Upper limb exoskeleton steering mechanism driven by pneumatic muscles
A technology of pneumatic muscles and power-assisted mechanisms, which is applied to manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of low power/mass, low system work efficiency, and high system cost, so as to improve lifting strength, improve machine capacity, good flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and embodiments.
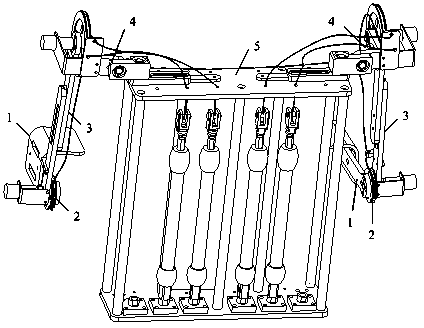
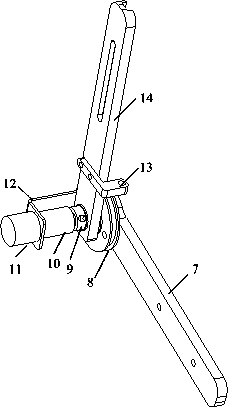
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention comprises two single-arm components and a back support 5 with the same structure; the single-arm components are sequentially composed of forearm 1, elbow joint 2, upper arm 3 and shoulder joint 4 from bottom to top, and in the two single-arm components Shoulder joint 4 is installed on the both sides of back support 5 top plates respectively, and two elbow joint shafts are connected with respective pneumatic muscles in back support 5 through respective elbow steel wire traction lines 36, and two shoulder joint shafts are respectively passed through respective shoulder joints. The steel wire pull line 37 of the part is connected with the respective pneumatic muscles in the back support 5. There are four degrees of freedom in the single-arm component, which are flexion-extension of the elbow, flexion-extension of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com