Solid-state imaging device and switching circuit
A technology of solid-state imaging device and amplifying circuit, which is applied to circuits, electric solid-state devices, radiation control devices, etc., can solve the problem of random noise becoming larger, and achieve the effect of reducing noise.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach )
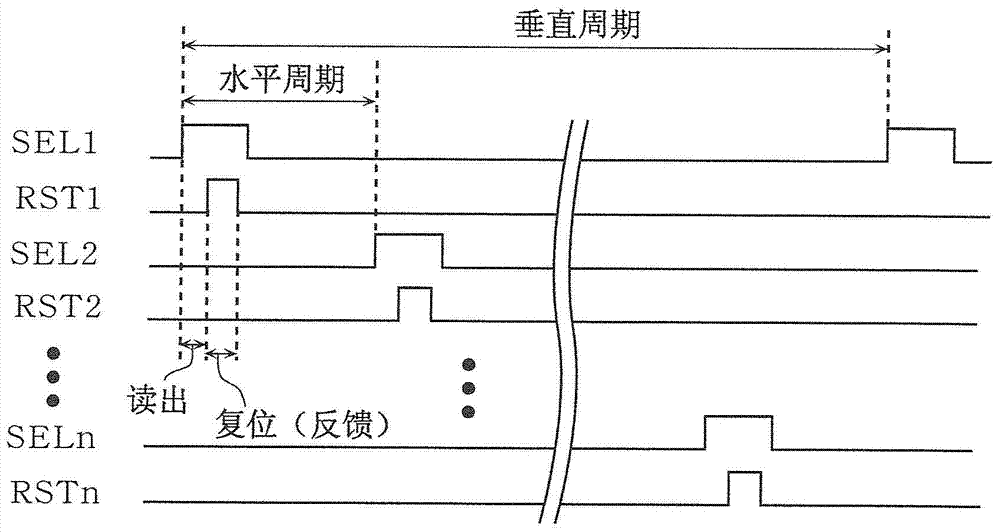
[0062] Hereinafter, a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Here, the same symbols are assigned to the same elements as those already described, and description thereof may be omitted. In the following, the transistor is assumed to be an n-type MOS, but a p-type MOS can also perform the same operation. In addition, what is described below as the source / drain of a transistor means either the source or the drain (in an actual device, the source and the drain are the same thing and cannot be distinguished). However, when one of them is given a higher voltage than the other, it is called a drain.
[0063] First, the configuration of the solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
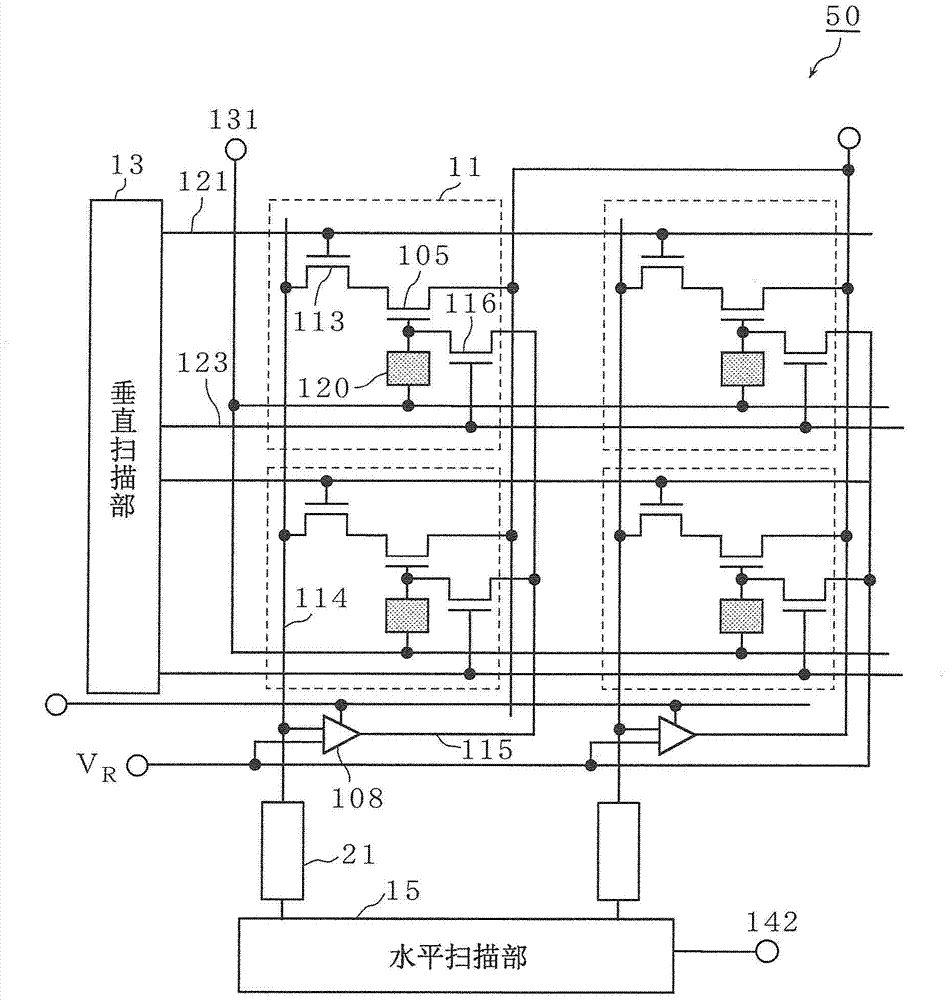
[0064] Figure 5 It is a circuit diagram of the solid-state imaging device 200 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. exist Figure 5 In , in order to simplify the...
no. 2 Embodiment approach )
[0133] Hereinafter, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Here, differences from the first embodiment will be mainly described, and descriptions of overlapping parts will be omitted.
