Intelligent file cabinet, file management system and file positioning method
A file cabinet and intelligent technology, applied in cabinets, cabinets for storing books, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of improving the positioning accuracy of files, and achieve real-time rapid inventory, high security, and accurate positioning.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0030] The present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
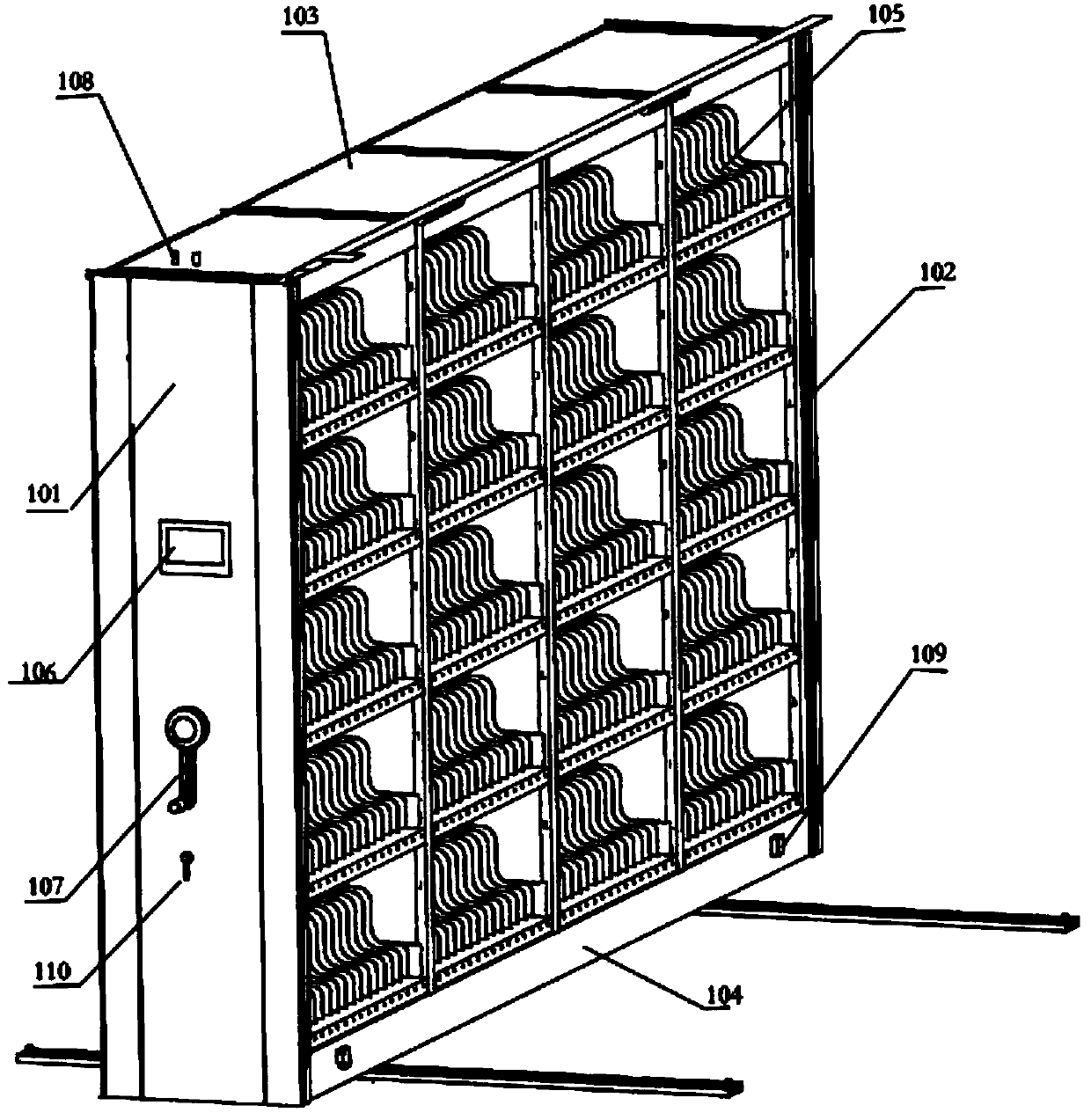
