An Adaptive Interactive Multi-model Maneuvering Target Tracking Method
An interactive multi-model, maneuvering target tracking technology, applied in special data processing applications, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unreasonable Markov transition probability matrix design, target loss, and traffic accidents And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0100] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
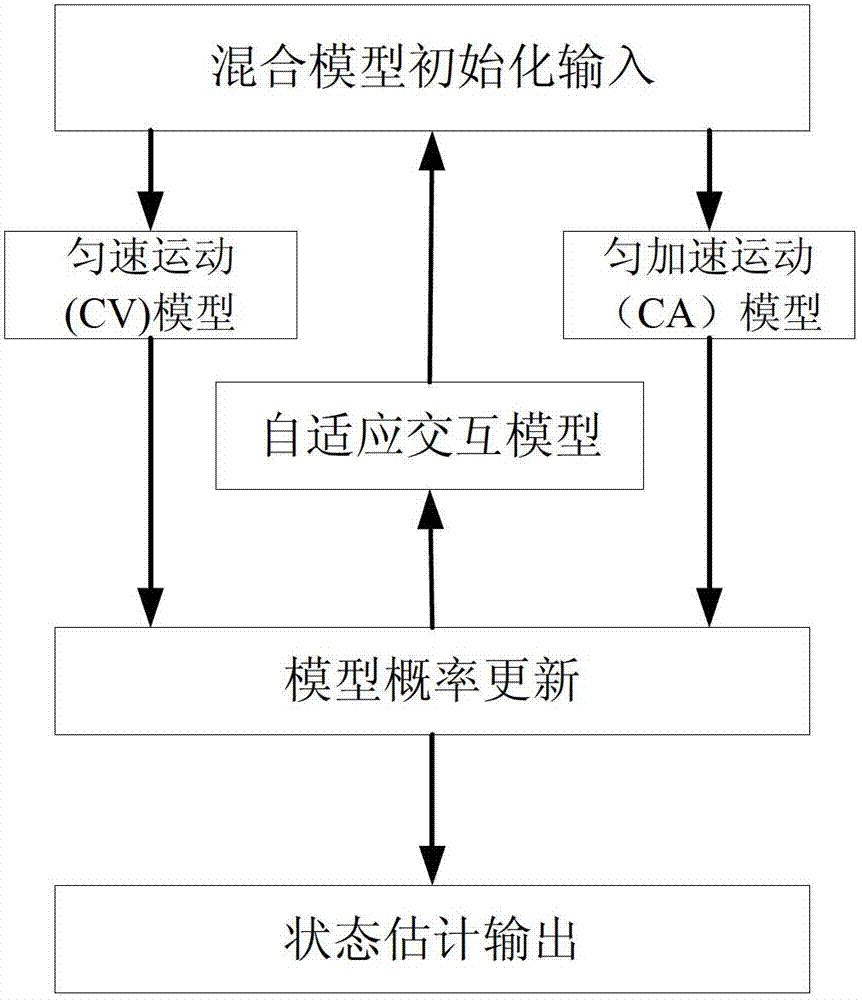
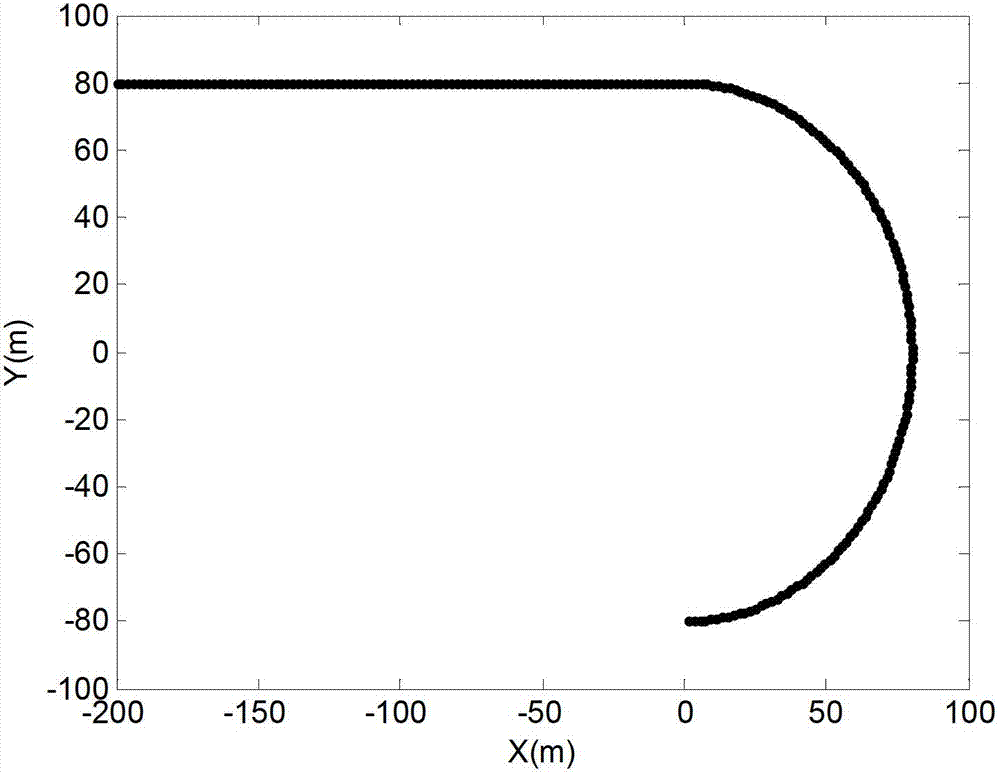
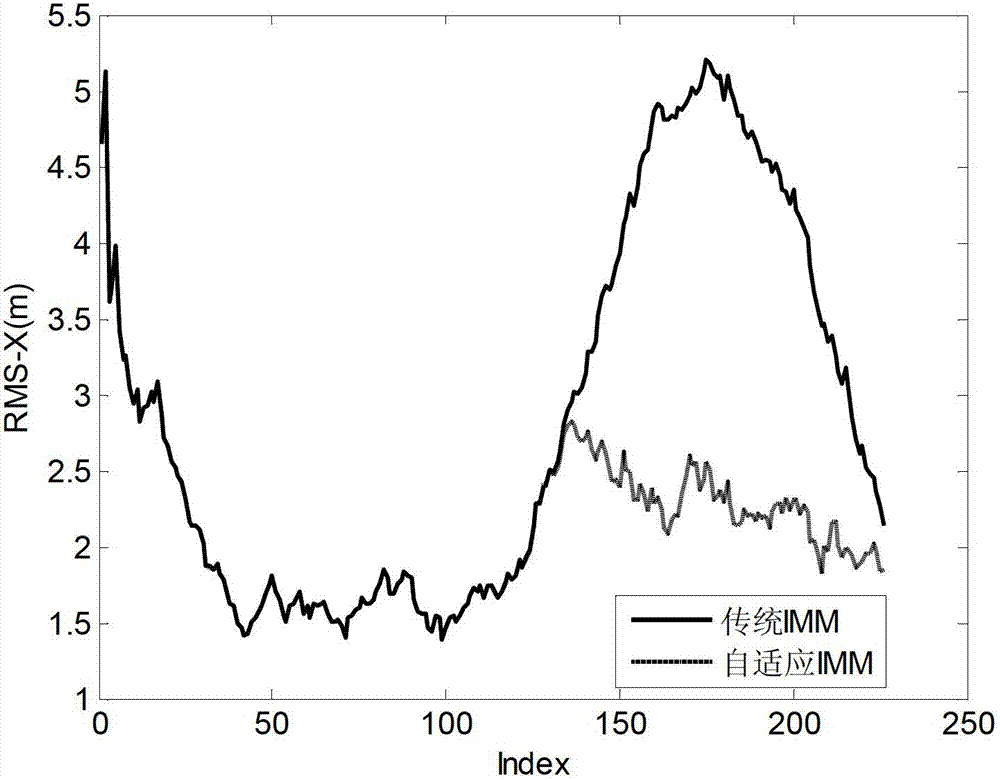
[0101] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the model estimation process of the present invention.
[0102] Step 1, establish the mixed initialization input of various models in the IMM tracking model.
[0103] 1a) The motion state equation and observation equation of the target, assuming that there are r motion models, and the state transition matrix corresponding to each motion model is Φ j (1≤j≤r), the equation can be expressed as:
[0104] X(k+1)=Φ j (k|k-1)X(k)+Г j W j (k),j=1,...,r
[0105] Z(k)=C j (k)X j (k)+V j (k)
[0106] In the formula, X(k) is the system state vector at time k, Z(k) is the system observation (measurement) vector at time k, Φ j is the state transition matrix corresponding to the jth motion model, Г j is the system control quantity corresponding to the jth motion model, W j (k) represents th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com