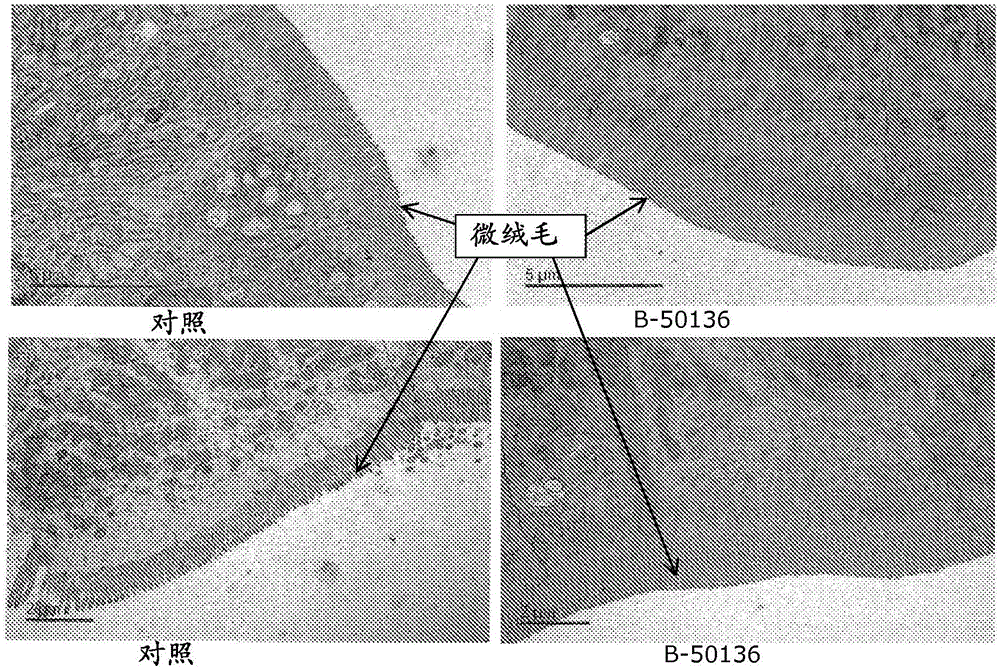
Compositions and methods for improving the health of aquatic animals
A technology for aquatic animals and compositions, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, methods using bacteria, etc., which can solve the problems of aquatic animal death, infection of aquatic animals, yield loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0296] Example 1: Inhibition potential in vitro
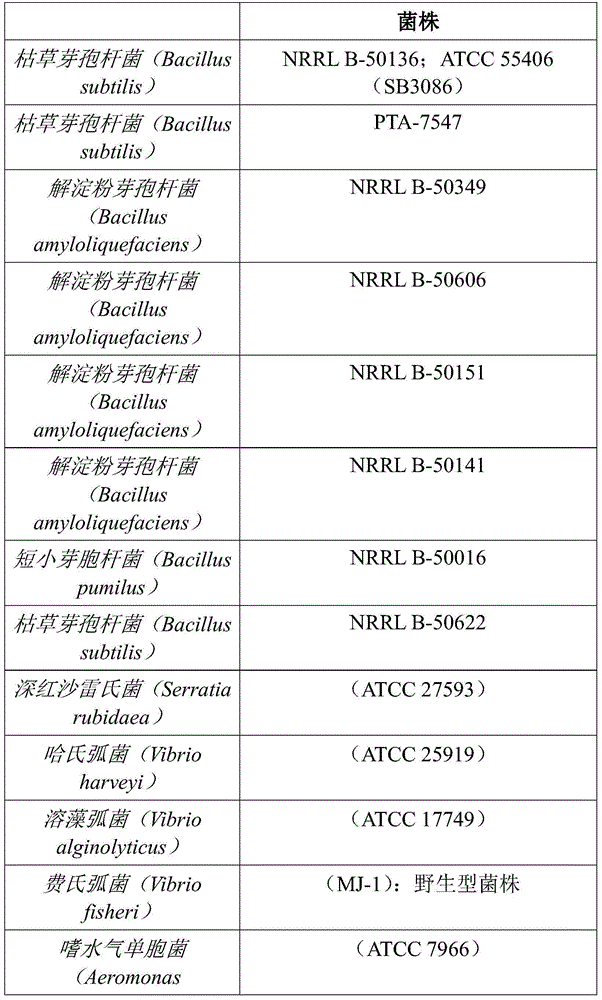
[0297] Competitive inhibition of a panel of Bacillus candidate strains was evaluated against a range of targeted pathogenic bacterial strains including Serratia rubidaea, Vibrioharveyi, Fischeri Vibriofischeri, Vibrio alginolyticus, and Aeromonas hydrophila. Selected Bacillus strains were quantitatively evaluated by their ability to inhibit the growth of "lawns" of target bacterial pathogens (as mentioned in Table 1) growing on petri dishes. This is best quantified by using defined "wells" (holes) inserted into the agar into which a defined amount of viable culture of the test Bacillus strain is placed.
[0298] Diffusion assays were performed when the test strain Bacillus candidates were grown in nutrient broth that was autoclaved and cooled prior to strain inoculation. For tests involving inhibition of Vibrio species, the nutrient broth was supplemented with 1.5% (w / v) sodium chloride. Bacillus strains were grown in nutrient...
example 2
[0303] Example 2: Quorum Sensing Inhibition
[0304] Vibrio fischeri (MJ-1) was used as the indicator because its coloration depends on an intact quorum sensing pathway. The greater the effect of the QSI on V. fischeri, the less fluorescence was observed. Quorum-sensing compounds allow bacteria to "communicate" and affect phenotypes such as colouration, motility, pathogenicity, and Vibrio colonization in shrimp gills or gut. Thus, quorum sensing inhibition is, for example, the mode of action against Vibrio colonization in the gut.
[0305] The Bacillus candidate and indicator bacterium Vibriofischeri (MJ-1) were grown according to the method described in Example 1. The results are provided in Table 2. Inhibition of pigmented areas, but not total cell growth, was scored as QSI positive and its major diameter was measured for semi-quantitative results. Total growth inhibition of V. fischeri is expressed as "VC" for vibriocidal drugs.
[0306] Table 2: Relative areas of QS...
example 3
[0308] Example 3: Survival of spores in extruded fish feed pellets
[0309] For a Bacillus strain to be effective in aquafeed itself, the inoculated spores must survive at effective levels during the pelleting process. Typically, optimal fish feed values are obtained when feed pellets are passed through nozzles at high temperatures (100°C to 120°C) before drying and subsequent use in feeding, while other animal feed types are well formed at 85°C-95°C .
[0310] Microbial spores were assessed for viability potential during the standard fish food pelleting process. Commercial fish feed is generally produced using a high temperature extrusion process, in which a feed meal is extruded through a heated nozzle under a defined temperature and pressure profile. The tests were carried out using a Werner & Pfleiderer 37 screw extruder through a 2.7 mm dye nozzle with horizontal mixing at the temperatures described in Table 3.
[0311] Prior to extrusion, the microorganisms were add...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com