Acquisition method and device for cross-domain end-to-end route and secondary route computation element
A cross-domain and routing technology, applied in the communication field, can solve the problems of low computing efficiency, poor cross-domain end-to-end optimal routing accuracy, and complicated methods, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
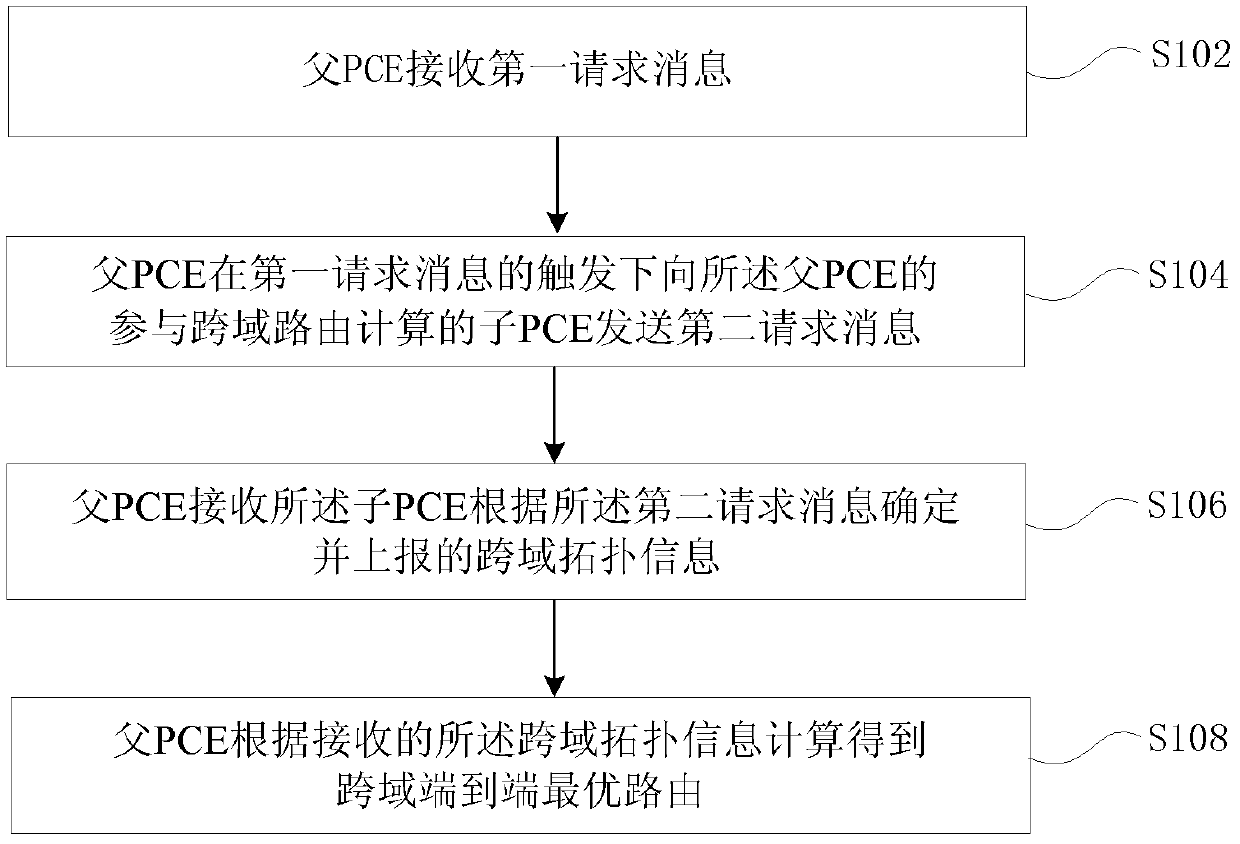
[0081] In order to calculate the optimal route that meets the routing request conditions and domain local policies, the topology of the entire network is composed of the following types of links: inter-domain links; virtual links corresponding to the optimal path in the domain; physical links corresponding to the optimal path in the domain Link: a cross-domain intra-domain link planned in advance by domain local policy (the two endpoints of the link are in the same domain)
[0082] In this embodiment, two types of routing calculation entities are involved, the parent PCE and the child PCE. The parent PCE is responsible for calculating cross-domain end-to-end routes according to the network topology of the entire network. The sub-PCE is responsible for calculating intra-domain routes according to the network topology of the domain it serves. A sub-PCE is allowed to serve multiple domains, that is, to calculate intra-domain routes for multiple domains.
