Method for detecting caves based on similarity lateral change rate of frequency domain dip angles
A technology of dip angle and detection method in the frequency domain, applied in seismic signal processing and other directions, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish the development characteristics of fractures and karst caves, inability to consider the relationship between adjacent multi-channels, and reducing the continuity of spatial resolution capabilities. The effect of abnormal response and good calculation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention is described in further detail:
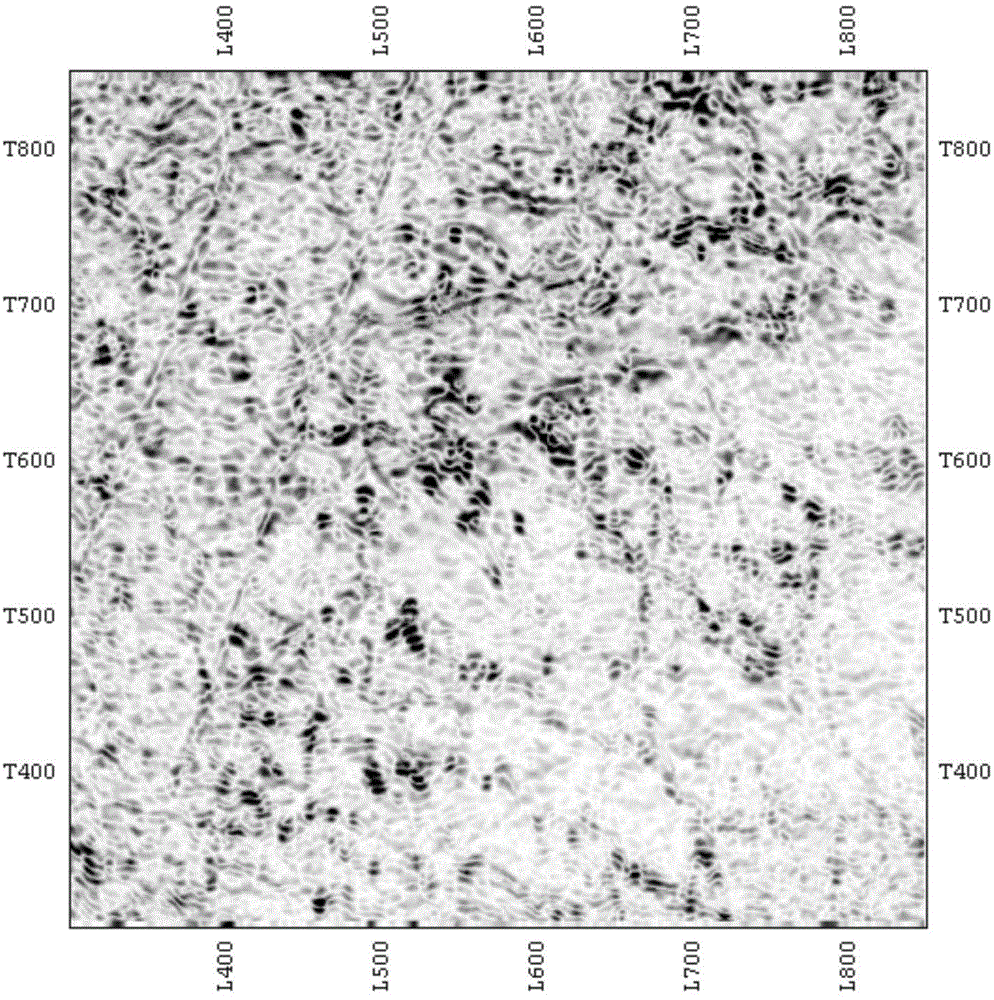
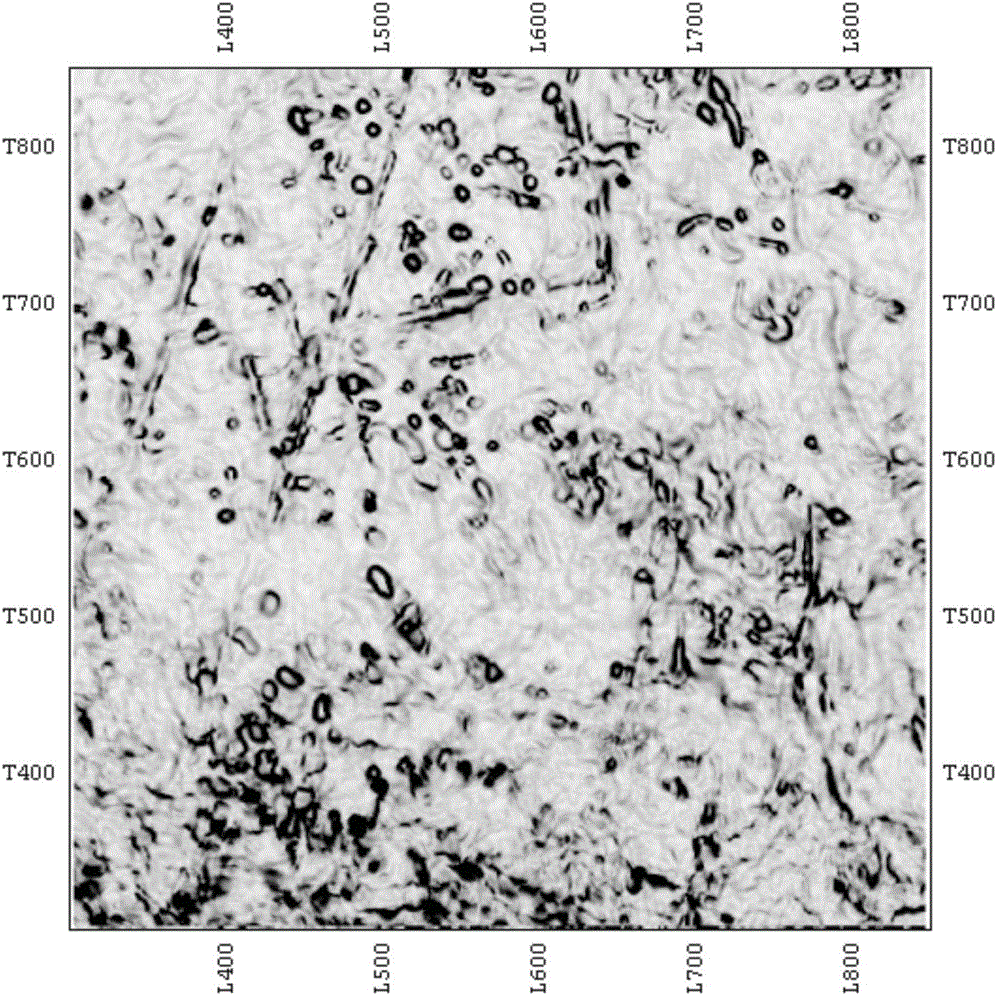
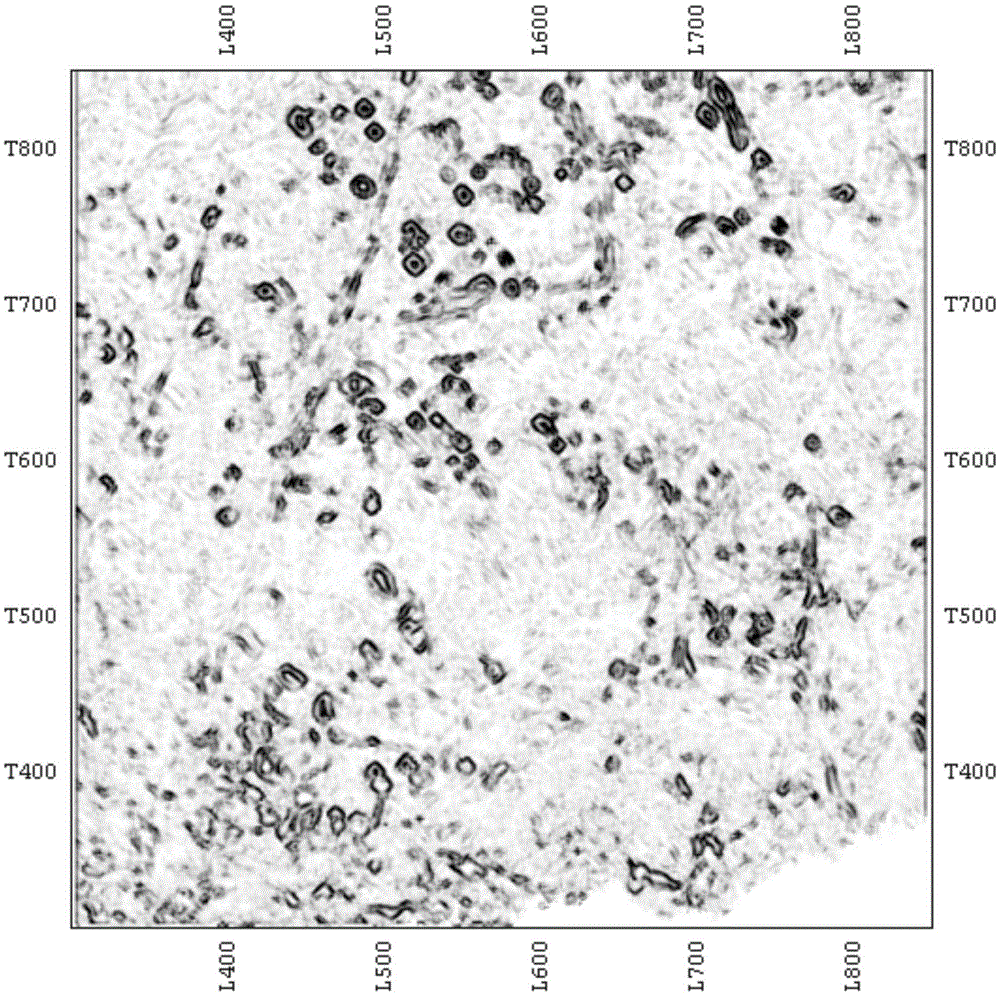
[0033] The similarity lateral change rate technology based on the frequency domain scanning dip attribute, first scan the dip in the frequency domain, and then use the high precision similarity detection method to find outliers with poor continuity, on this basis, carry out the similarity lateral change High-rate edge detection, eliminating abnormal points caused by fractures, so as to determine the development area of karst-vug reservoirs.
[0034] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the specific implementation steps are:
[0035] (1) Frequency domain tilt scan
[0036] The frequency-domain seismic dip attribute is an attribute that uses the instantaneous phase spectrum to calculate the seismic dip. First, Hilbert transform is performed on the seismic data to obtain the Hilbert seismic trace, so that the seismic trace information is transformed from the time domain to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com