[0134] Figure 8 It is a circuit diagram of the solid-state imaging device 300 according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0135] Figure 8 The solid-state imaging device 300 shown is different from Figure 5 The illustrated solid-state imaging device 200 is characterized in that the output terminal of the second amplifier circuit 206 is connected to the source of the amplifier transistor 105 . That is, the pixel sharing circuit 311 does not have Figure 5 The capacitive element 204 is shown. In addition, the solid-state imaging device 300 further includes a switch 317 and a power supply line 318 .
[0136] Specifically, the output terminal of the second amplifier circuit 206 is connected to the drain of the amplif...
no. 3 Embodiment approach )
[0145] Hereinafter, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Hereinafter, differences from the first embodiment will be mainly described, and overlapping descriptions will be omitted.
[0146] Figure 9 It is a circuit diagram of the solid-state imaging device 400 according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
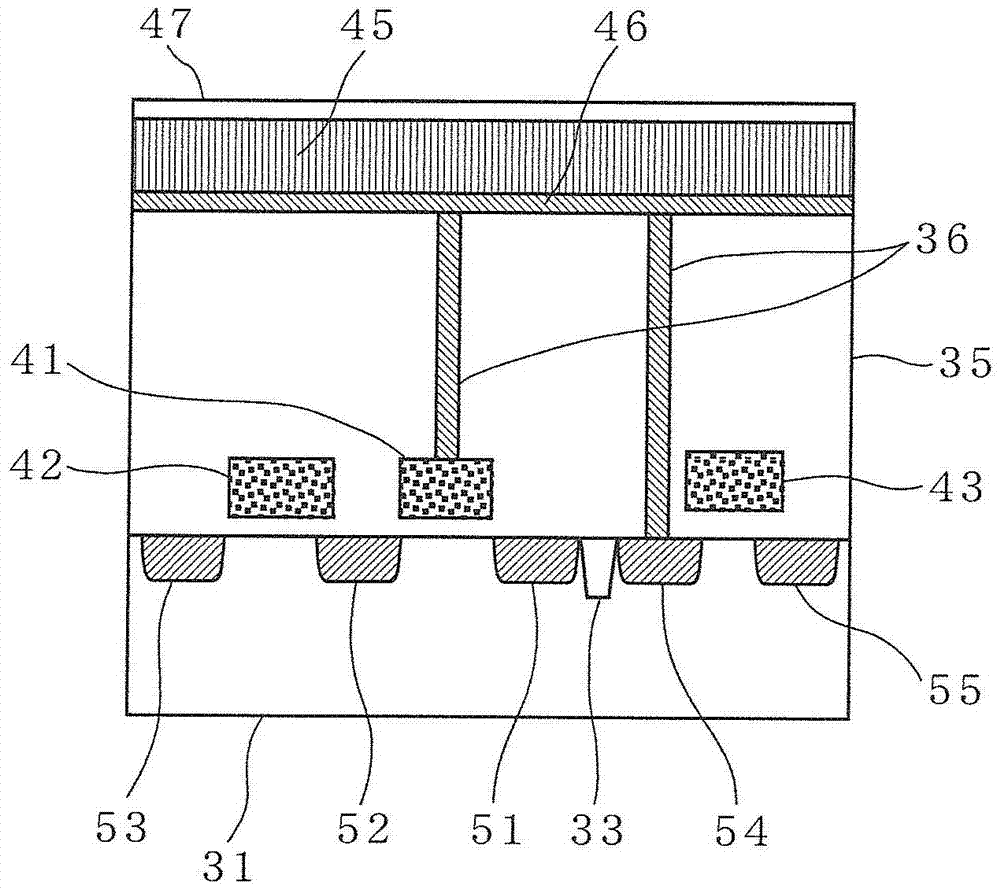
[0147] Figure 9 The solid-state imaging device 400 shown is different from Figure 5 The illustrated solid-state imaging device 200 is characterized in that the output terminal of the second amplifier circuit 206 is connected to the node of the transfer transistor 101 on the photoelectric conversion unit 120 side through the capacitive element 404 .
[0148] Specifically, the pixels 410 ( 410 a and 410 b ) further include capacitive elements 404 ( 404 a and 404 b ). The output terminal of the second amplifier circuit 206 is connected to one end of the capacitive element 404 through the switch 207 . T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com