Velocity control for an unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle, speed limit technology, applied in the field of speed control of unmanned aerial vehicles, can solve the problem that the unmanned aerial vehicle is relatively far away from the user
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
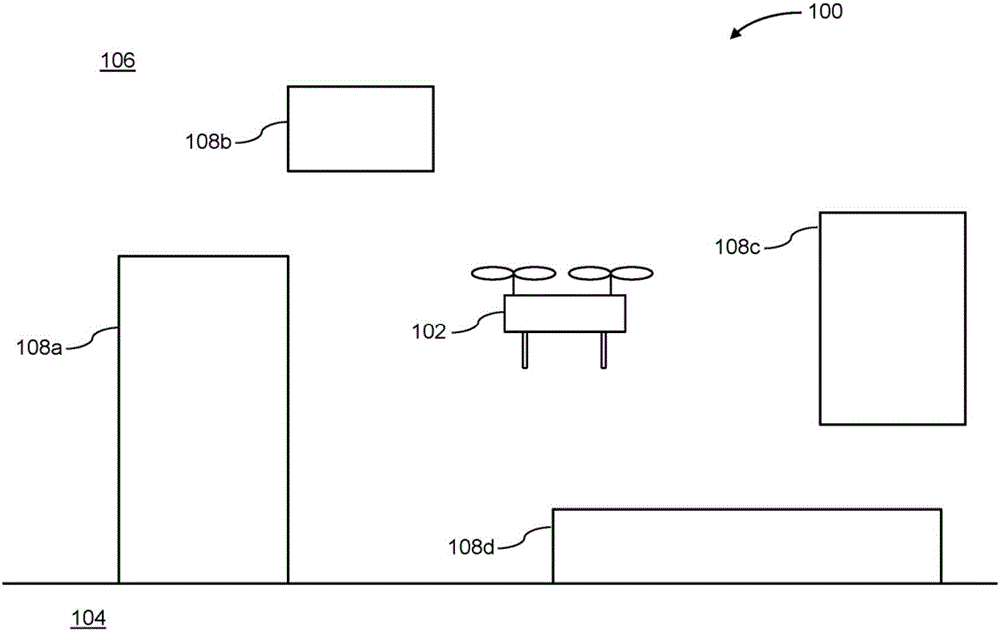
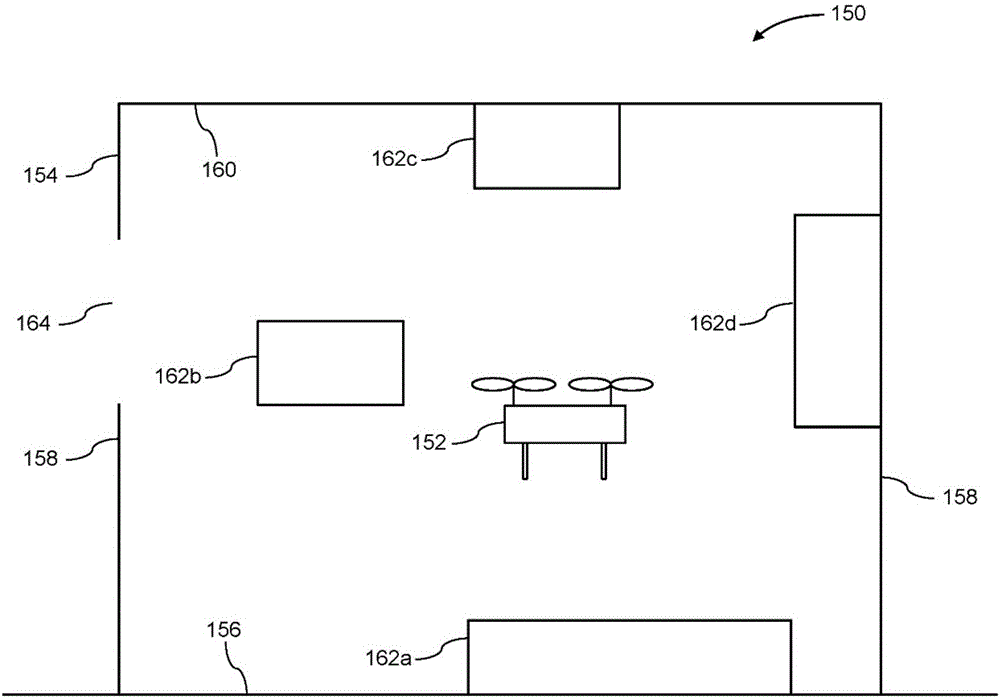
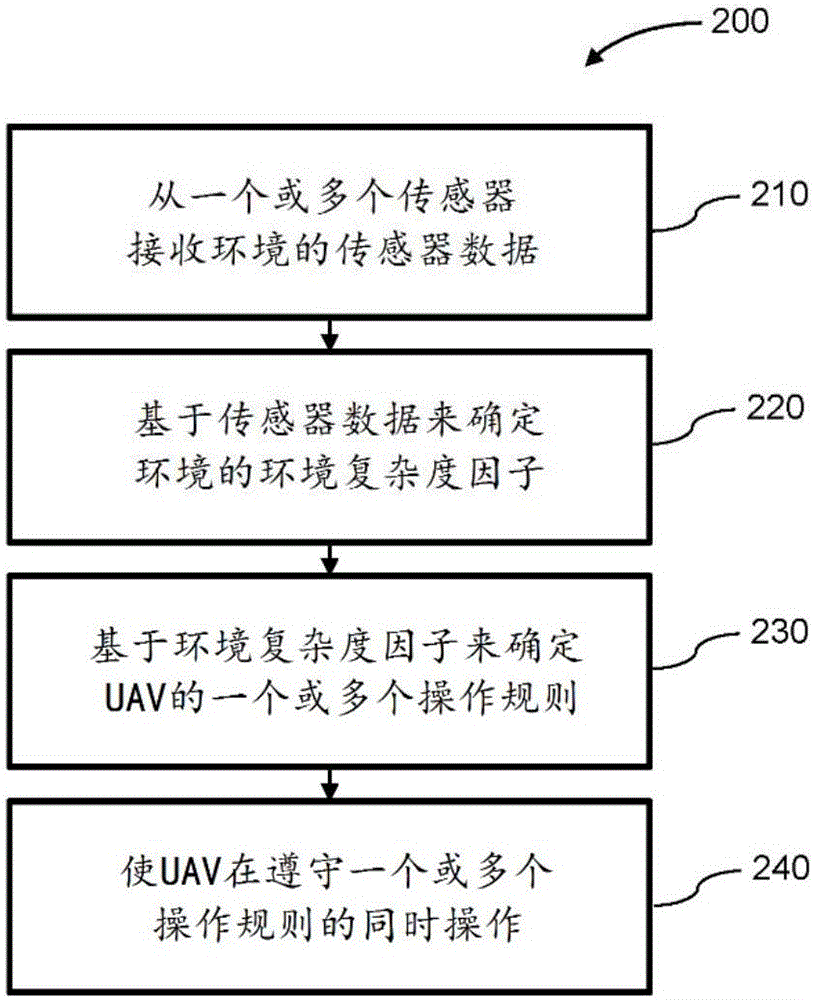
[0041] The present disclosure provides improved systems and methods for determining operating rules to operate an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). The UAV may carry one or more sensors that acquire data about the surrounding environment, and that data may then be processed in order to detect the extent to which obstacles and other potential safety hazards are present in the surrounding environment, which may be referred to herein as "environmentally complex degree factor". The environmental complexity factor may be used to determine a set of operating rules (eg, speed rules, such as speed limits or speed ranges) that will be observed when operating the UAV within the environment. For example, when the UAV is operating in a "complex" environment (environment with high obstacle density, such as indoors, urban areas, or low-altitude environments), the maximum speed limit of the UAV may be relatively low, thereby reducing the risk of accidental collisions. Conversely, when operatin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com