A method and system for obtaining user personalized features
A technology for users and user groups, applied in the Internet field, can solve problems such as updates, semantic differences and cumbersomeness of personalized information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
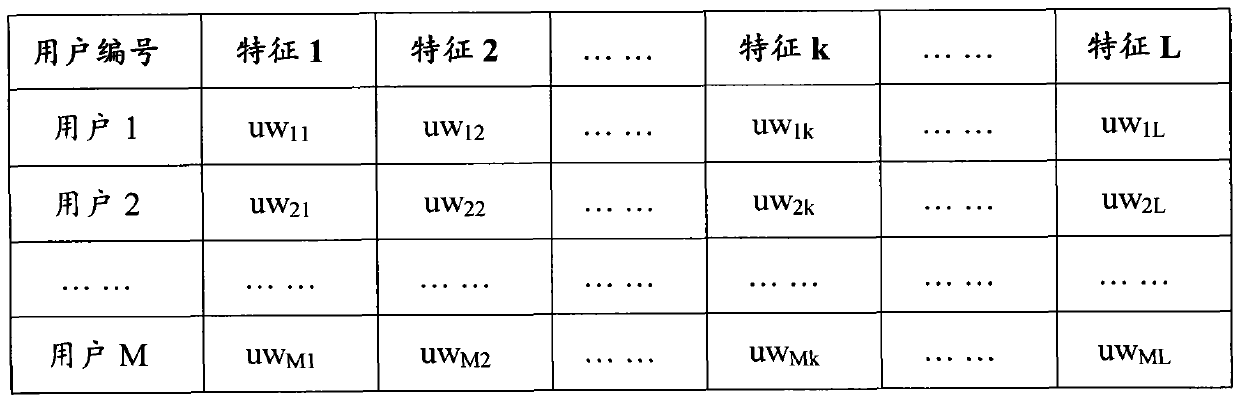
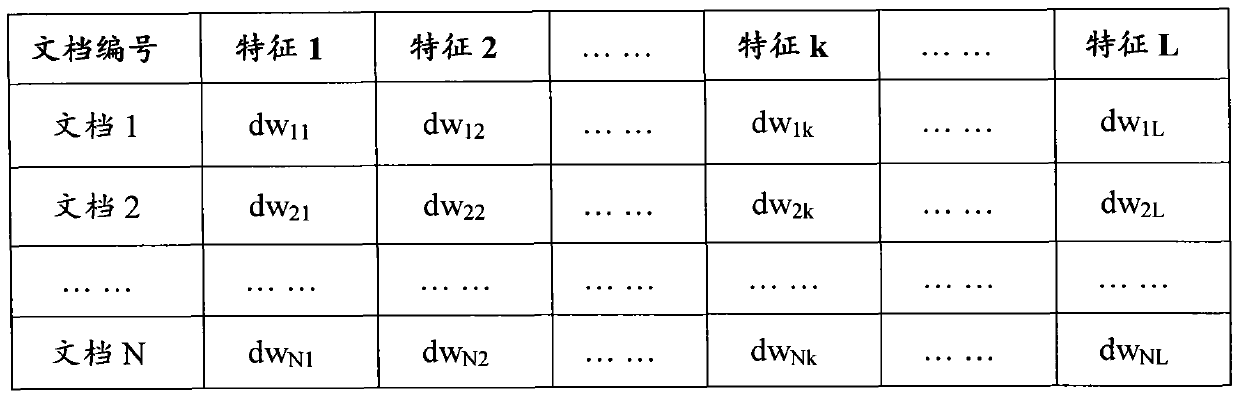
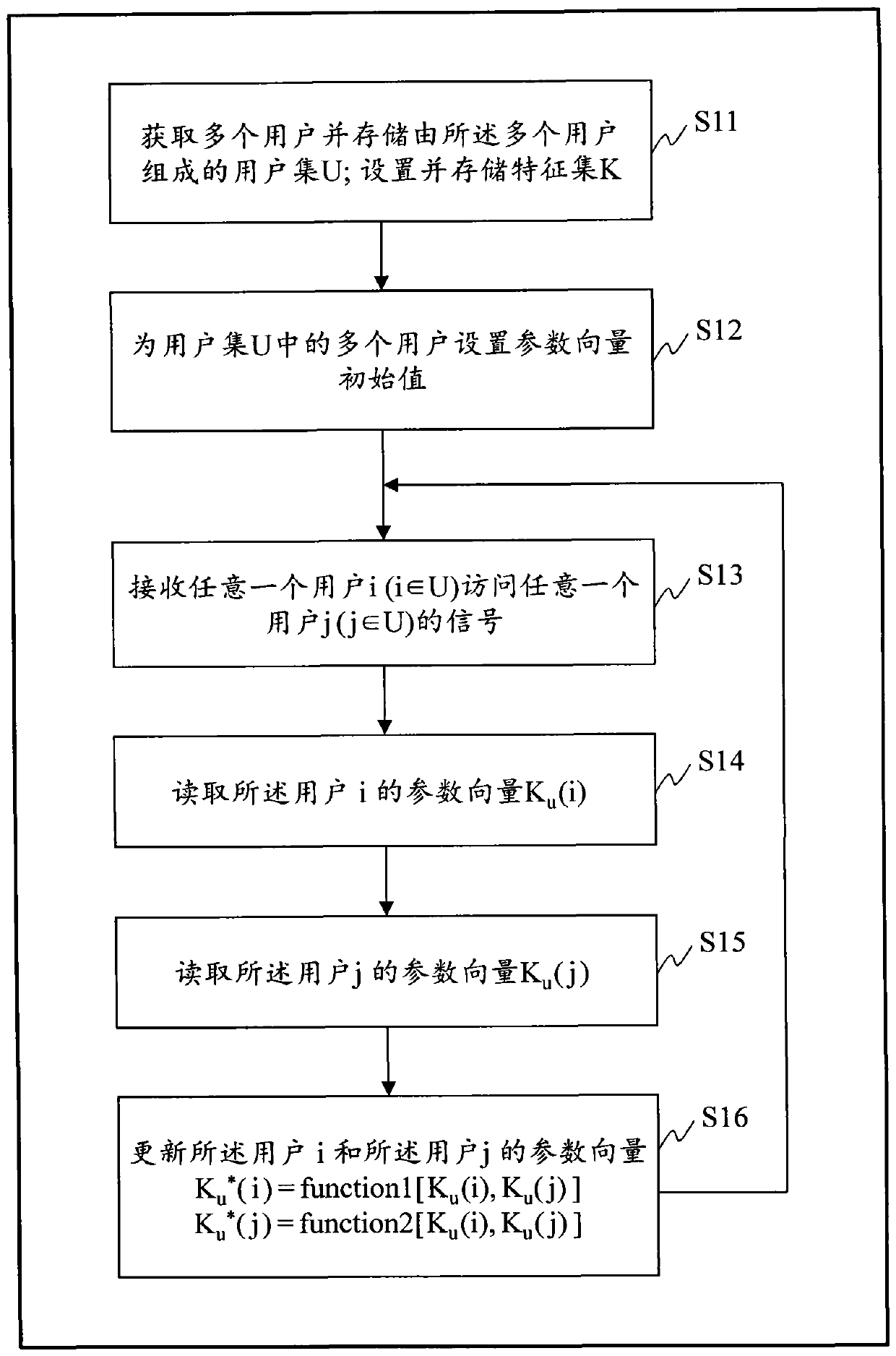
[0037] Example 1 is a method of manually setting the initial value of the parameter vector of user i (i ∈ U) or document n (n ∈ D). For example, set the total number of features L = 5, feature set K = (science, finance, education, music, sports), set K u (i)=(uw i1 , uw i2 , uw i3 , uw i4 , uw i5 )=(0, 0.00032, 0, 0.00059, 0). That is, the correlation between user i and the "financial" feature is 0.00032, the correlation with the "music" feature is 0.00059, and the correlation with other features is zero. Using a similar approach, one can set the parameter vector K for any document n d (n)=(dw n1 , dw n2 ,...,dw nk ,...,dw nL ) initial value.
[0038] Example 2 is a method of setting the initial value of the parameter vector of user i(i∈U). A set of documents H={...,r,...} submitted by the user i The parameter vector of the document r(r∈H) is K d (r)=(dw r1 , dw r2 ,...,dw rL ), so for each k ∈ K, set uw ik =(σ 1 / s) ∑ (r∈H) [dw rk / (∑ (k∈K) dw rk )], w...