[0083] Considering tha...
Embodiment 2
[0099] This embodiment relates to a connection-oriented network, including a connection-oriented packet switching network Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS for short), such as MPLS / MPLS_TP (Transport profile, transport plane) network, Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy, SDH for short). ) network, Optical Transport Network (OTN for short), etc., are technologies for computing cross-domain end-to-end optimal routing in a connection-oriented multi-domain network.
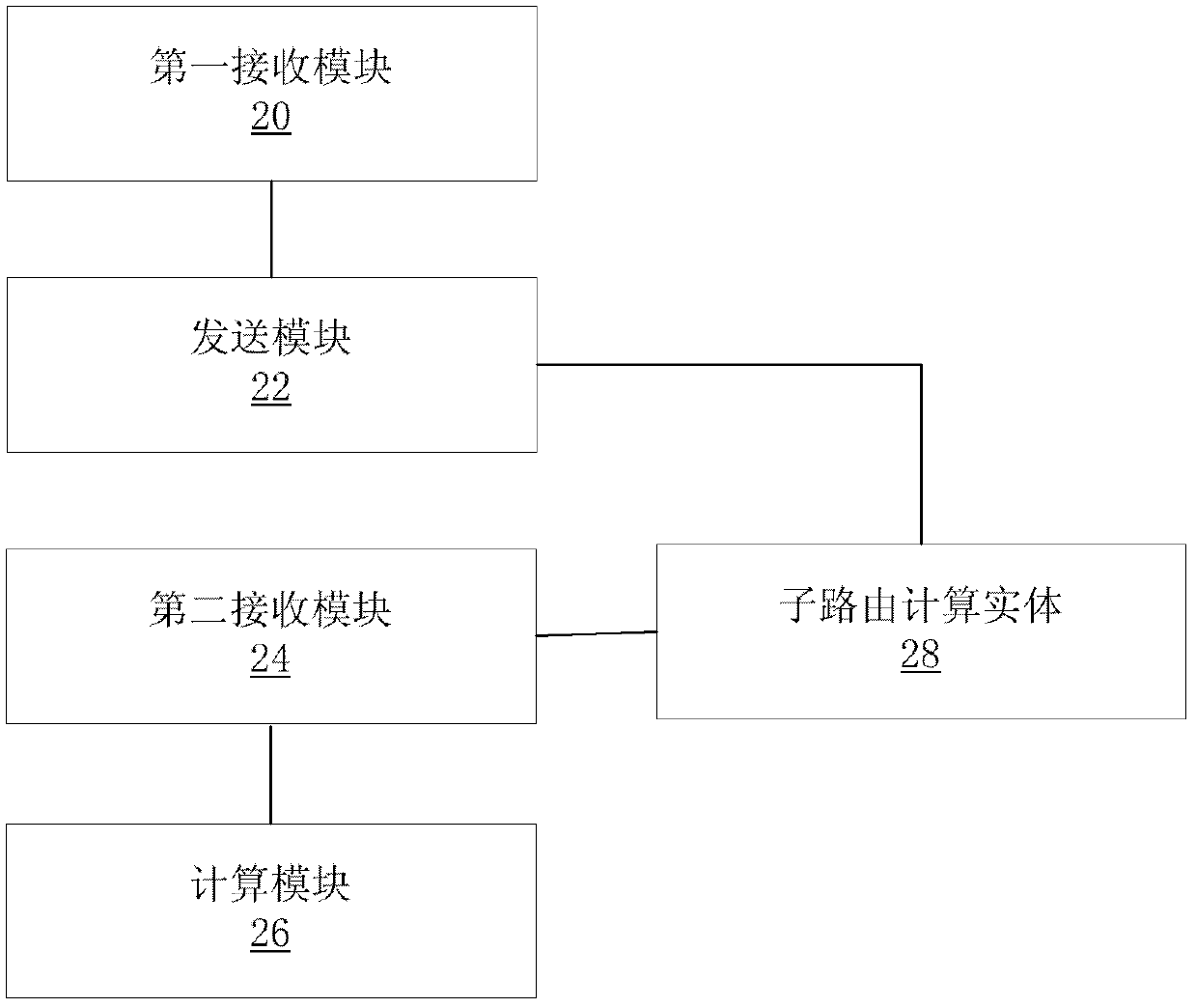