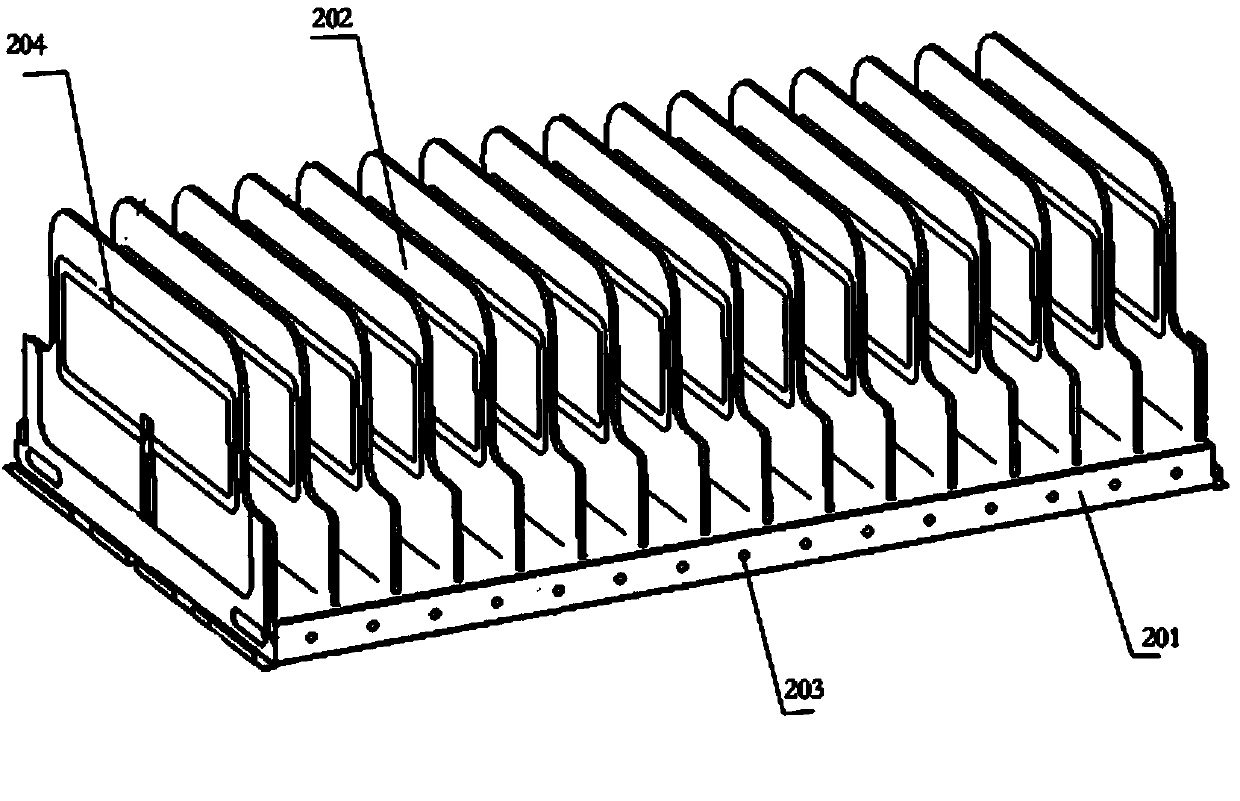
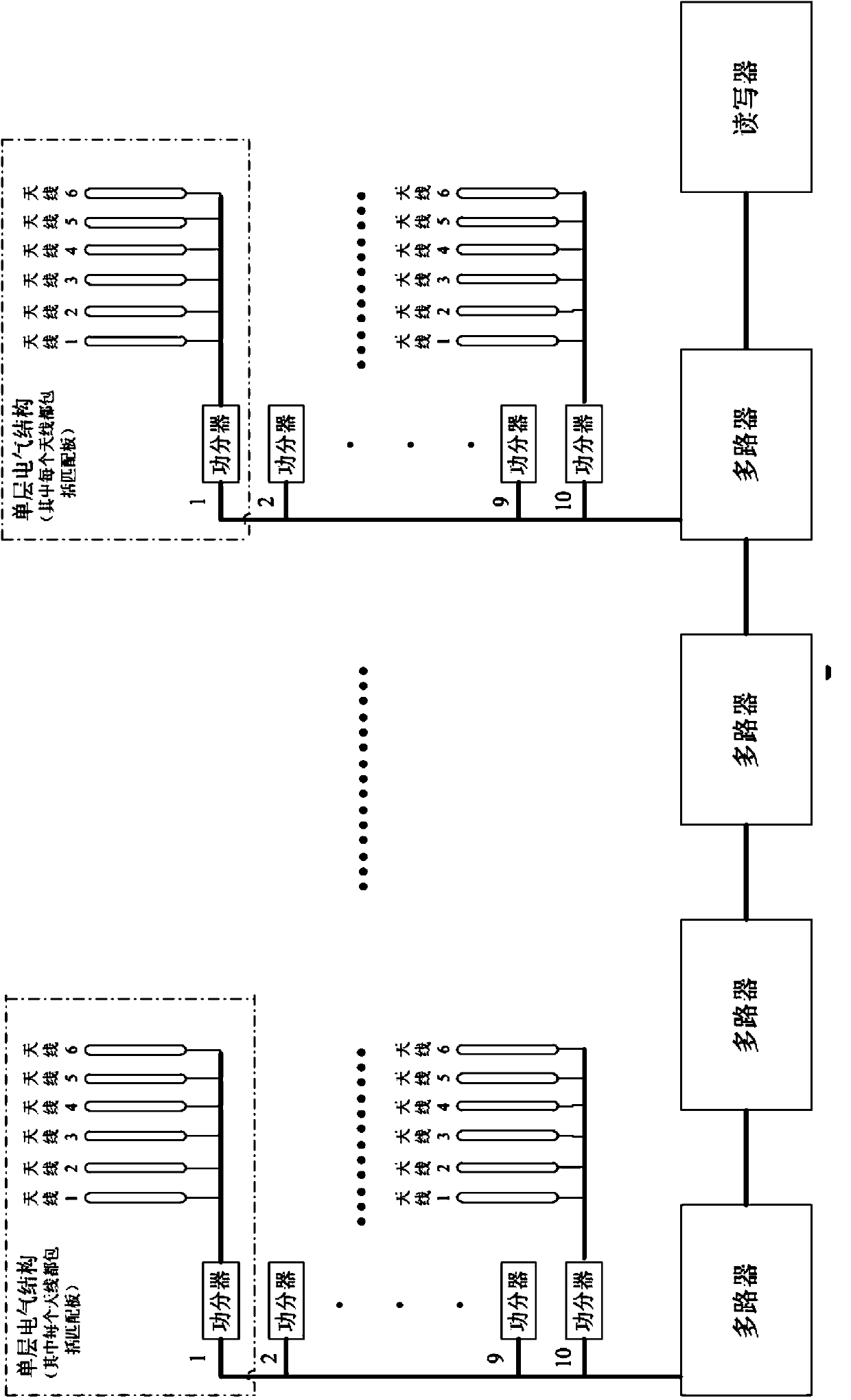
[0031] The intelligent filing cabinet provided by the present invention includes a cabinet body, several storage units inside the cabinet body, an electronic label, an RFID reading and writing module, a storage position indication module, a storage position sensing module and a main control system. The position sensing module and the RFID reading and writing module communicate with each other, and on the other hand, communicate with the computer on the workbench to realize the remote control of the intelligent filing cabinet by the computer.
[0032] see figure 1 , the cabinet body includes a front panel 101 , a rear panel 102 , a cabinet door, a top panel 103 and a chassis 104 . The front panel 101, the rear panel 102 and the top panel 103 are all made of steel plates; the cabinet doors are located on both sides of the cabinet body an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com