Method for feeding dermaptera being natural enemy of tirathaba rufivena walker
The technology for the red-veined ear borer and the pad tarsus is applied in the field of raising the red-veined ear borer's natural enemy, the pad tarsus. reproductive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
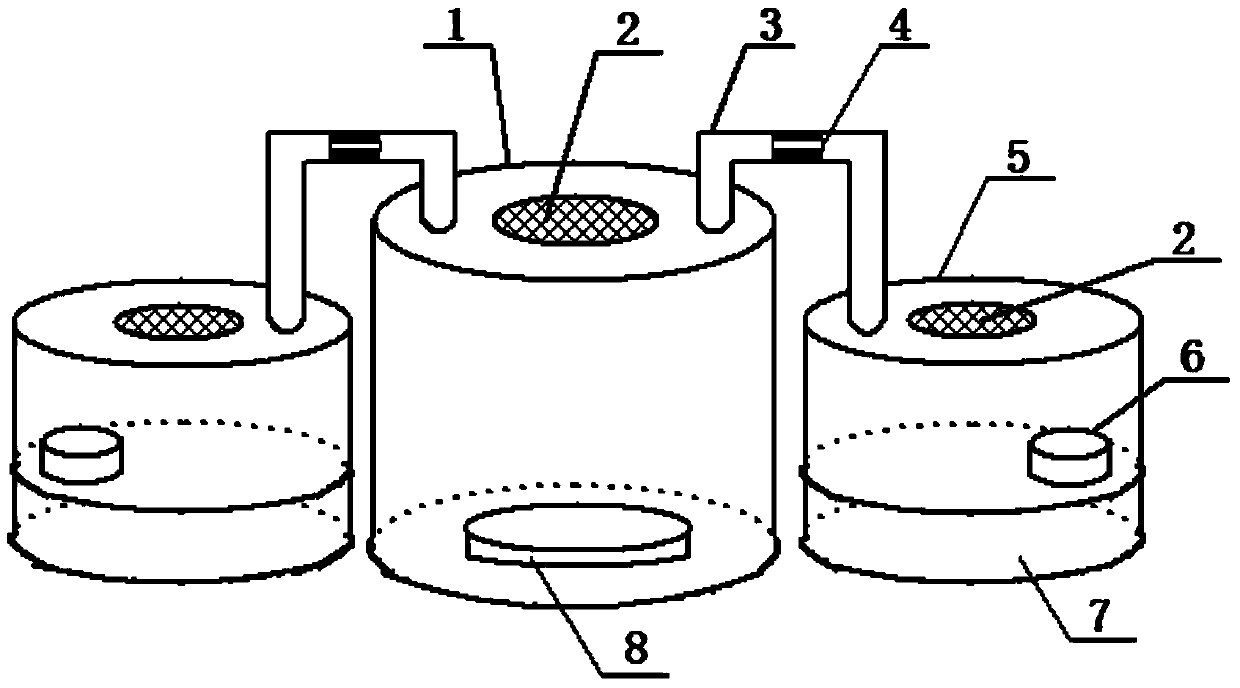
[0021] 1. Introduce about 200 fruit flies into the fruit fly breeding box 1, and insert fruit flies every 5 days for 5 consecutive times. After the fruit flies are inserted, they are allowed to lay eggs and reproduce voluntarily in the box (when there is water seepage in the feed tray, clean the seepage in time, and add fruit when the fruit is completely eaten). After the fruit flies have emerged, they can enter the insect culture box of the tarsus tarsus by themselves through the plastic connecting pipe to provide fresh living prey for the tarsus tarsus. From the 10th day, the number of fruit flies eclosion increases rapidly, and thereafter they can fully satisfy the tarsus tarsus. Reproductive and life needs.
[0022] 2. Put 30 female adults of the tarsus tarsus and 15 male adults of the tarsus tarsus into the insect breeding box of the tarsus tarsus together, use fruit flies as food, and supplement nutrition with 10% honey water. Every 3 days, the status of the female indi...
Embodiment 2
[0025] According to the method of Example 1, 25 female adults of the tarsus tarsus and 15 male adults of the tarsus tarsus were selected for breeding, and the breeding environment temperature was 23±1°C, the relative humidity was 70-85%, and the light time was 12L:12D. The experimental data during the recording process are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0027] According to the method of Example 1, 38 female adults of the tarsus tarsus and 15 male adults of the tarsus tarsus were selected for breeding, and the breeding environment temperature was 27±1°C, the relative humidity was 70-90%, and the light time was 12L:12D. The experimental data during the recording process are shown in Table 1.
[0028] Table 1 Feeding data of tarsus tarsus
[0029] project
egg production
hatching number
Hatch rate
Number of nymphs
Number of adults
Embodiment one
1414
1254
88.68%
1187
1047
88.21%
Embodiment two
1161
1082
93.20%
1005
941
93.63%
Embodiment three
1258
1101
87.52%
986
899
91.18%
[0030] Note: a. Hatching rate = hatching number / egg laying number×100%. b. The number of nymphs refers to the number of nymphs that survived when the female adults no longer provide protection; c. The number of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com