A way to achieve mapreduce data localization within a job
A job and data technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as low practicability, low applicability, and network bandwidth consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
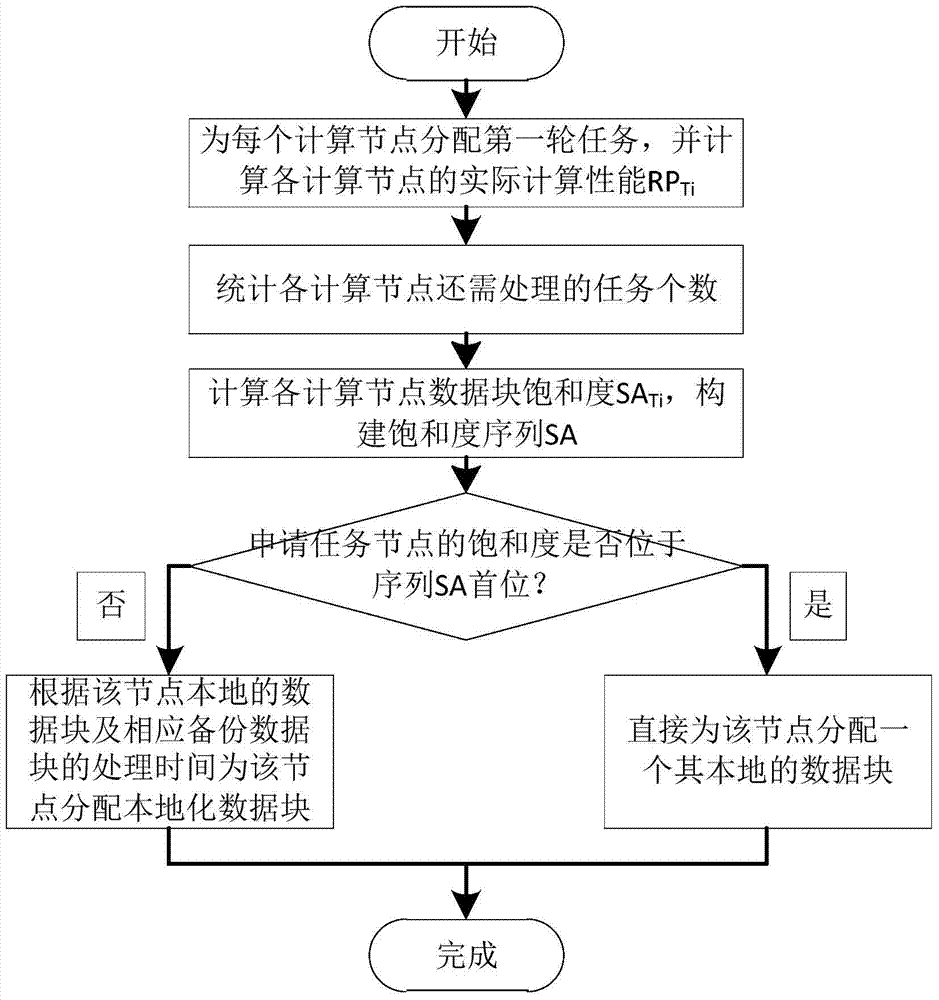
[0036] A method for realizing the localization of MapReduce data within a job, the process of which is as follows figure 1 As shown, on a cluster with n physical computing nodes, for a specific scheduled job A, localization is realized in the following way during its implementation:
[0037] Step 1: Since clusters can be divided into homogeneous and heterogeneous, it is assumed that the cluster is homogeneous when the calculation has not yet started, that is, it is assumed that the computing performance of all physical computing nodes P i are all 1, where i∈[1,n]; for job A, assuming that the number of data blocks corresponding to the job is b, and the default number of backups for each data block on HDFS is 3, set The number of data blocks is F Ti , then the total number of data blocks ∑F Ti = 3b;
[0038] The number of localized data blocks of job A on each computing node is used as a parameter to establish a small top heap and perform the first round of task assignment o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com