An East Asian locust atp synthase alpha subunit gene and its application in pest control
A technology for locusts and migratory locusts, applied in the direction of DNA/RNA fragments, applications, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problems of long killing time, high cost of control, unstable insecticidal effect, etc., to achieve strong species specificity, gene Strong specificity and fast onset of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
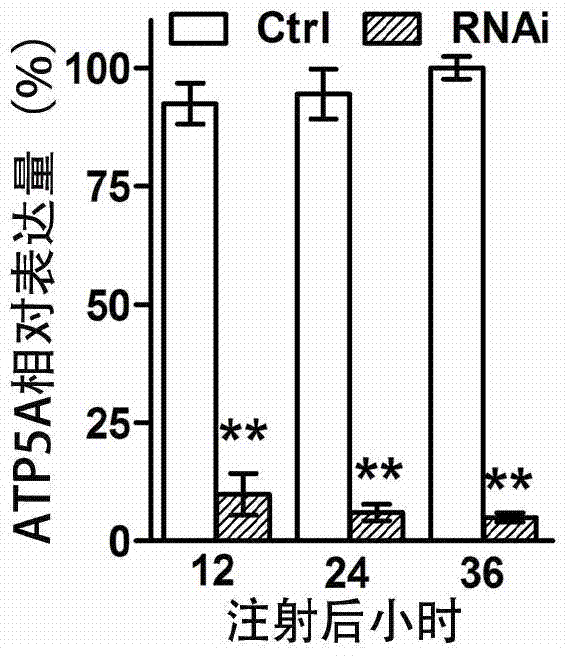
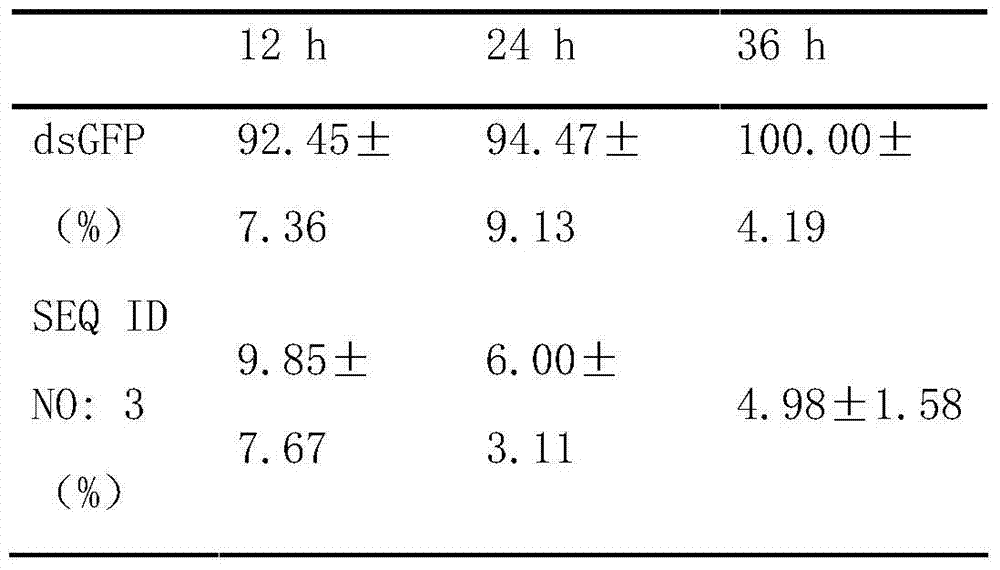
[0023] Example 1: Obtaining of migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene and its dsRNA
[0024] i. Acquisition of migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene
[0025] 1) Searching of migratory locust ATP synthase α subunit gene in migratory locust EST database
[0026] Based on the migratory locust EST database, a bioinformatics method was used to search the migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene. After sequence splicing and alignment, a total of 1 migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene was obtained.
[0027] 2) Design of primers for migratory locust ATP synthase α subunit gene
[0028] Based on the obtained base sequence of LmATPSB, primer premier5.0 software was used to design primers. All primers were synthesized by Nanjing Jinsirui Biological Co., Ltd.
[0029] 3) Obtaining total RNA of migratory locust
[0030] Select 5th instar nymphs of the same size male and female half migratory locusts, 3 heads in a group, frozen in liquid nitrogen, to be extract...
Embodiment 2
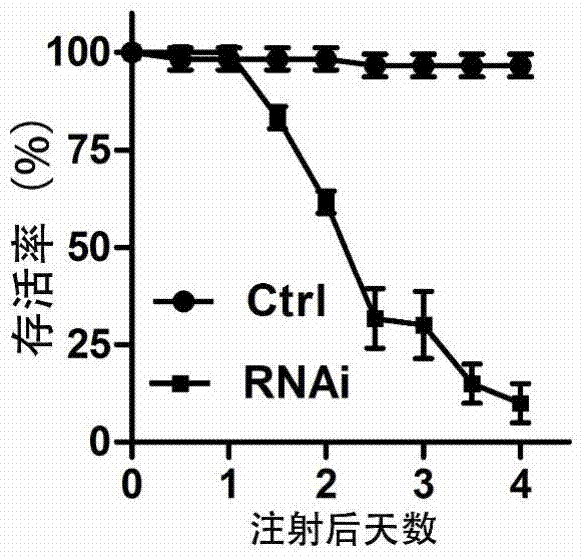
[0044] Example 2: Migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit dsRNA killed the fifth instar locust
[0045] 1. Injection of migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit dsRNA
[0046] Select the nymphs of the third day of fifth instar, uniform size, and consistent health status to inject the above-mentioned synthetic dsRNA (SEQID NO: 3), and 25μl micro syringe for injection. Do not use excessive force during injection and follow the direction of blood flow. , The junction of the second to third abdominal segments of the flanks is used as the injection point, avoiding the valve. The amount of dsRNA injected was 100ng, and a control group of dsGFP (100ng) was set up. Each group had 20 worms, 3 biological replicates, and a total of 60. After the injection, the test insects were reared in plastic cages (light:dark time 14h:10h, temperature 30±2°C), and fresh wheat seedlings were given.
[0047] 2. Observation of the phenotype of the fifth instar migratory locust after injection of dsRNA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com