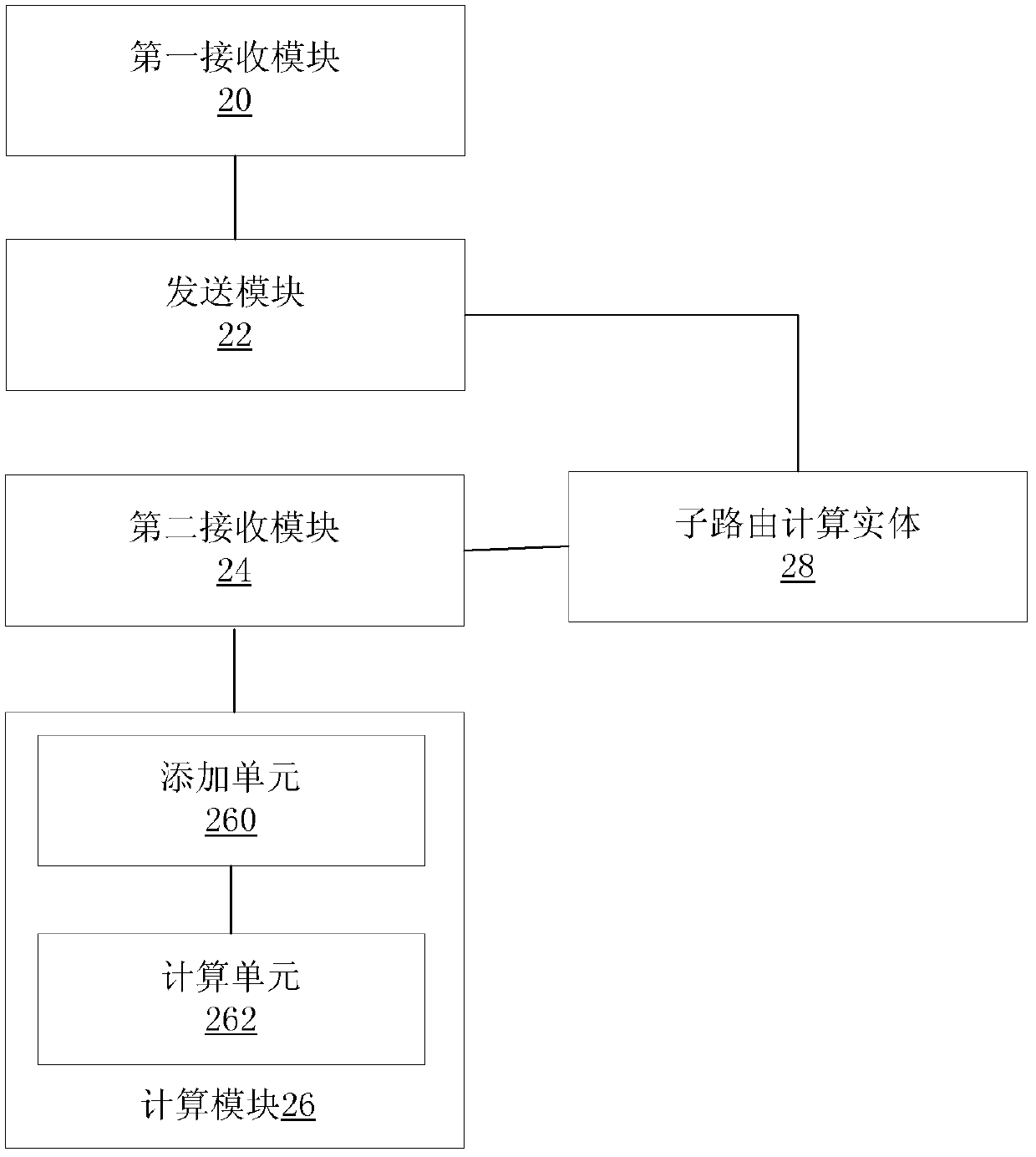
[0100] In this example, if Image 6 As shown, the parent PCE and the child PCE run on different servers, and the parent PCE has been configured with {Domain1, child PCE1}, {Domain2, child PCE2}, {Domain3, child PCE3}, {Domain4, child PCE4}, { Domain5 and sub-PCE5} respectively correspond to domain information and sub-PCE information, the domain information includes a domain identifier, and the sub-PCE information includes a sub-PCE identifier and a corresponding communication address.
[0101...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com