Long term adverse effect of polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid on lung antibacterial defence mechanism
A technology of polyinosinic acid and defense mechanism, which is used in preparations for in vivo experiments, pharmaceutical formulations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
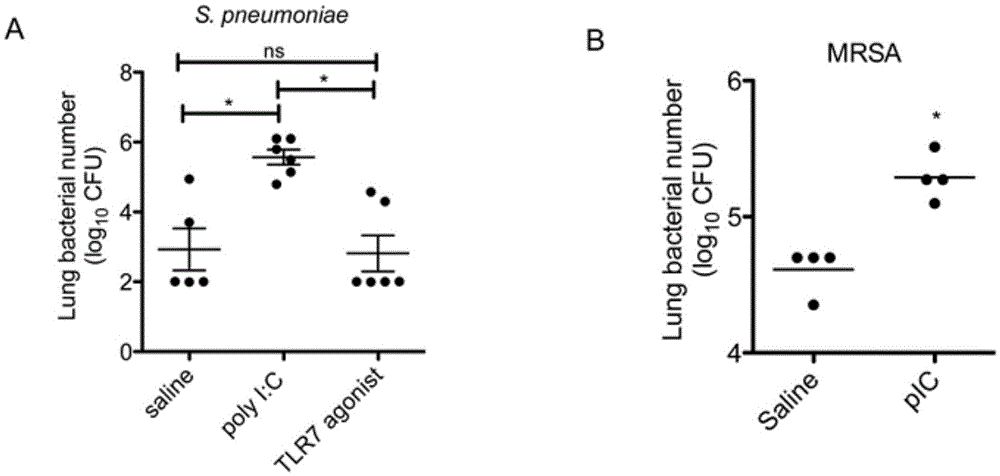
[0060] Polyinosinogenic acid increases susceptibility of lung tissue to bacteria
[0061] We first examined the effect of polysinosinate administration on bacterial clearance following bacterial infection. Experimental animals receive intranasal administration of polyinosine or imiquimod for two consecutive days (eg, double dose). On the third day (ie, 24 hours after the last polyinosinate dose), animals were injected intrathecally with S. pneumoniae. We found a significant increase in bacterial counts in the lungs of animals administered nasal polyinosinosinate. Interestingly, imiquimod or gademotel (TLR7 agonists such as figure 1 A) There was no significant difference in bacterial clearance between the treatment groups. But both groups showed robust clearance during the initial challenge phase. Administration of TLR7 ligand alone was therefore not sufficient to reduce bacterial clearance.
[0062] Second, we examined whether polyinosinogenic acid also reduced the clear...
Embodiment 2
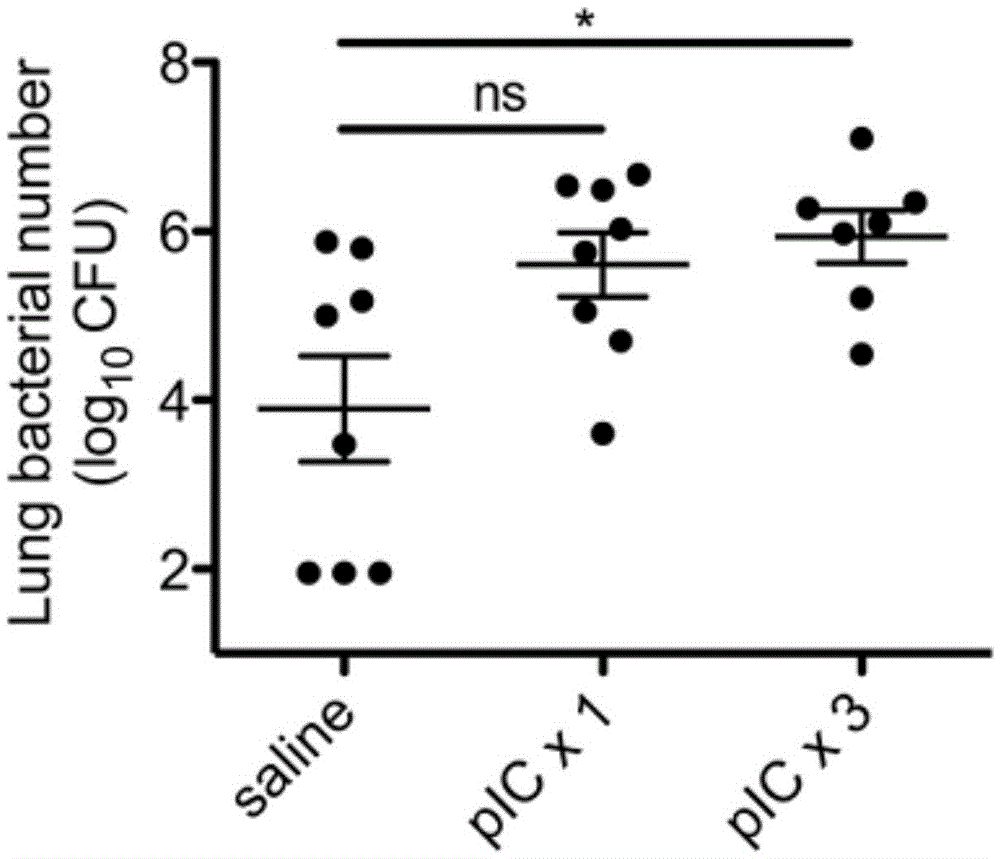
[0064] The degree of impairment of bacterial clearance is directly proportional to the duration of polyinosarglycine administration
[0065] We observed a time point at which the rate of bacterial clearance in animals decreased after administration of polyinosinogenic acid. Since viral infections, such as influenza, usually last for several days or even longer, we conducted related experimental studies, taking polyinosinogenic acid in 1 dose or 3 doses to simulate the effect of viral infection. After 24 hours of intranasal administration of polyinosinogenic acid or saline once or three times, the experimental animals were intrathecally injected with Streptococcus pneumoniae. At 48h, the amount of bacteria in the body was recorded. We found that the dose of polysarcocytate correlates with the rate of bacterial clearance. The bacterial clearance rate in the experimental animals with one-time administration of polyinosinic acid will tend to decrease (the average CFU value is 8 ...
