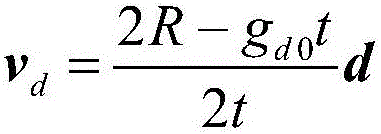Active control method for adhesion motion on small celestial body surface
A technology for active control and small celestial bodies, which is applied in the aerospace field and can solve problems such as low control accuracy and inability to achieve fixed-point movement.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
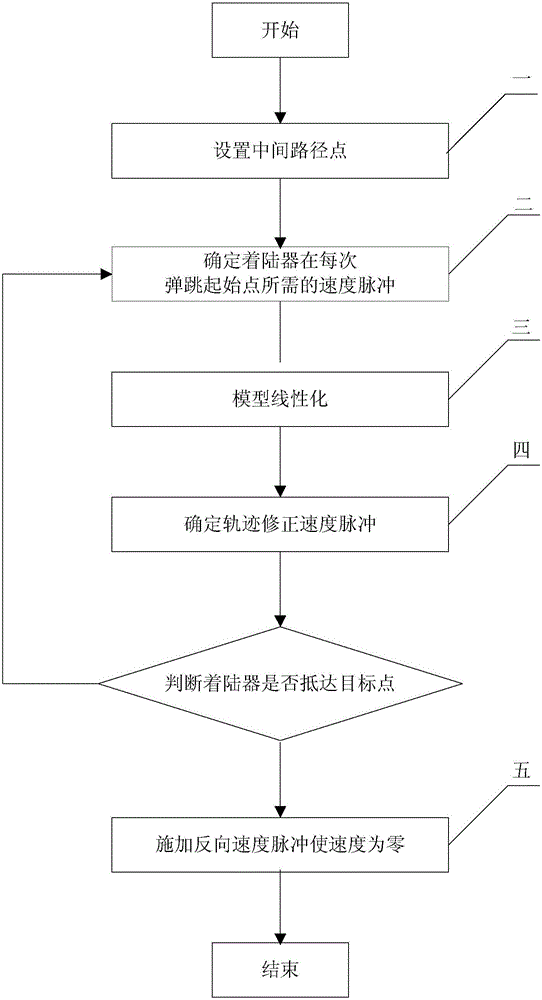
[0054] A method for active control of small celestial body surface attachment movement, comprising the following steps:
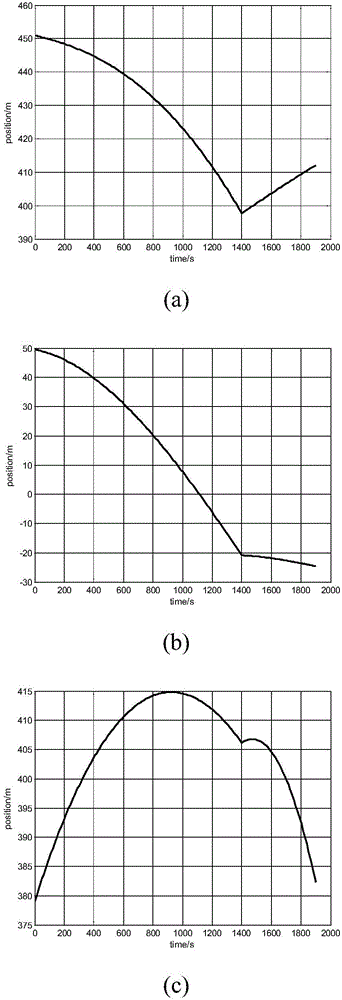
[0055] Step 1. Under the fixed connection system of small celestial bodies, the initial position r t 0 with the target position r t N Between, set N-1 intermediate path points r t 1 ,r t 2 ,r t 3 ,...,r t N-1 , then the detector reaches the target position r after a total of N bounces t N .
[0056] Step 2. Determine the velocity pulse v required by the detector at the starting point of the i-th bounce i (i=1,2,...N):
[0057] The starting point of the i-th bounce is r t i-1 , R is due to r t i-1 point to r t i , g is the gravitational acceleration vector of the contact point, the n-d plane is formed by R and g, n represents the unit vector along the R direction, and d represents the unit vector along the g direction. The coordinate system is constructed in the n-d plane, the origin is located at the contact point, the horizontal axis i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com