Block chain data comparison and consensus method
A data comparison and blockchain technology, applied in the field of blockchain technology, can solve problems such as the inability to find the source of data for download, the inflexibility of data storage, and the high probability of repeated transaction data transmission.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
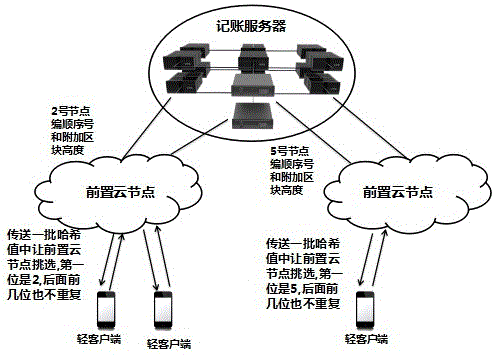
[0052] Embodiment 1, with reference to attached figure 2 :
[0053] This example shows how to generate unique numbers.
[0054] Here it is assumed that the number 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, a, b, c, d, e, f (hexadecimal) number is assigned to the front cloud node to get the number for the user.
[0055] In addition to the fact that the first digit must be 2, the No. 2 node also stipulates that the second and third digits cannot be repeated, that is, 16*16=256, that is, it is stipulated that this node can only send up to 256 different numbers in each block. transaction number.
[0056] The user can stipulate that the several transactions sent are the fourth transactions of the wallet. The system stipulates that only one transaction will take effect each time, so there is no need to worry about overpayment.
[0057] If the user chooses node 2 to send transactions, a batch of transaction hash values will be generated, and several transactions whose first digit is 2 wil...
Embodiment 2
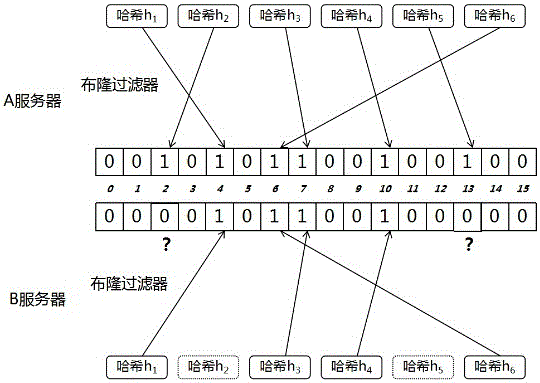
[0060] Embodiment 2, with reference to image 3 :
[0061] This example shows that using the Bloom filter can check the omission of data. By changing the hash value generated by the random number within a period of time, it will not be repeated in the Bloom filter, and the data can be transmitted from the A server to the B server. The misjudgment rate of the post-post comparison is reduced to 0 (assuming that the data will only be missed and no new data will appear).
[0062] Step S1: Here, a total of 6 hash values are to be transmitted from server A to server B, and the number of Bloom filter groups is set to 16 bits.
[0063] Step S2: Change the hash value generated by the random number so that it will not be repeated in the Bloom filter on the A server, and each time the hash value is added to the Bloom filter, there is at least one in the binary bit array Position 1 is uniquely corresponding to the added hash value, and the six hash values of h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, an...
Embodiment 3
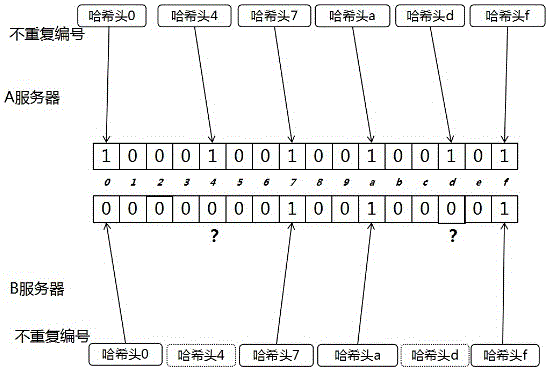
[0066] Embodiment 3, with reference to figure 1 :
[0067] This example illustrates how to use unique numbers to look up missing data.
[0068] Using non-repeating numbers to compare missing data, the number of transactions in the new block is estimated to be 6, and the total number is set to the 4th power of 2, represented by the first two digits of the transaction hash value.
[0069] There are a total of 16 numbers (0 to 15) to choose from. Create a 16-digit string StringA16 with all "0". After the front node A server selects a non-repeating number, match the number with the string position one by one. Get up, replace the 0 string in the corresponding position with 1, and the 16-bit string position numbers are 0 to 15 from left to right. Here, the characters at the 0, 4, 7, a, d, and f positions of the string are "1".
[0070] Server B also creates a 16-bit string StringB16 with all 0s like server A. After receiving the transaction data from server A, the server replaces...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com