Light source driving device and display device
A light source driving and light source technology, applied in optics, optical components, static indicators, etc., can solve the problems of minimum current increase, inability to ensure display brightness, and difficulty in achieving low brightness display, and achieve the effect of ensuring dynamic range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 2 Embodiment approach
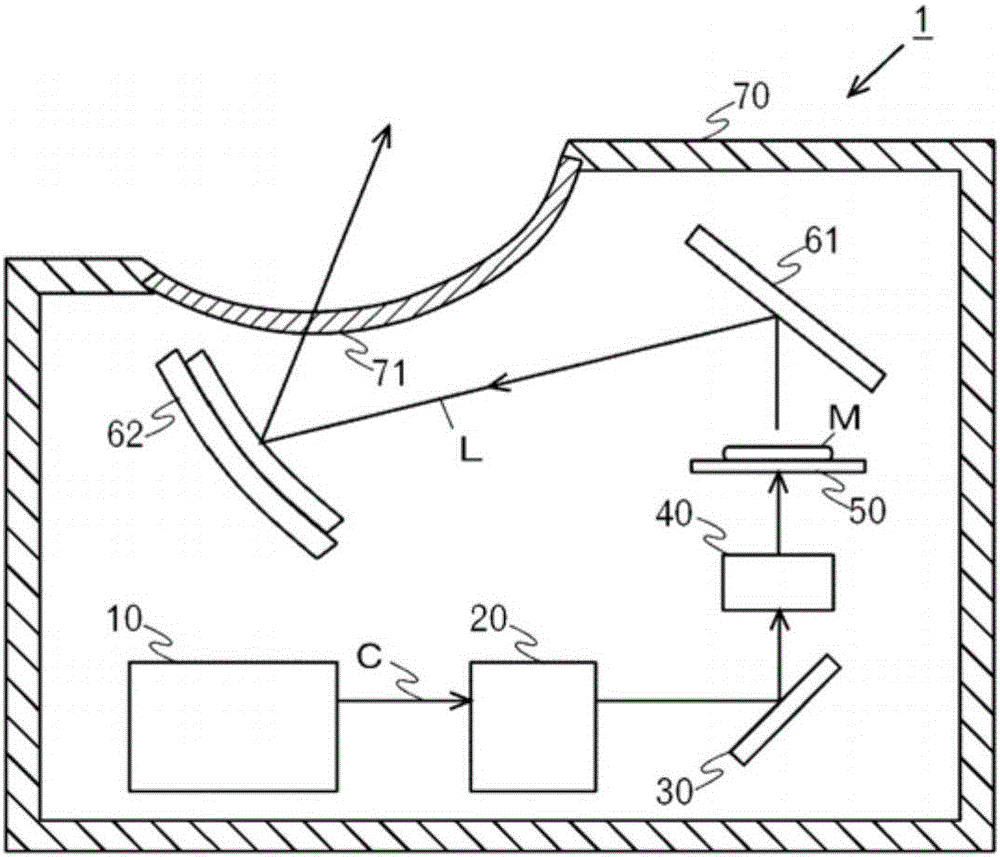
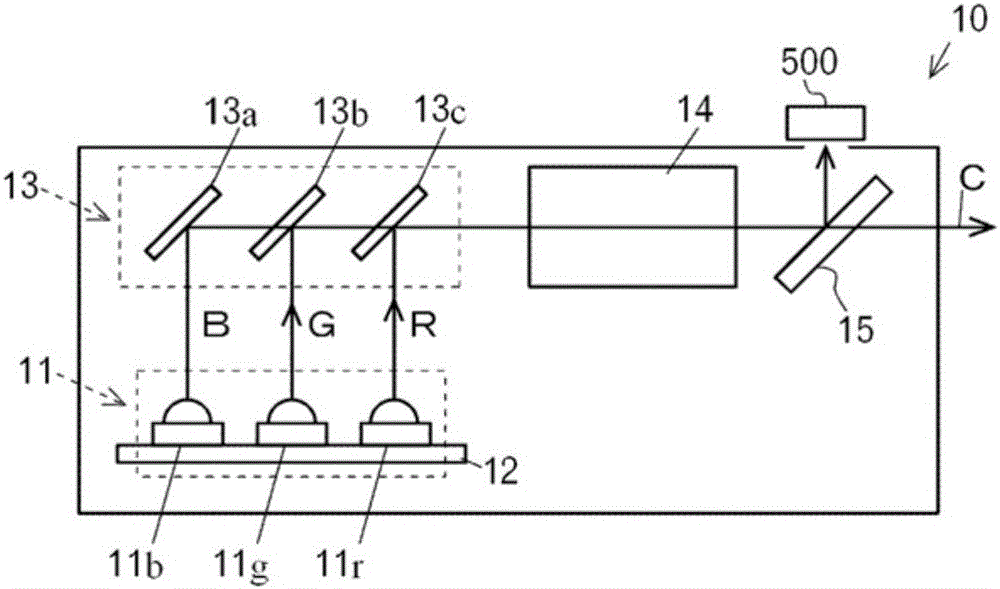
[0120] In the embodiment described above, the light source driving device 5 inputs the light intensity detection signal SFB from the light intensity detection unit 500 as a feedback signal into the comparison circuit 410, and the comparison circuit 410 detects the light intensity from the light intensity detection unit 500. The signal SFB is compared with the reference signal SA from the first control unit 100 to form a comparison signal SB as a pulse signal, and the light source driving device 5 of the second embodiment is different in that: Figure 10 As shown, the driving currents lr, lg, lb flowing through the light source 11 are detected by the current detection unit 600, a voltage value is calculated based on the current detection unit 600, and a voltage signal VFB related to the voltage value is output to the comparison circuit 410 as a feedback signal.
[0121] The comparison circuit 410 of the second embodiment compares the voltage signal VFB input from the current det...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0124]In the above-mentioned embodiment, the light source driving mechanism 400 outputs the lighting signal SD1 only in the predetermined driving period T for each sub-frame, but the light source driving device 5 of the third embodiment is different in that only the The lighting signal SD1 is output for the number U of pulses determined for each sub-frame. That is, switching timings of the enable signal SC1 (disable signal SC2 ) output from the second control unit 200 to the logic circuit 420 are different. Next, the switching operation of the enable signal SC1 (disable signal SC2 ) of the second control unit 200 in the third embodiment will be described using the timing chart of FIG. 11 .
[0125] The second control unit 200 controls the limit signal SC (permission signal SC1) in such a manner that only a predetermined number of pulses U (U1 in FIG. Or the prohibition signal SC2) is output to the logic circuit 420. Specifically, the second control unit 200 starts counting t...
no. 4 Embodiment approach
[0127] In addition, in the above-mentioned embodiment, the second control unit 200 determines the presence or absence of the non-lighting signal SD2 (prohibition signal SC2 ) in the limit signal SC based on the value of the external illuminance signal SL. However, the second control unit 200 of the fourth embodiment The control unit 200 controls the proportion of the prohibition signal SD2 in each sub-frame period based on the value of the external illuminance signal SL. Figure 12 is a timing diagram showing how T changes during the driving period according to the value of the external illuminance signal SL. It is a diagram showing the state of the limit signal SC at different times. 12( b ) shows a case where the external illuminance signal SL is large (large dimming value), and FIG. 12( c ) shows a case where the external illuminance signal SL is small (small dimming value). Specifically, for example, the second control unit 200 of the fourth embodiment reduces the proporti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com