example 2
[0059] Example 2: For the kth user column vector in the user set U (uw 1k , uw 2k ,...,uw Mk ) is normalized as follows. First calculate temp = ∑ (t∈U) uw tk , and for each i∈U compute uw ik =uw ik / temp; then to uw 1k , uw 2k ,...,uw Mk Sort and sort uw according to the sorted result 1k , uw 2k ,...,uw Mk Divide into r groups equally, and take out the smallest data in each group to form a set {s 1 , s 2 ,...,s r}, and s 1 2 r ; finally to uw 1k , uw 2k ,...,uw Mk Proceed as follows: for each i ∈ U, if uw ik 1 , then set uw ik = a; if s m ≤uw ik ≤s m+1 , then set uw ik =g(s m ); if uw ik >s r , then set uw ik =b. where g(s m ) is an increasing function, and g(s m )∈(a, b), 1≤m<r, a and b are non-negative constants, and r is a setting parameter.
example 1
[0067] Example 1: The f 1 [K u (j)] is the uw jk The increasing function of , is ∑ (k∈K) uw jk the decreasing function of ; the f 2 [K u (i)] is the uw ik The increasing function of , is ∑ (k∈K) uw ik the decreasing function.
[0068] Example 2: f 1 [K u (j)]=σ 3 ·uw jk / (∑ (k∈K) uw jk ), f 2 [K u (i)]=σ 4 ·uw ik / (∑ (k∈K) uw ik ), where σ 3 and σ 4 to set constants.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com