Construction method of plasma cell-free dna library
A DNA library and construction method technology, applied in chemical libraries, combinatorial chemistry, library creation, etc., can solve problems such as self-ligation of adapters, DNA loss, and reduction of purification steps, so as to avoid self-ligation of adapters, reduce DNA loss, and reduce Effects of purification steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the examples.
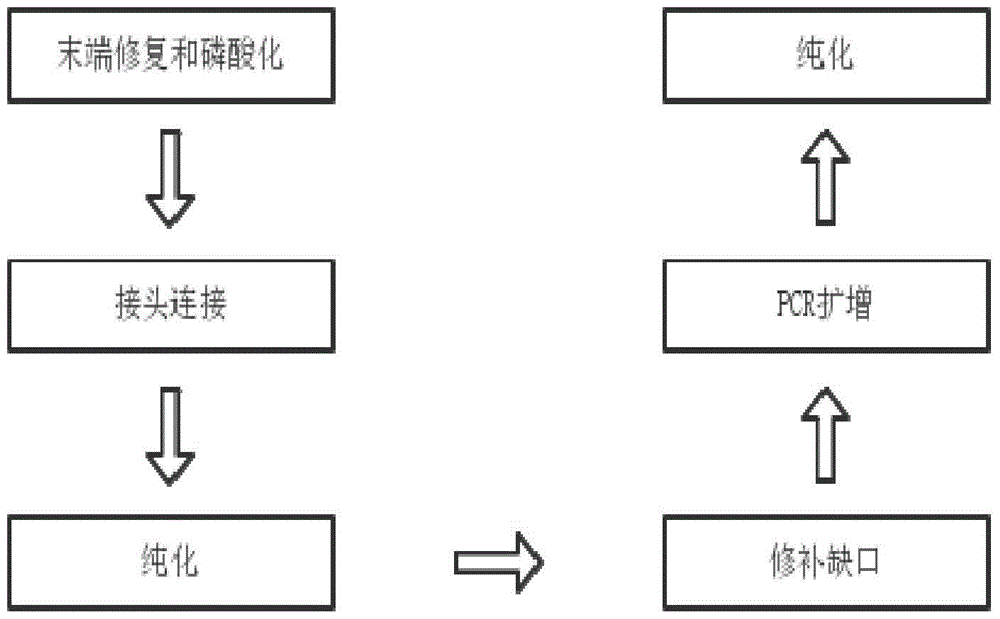
[0035] according to figure 1 The library construction procedure shown was carried out. The linker sequence used is the sequence listed in claim 7 above. Wherein sequence 1 and sequence 2 are annealed in equimolar amounts to form linker A, and sequence 3 and sequence 4 are annealed in equimolar amounts to form linker B.
[0036] SEQ ID NO1:
[0037] 5'-AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCT-3'
[0038] SEQ ID NO2:
[0039] 5'-AGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGTGTAGATC-3',
[0040] SEQ ID NO3:
[0041] 5'-AGATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCTGAACTCCAGTCACIIIIIIATC-3',
[0042] SEQ ID NO4:
[0043]5'-CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCGTGATGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCT-3', the six bases "IIIIII" in the sequence 3 represent the tag sequence in the multi-sample mixed library of the sequencing platform.
[0044] The samples used in the following examples are normal human pl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com