Embodiment 3
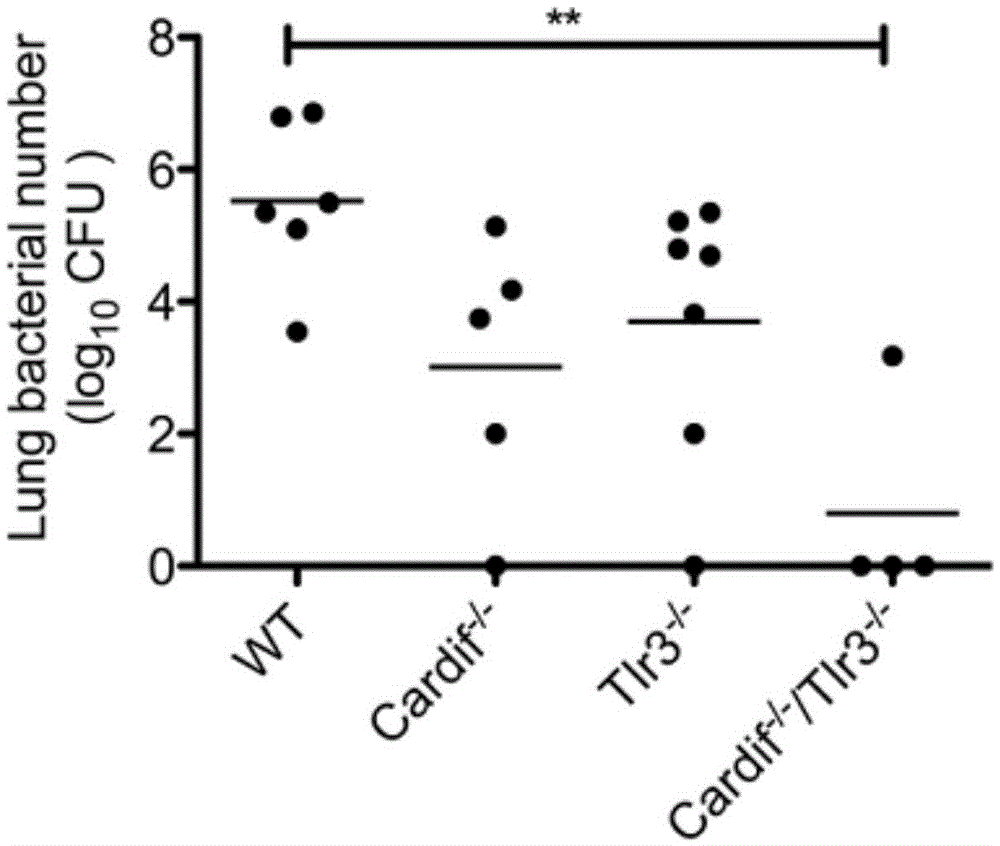
[0067] TLR3 and Cardif pathways enhance host susceptibility to bacteria induced by polyinosinogenic acid
[0068] Since polysinosine activates both TLR3 and the Cardif-dependent helicases RIG-I and MDA5, we sought to determine whether either or both pathways are involved in polysinosine impairing host bacterial clearance. For such studies, we use polyinosinocytosine in animals lacking TLR3 (Tlr3- / -), Cardif (Cardif- / -), or both (double knockout). Cardif acts as an adapter molecule for RIG-I and MDA5 signaling early in the antiviral response [25][26][27][28] . We found that TLR3 (Tlr3- / -) deletion or Cardif (Cardif- / -) experimental animals had improved bacterial clearance rate after administration of polyinosinogenic acid. Compared with the normal saline group, the double-knockout (Cardif- / - / Tlr3- / -) group was administered polyinosinogenic acid under the environment of secondary bacterial infection, and the bacterial clearance rate in the body was significantly improved ( i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com