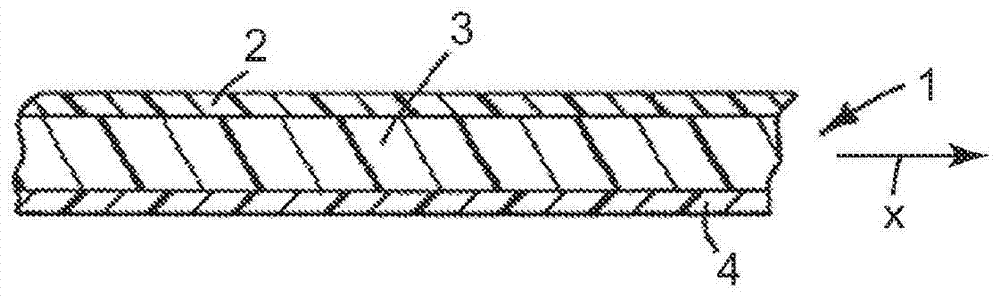
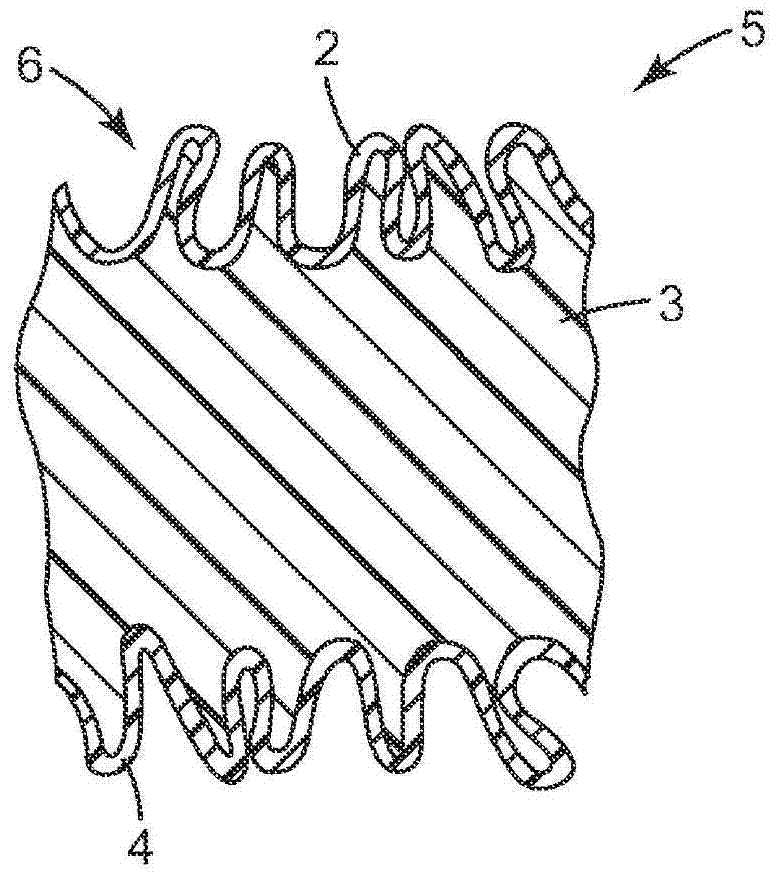
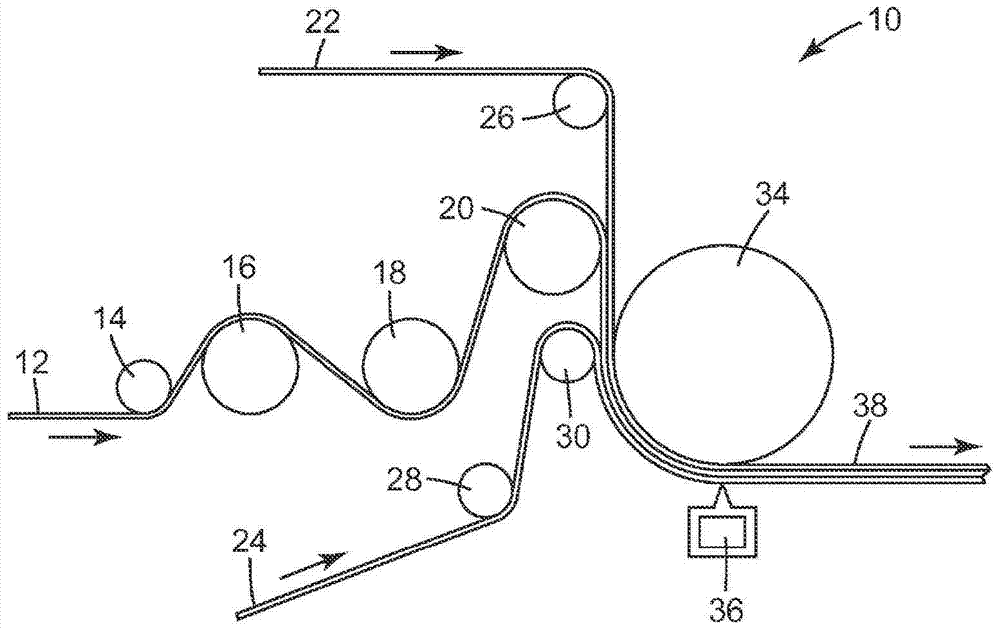
Method of making extensible web laminates
A technology of laminates, webs, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, lamination, lamination devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0164] Example 1 (Laterally activated M-235)
[0165] M-235 was incrementally stretched in the transverse direction using intermeshing stretchers similar to those described in the following U.S. Patent 5,422,172: "Elastic Laminated Sheet of an Incrementally Stretched Nonwoven Fibrous Web and Elastomeric Film and Method (Incrementally Stretched Nonwoven Fibrous Web and Elastomeric Film Elastic Laminate Sheet and Process)" (Wu). The stretcher was configured to apply 224% strain to the entire multilayer film. The basis weight of activated M-235 is 35g / m 2 .
[0166] Control 2 (unactivated membrane)
[0167] A three-layer laminate film having an elastomeric core layer sandwiched between two outer skin layers was prepared using conventional coextrusion techniques. The skin layer was 5 microns thick and was made of PPH8069 resin (polypropylene available from Total Petrochemicals of Houston, Texas, USA). The core layer was 40 microns thick and consisted of 70% by weight of D...
example 2
[0168] Example 2 (transversely activated membrane)
[0169] Control 2 was stretched in the transverse direction using a diverging disc arrangement similar to that described in the following U.S. Patent 5,043,036 figure 1 Diverging disk device shown in: "Width Stretching Device (Width Stretching Device)" (Swenson). The film was stretched to 400% of its original width and then allowed to fully recover. The basis weight of activated Example 2 was 50 gsm.
[0170] Control 3 (unactivated membrane)
[0171] A three-layer laminate film having an elastomeric core layer sandwiched between two outer skin layers was prepared using conventional coextrusion techniques. The surface layer is made of PPH8069 resin. The core layer was made from a blend of 95% by weight D1114 and 5% EMPERA 124N. Basis weight is 45gsm. The core / surface ratio is 4.1:1.
example 3
[0172] Example 3A (transversely activated membrane)
[0173] Control 3 was incrementally stretched in the cross direction using the process described in Example 1. The stretching machine was configured to apply a local strain of 117%. The activated Example 3A had a basis weight of 42 gsm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com