams of sterile chow containing different forms of probiotic NP51 per day until the end of the study, where the dose of probiotic NP51 was about 1x10 per mouse per day. 6 CFU. The NP51 strain was provided by Nutrition Physiology Company LLC.
[0049] Mice were placed on a diet containing the NP51 probiotic for 45 days (day 1 to day 45). On day 45, by intraperitoneal injection with 1 × 10 8 CFU heat-inactivated or live MAP challenged mice. Mice were randomized into 10 treatment groups in a factorial design, which included, for example, mice fed with heat-inactivated or live NP51 and mice challenged wi...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2. NP51 Dosage Study of Balb / c Mice
[0062] To assess the health effects of long-term probiotic supplementation to animals, six-week-old Balb / c mice were fed different concentrations of probiotics over 45 days. The effects of probiotics on the histopathology of GI tissues and the gut microbiota were compared with negative controls (no probiotics fed). The health of these mice was assessed by histopathological analysis, including the following tissues: gastrointestinal tissue (esophagus, small and large intestine and stomach), liver and spleen. For the effect on the diversity of the microbiota, bacterial concentrations in intestinal tissue and fecal pellets were also analyzed.
[0063] During 45 days, 80 mice (10 mice per treatment group) were fed fresh sterile chow with either no probiotics or the inert filler maltodextrin or a concentration of 1×10 4 、10 5 or 10 6 CFU / g of mouse chow of live probiotic (NP51) or the same concentration of heat-inactivated pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com