Cellular Uplink Harmonic Spurious Suppression in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Receivers
A receiver, circuit technology, applied in the field of cellular uplink harmonic spurious suppression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
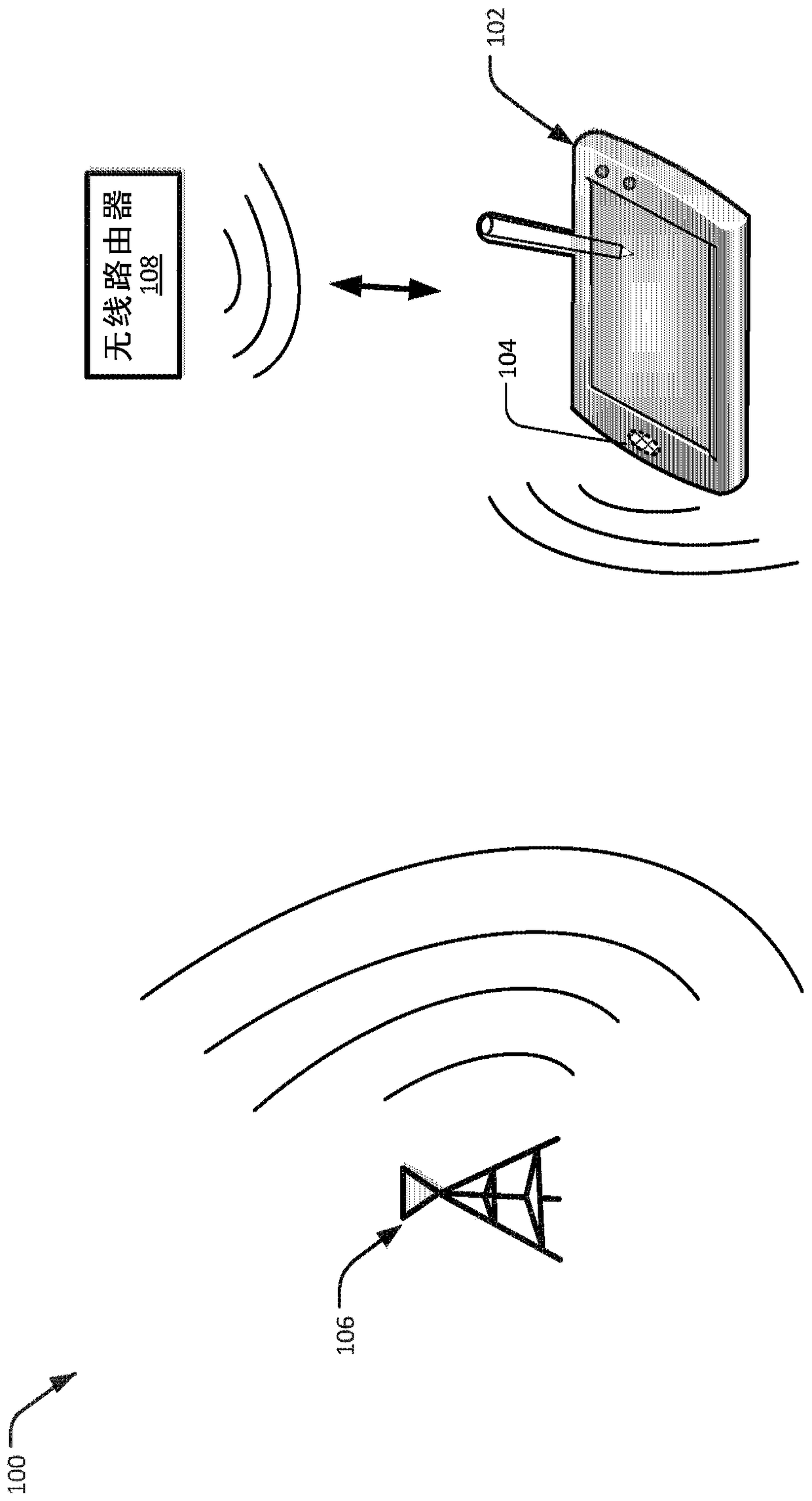
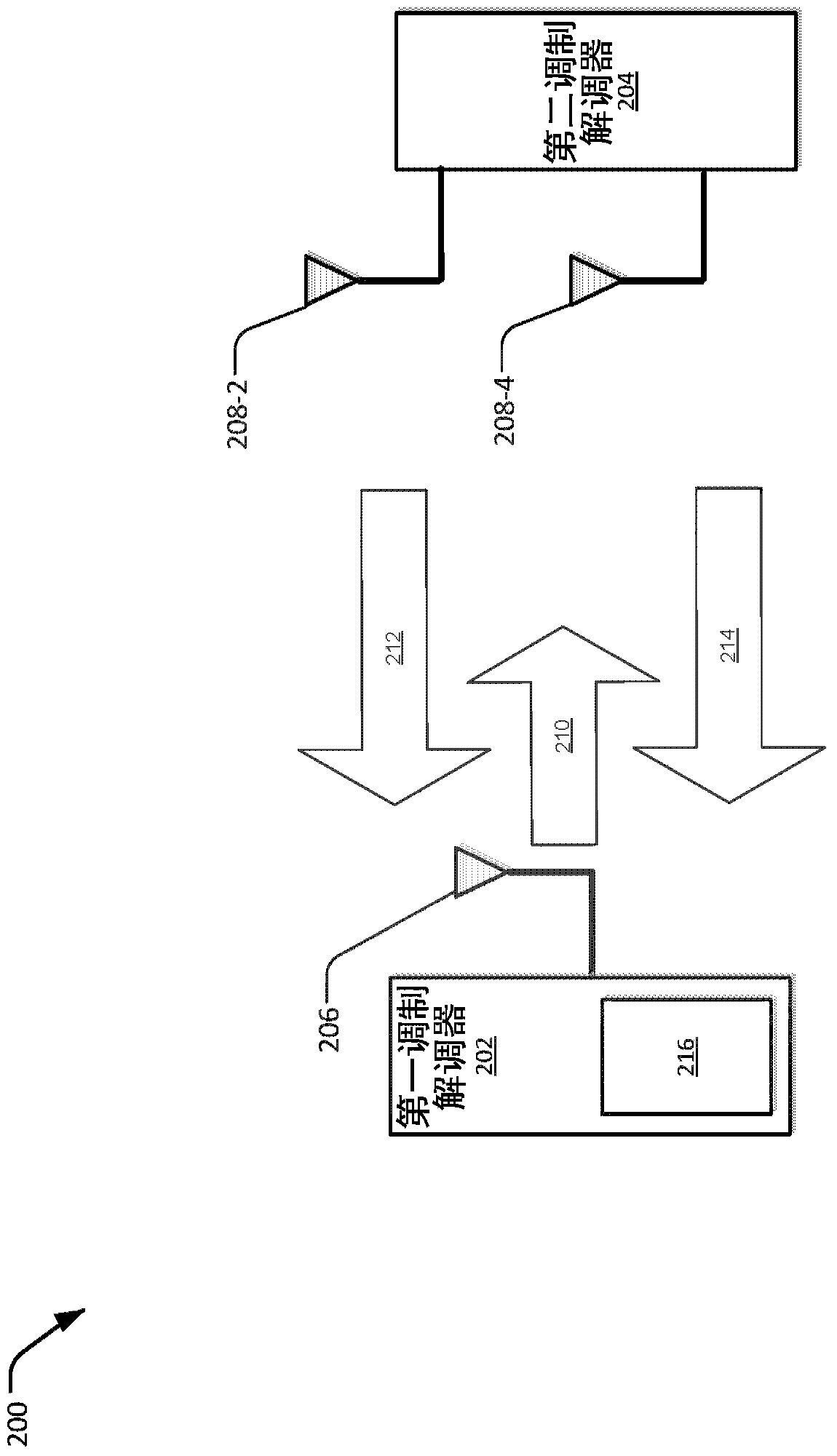
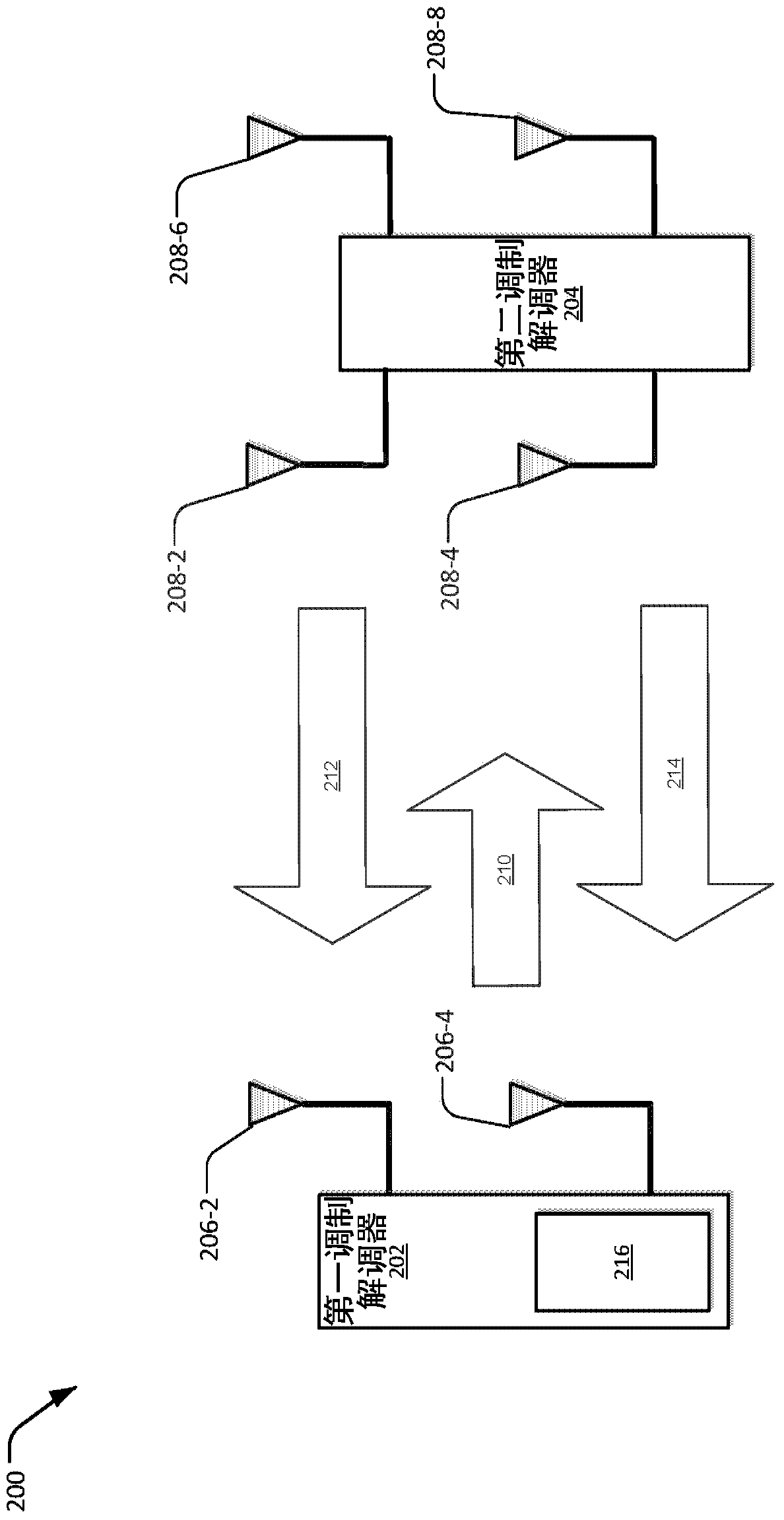
[0011] Described herein are techniques for increasing inverse sensitivity in a receiver circuit or system of a portable device. For example, such as during a downlink (LD) data communication operation via a first modem (eg, a cellular / LTE modem) the operating frequency is subjected to radio frequency (RF) interference from a second modem (eg, Wi-Fi, BT, etc.) ) signal, and vice versa. In this example, when the second modem is an aggressor modem, the RF signal from the second modem may provide out-of-band overload current or interference to at least one antenna of the first modem. As such, a calibration process may be performed to remove these effects on the at least one antenna of the first modem.
[0012] In an implementation, the first modem is configured to receive a first set of radio frequency (RF) signals (eg, a set of calibration RF signals) from a second modem during DL data communication or during a discontinuous reception (DRx) mode. In this implementation, the fir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com