Low-complexity LDPC dynamic scheduling decoding updating method based on variable node reliability
A variable node and update method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of variable node and edge selection methods that need to be adjusted, greedy, dynamic scheduling and high complexity of decoding strategies, so as to omit overhead, improve throughput, and reduce decoding complexity degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
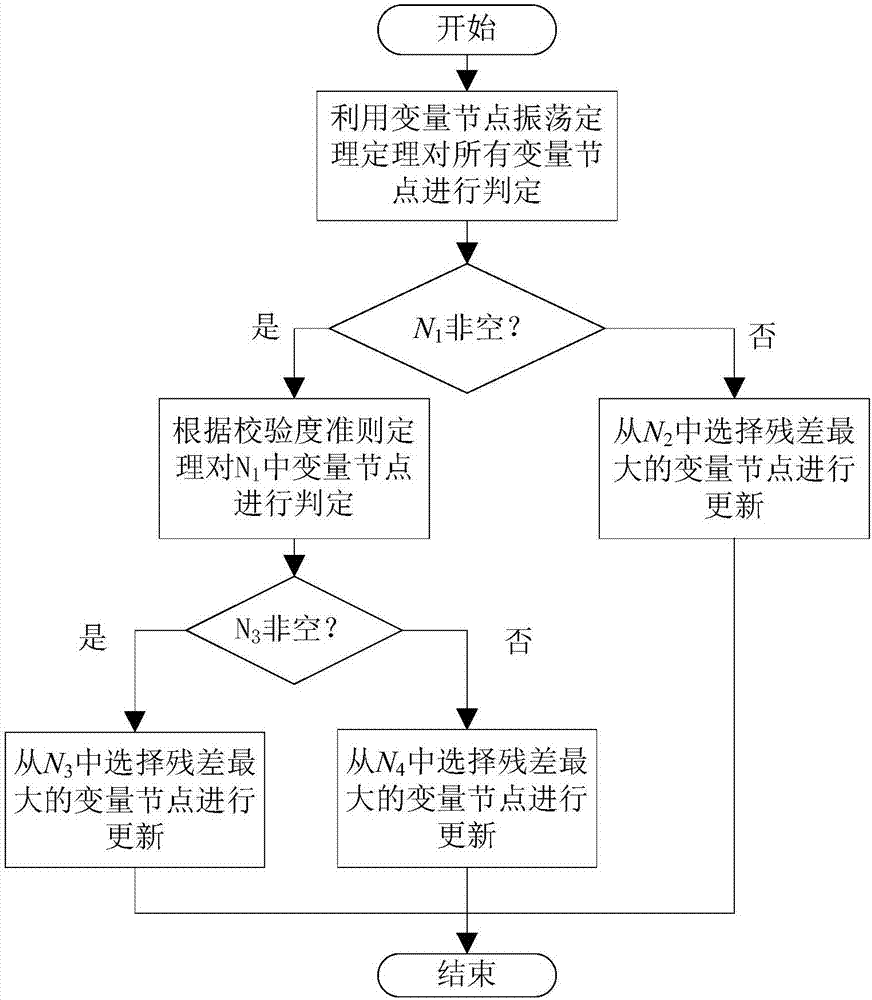
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, the low-complexity LDPC dynamic scheduling decoding update method based on the reliability of variable nodes, on the basis of the point residuals of variable nodes, uses the dynamic selection strategy of oscillation selection theorem and variable node check degree criterion to select a reliable The variable nodes of the external information are updated,
[0035] The variable node reliability dynamic selection strategy includes the following steps:
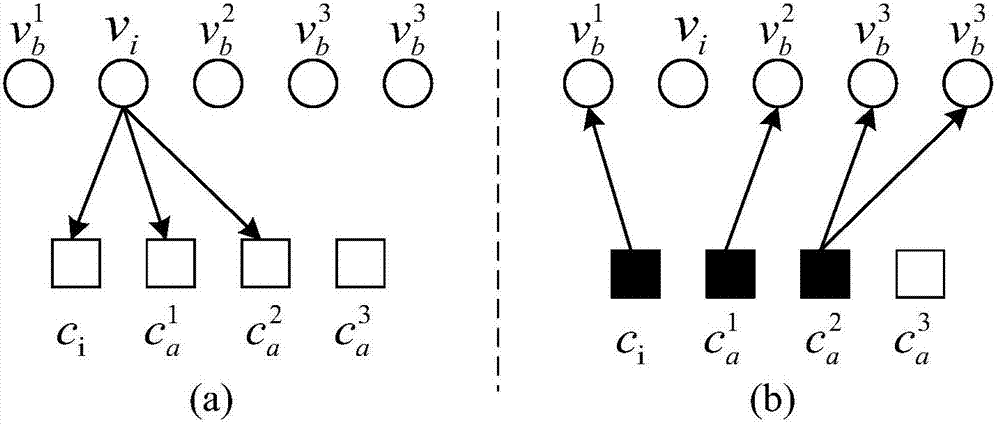
[0036] S11. Determine all variable nodes according to the oscillation selection theorem of variable nodes, where the set of oscillating variable nodes is the set of oscillating variable nodes, denoted as N 1 , N 1 The set of other variable nodes is denoted as N 2 ; If the oscillation variable node set N 1 If it is not an empty set, execute S12, if the oscillation variable node set is an empty set, then execute S13; wherein, the oscillation selection theorem of variable nodes means that in the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com