A method for dividing bus route operation time periods based on vehicle-mounted GPS data
A technology of GPS data and time division, applied in the field of transportation, can solve problems such as unreasonable division indicators and difficulties in obtaining division technical data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
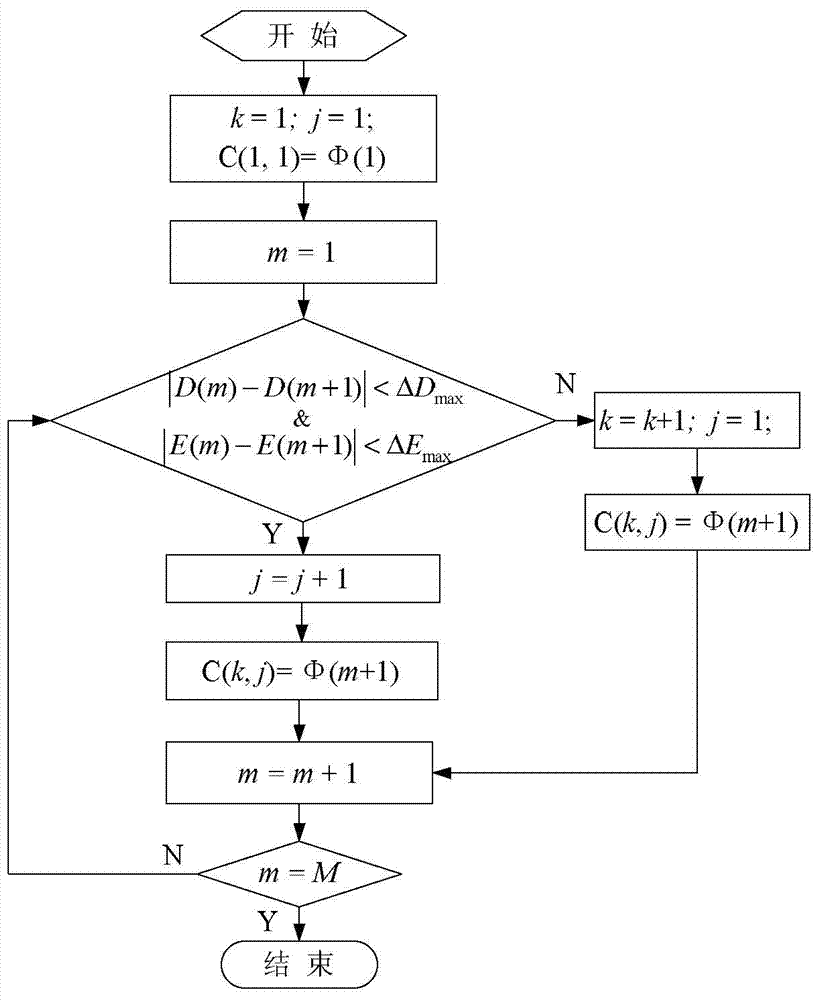
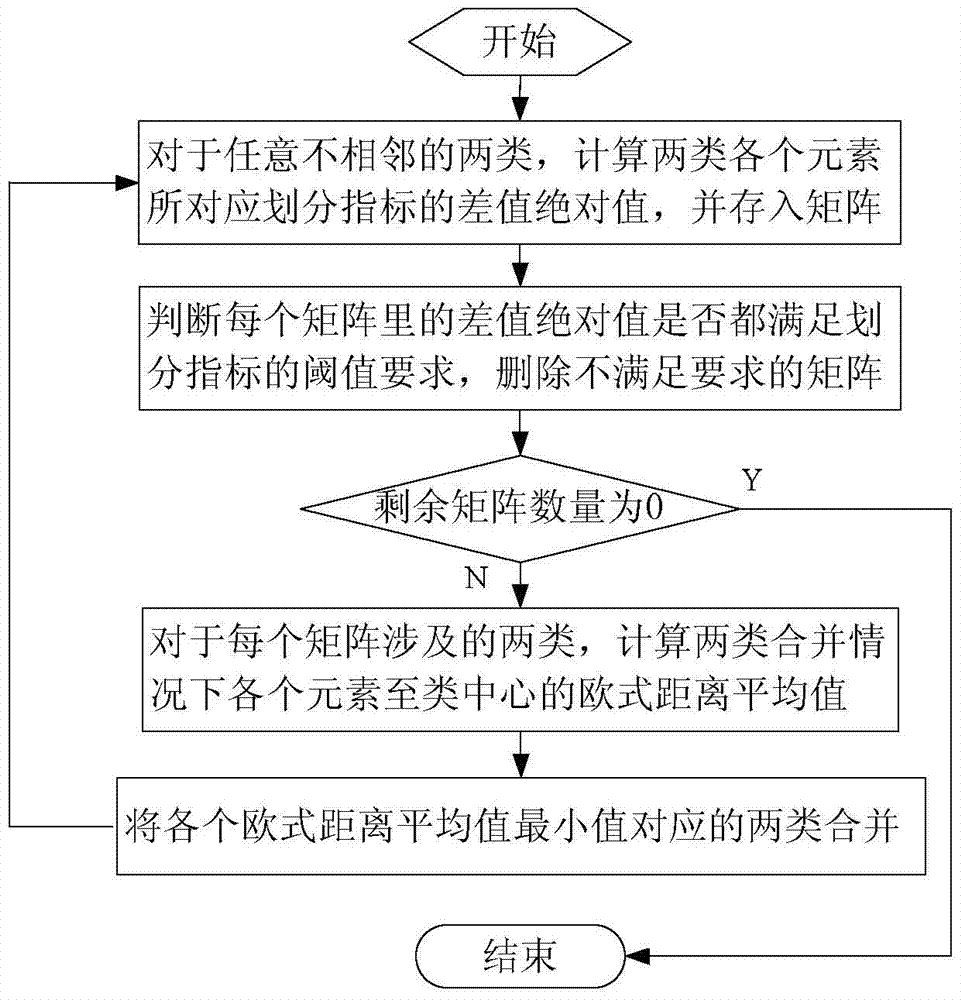
[0060] Specific implementation mode 1: Combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 To explain this embodiment, the method for dividing the operation period of a bus route based on on-board GPS data described in this embodiment is implemented through the following steps:
[0061] Step 1. Extract bus line operating time division indicators: suppose a bus line sends M buses from the departure station every day, the first bus is numbered 1, and so on, the last bus is numbered M, and the line has N operating hours , The headway of the nth operating period is H n , 1≤n≤N, suppose it belongs to the nth operating period and the number is m n The average line stopping time of the bus for J consecutive days is D(m n ), 1≤m n ≤M, its calculation method is shown in formula (1).
[0062]
[0063] In formula (1), I represents the number of stops of the bus line, J represents the number of days, and d ij (m n ) Represents the mth n The stop time of the bus at the ith stop on the j day, H min Represents th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
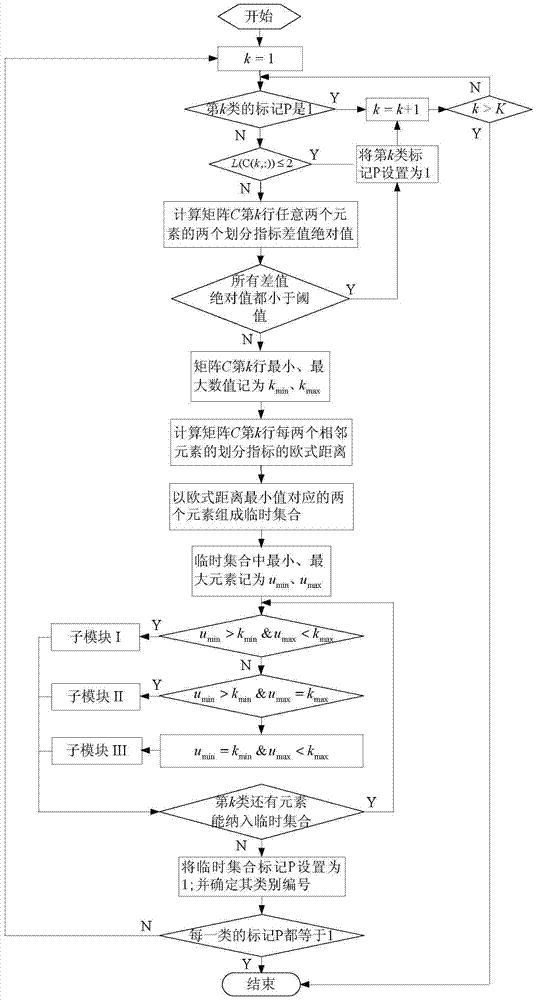
[0115] Specific implementation manner two: combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 To explain this embodiment, the sub-module I in step three (11) of the method for dividing the operation period of bus routes based on on-board GPS data in this embodiment is implemented through the following steps:
