Multi-target Continuous Imaging Bias Angle Compensation Method
A compensation method and technology of drift angle, applied in the field of aerospace remote sensing imaging tasks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
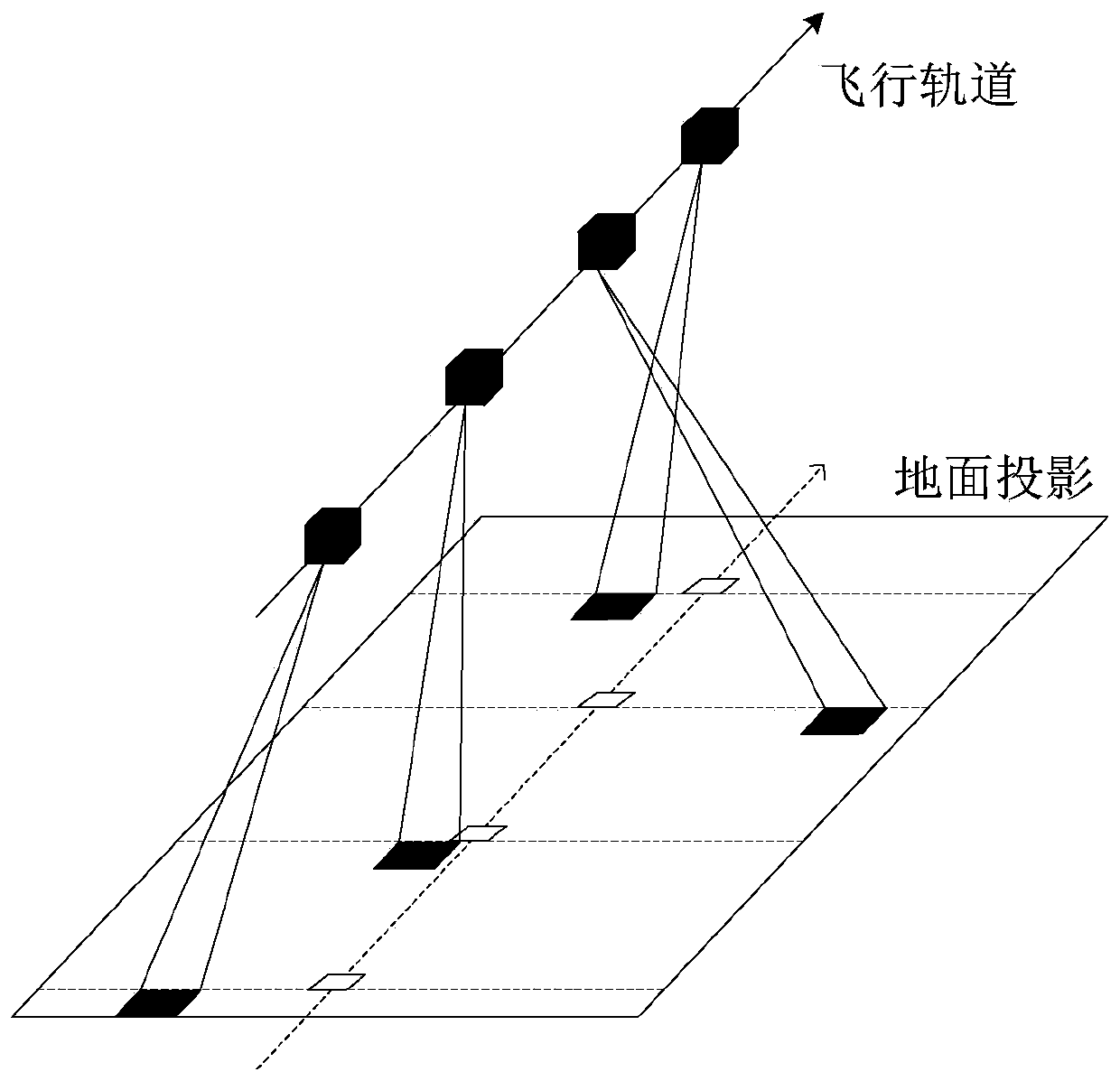
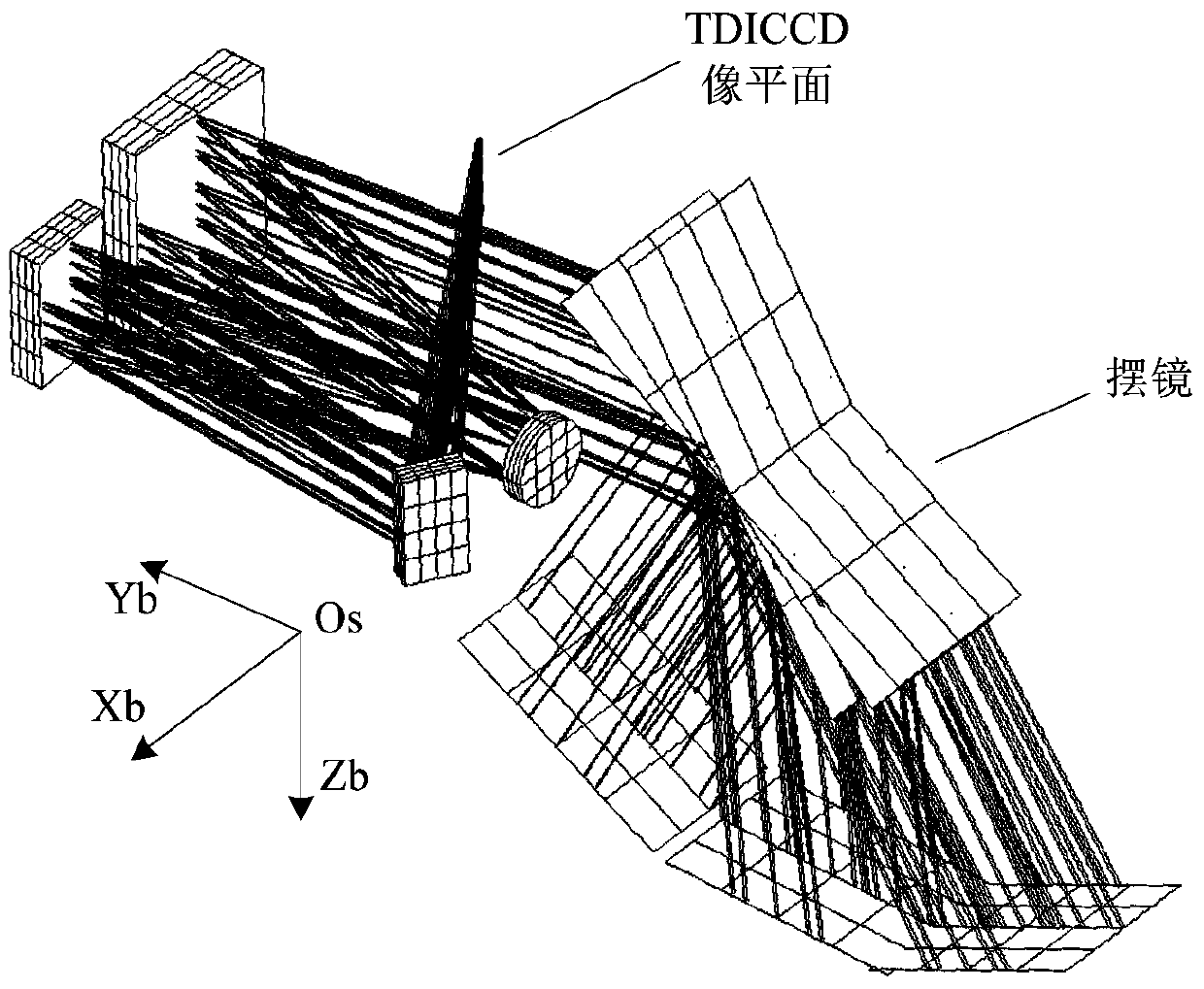
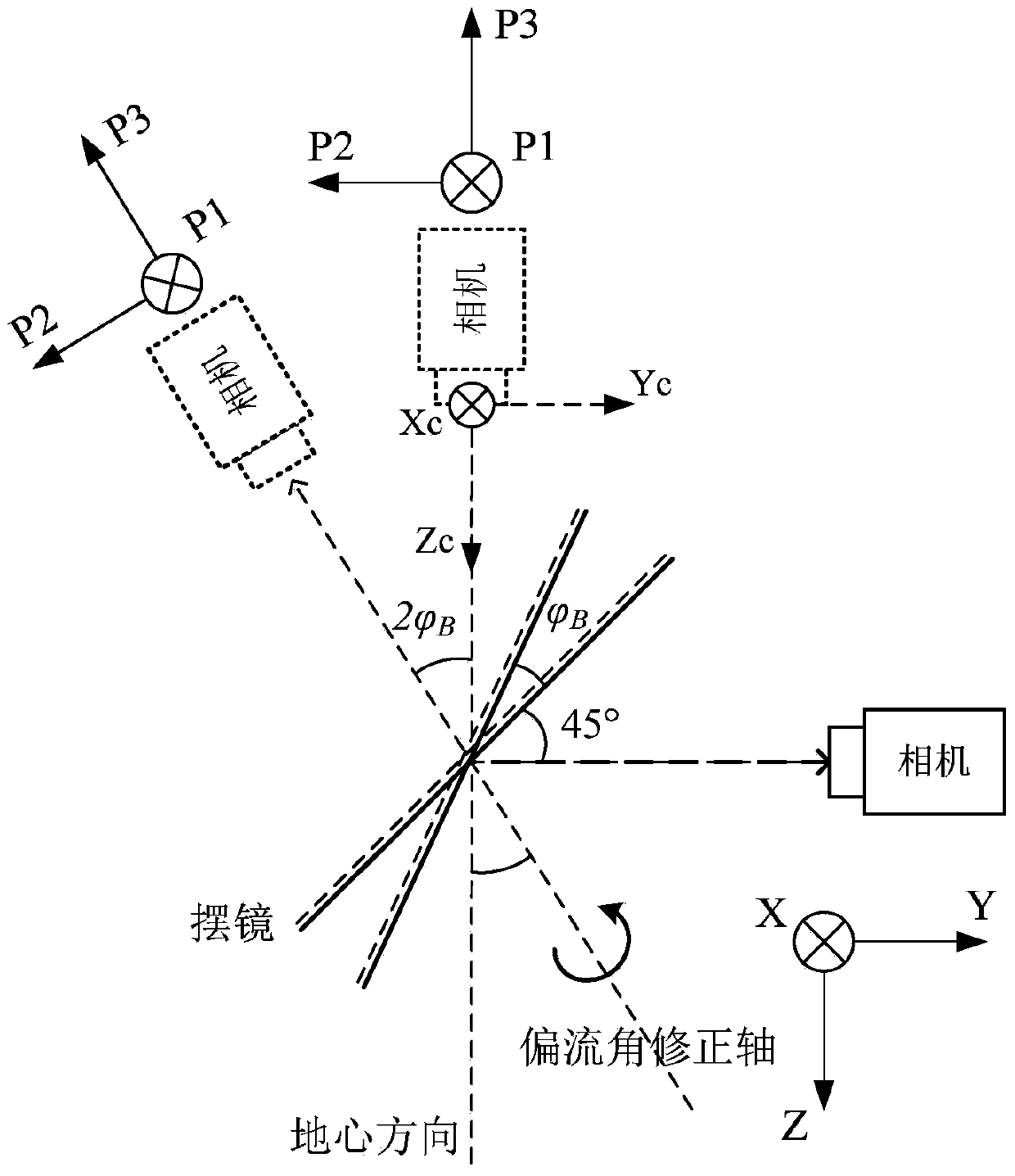
[0079] This embodiment provides a multi-target continuous imaging bias angle compensation method, which solves the problem that when a TDICCD camera equipped with a oscillating mirror performs a multi-target continuous imaging task, the camera realizes the expansion of the ground field of view through the oscillating mirror. The motion causes the continuous change of the optical axis of the camera, and the satellite cannot compensate the drift angle around the yaw axis in a conventional way.
[0080] In order to describe the technical content, structural features, achieved goals and beneficial effects of this embodiment in detail, this embodiment will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0081] The same-orbit multi-target imaging is to complete the imaging of multiple targets that can be observed in the orbit during the single-track imaging process. The satellite is equipped with a TDICCD push-broom camera, which relies on the rolling ax...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com