[0116] Step A (1), calculate the element u min -1 and the absolute value of the difference between the average line stop time of each element in the temporary collection and the average line-to-station travel time are stored in matrix Y respectively 1 The first and second rows of; calculate the element u max +1 and the absolute value of the difference between the average line stop time of each element in the temporary set and the average line travel time between stations are stored in matrix Y respectively 2 The first and second lines of;
[0117] Step A (two), judgment matrix Y 1 , Y 2 Whether the maximum absolute value of the difference between the two division indicators in the max , △E ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0127] Specific implementation mode three: combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 To explain this embodiment, the implementation fee is the step three (twelfth) of the method for dividing the operation period of the bus route based on on-board GPS data. The sub-module II is established through the following steps:
[0128] Step B (1), calculate u min -1 and the absolute value of the difference between the average line stop time of each element in the temporary collection and the average line-to-station travel time are stored in matrix Y respectively 1 The first and second lines of;
[0129] Step B (two), judge whether matrix Y 1 The maximum value of the absolute value of the difference between the two division indicators in is less than or equal to △D max , △E max , If yes, go to step B(3), otherwise go to B(4);
[0130] Step B (three), element u min -1 is included in the temporary collection, and proceed to step B (5);
[0131] Step B (4), add 1 to the class numbers of the k+1 to Kth ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com