Strain test equipment of nanometer resolution and method thereof
A strain measurement and resolution technology, applied in measurement devices, instruments, and the use of wave/particle radiation, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate and fine testing, poor applicability, and inability to perform real-time dynamic testing, achieving convenient testing process and comprehensive functions. Effect
Active Publication Date: 2017-08-25
常州满旺半导体科技有限公司
View PDF6 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
XRD or Raman spectroscopy is used to measure lattice constants to estimate strain. Due to the difficulty of focusing light waves and the fact that light spots are generally on the order of microns or submicrons, it is difficult to achieve nanometer-level resolution testing; and there are many test conditions, such as Raman spectroscopy. Fluorescence must be avoided, and a microscope must be used to focus t
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Login to View More
Abstract
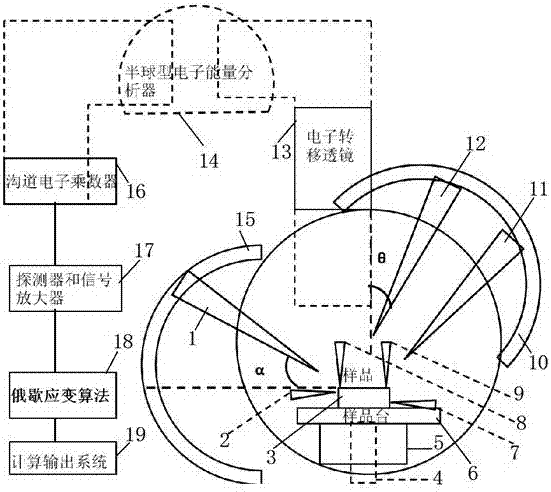
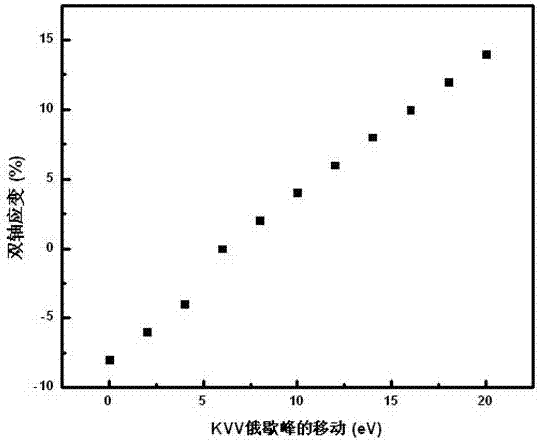
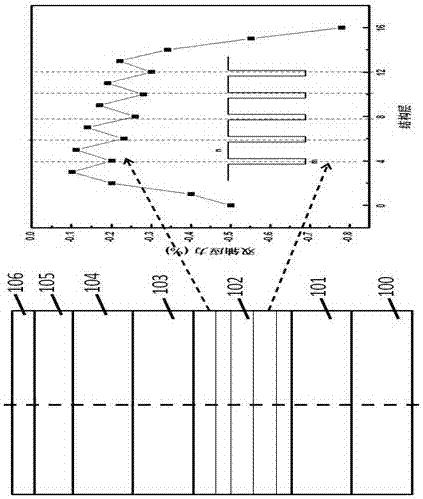
The invention discloses strain test equipment of a nanometer resolution and a method thereof. The equipment comprises a test chamber, a sample bench, a temperature magnetic field control apparatus below the sample bench, a mobile motor, a sample to be measured placed on the sample bench, a first probe, a second probe, a third probe, a fourth probe, an electronic gun, a first rotation track, an X ray gun, an ion gun and a second rotation track, wherein the first probe and the second probe are arranged above a sample; the third probe and the fourth probe are arranged on a sample side wall or a cross section; the electronic gun possesses multiple focusing electron beams; the first rotation track controls rotation of the electronic gun; and the second rotation track controls the rotation of the ion gun. An auger electron spectrums collected by the test chamber are transmitted to a detector and a signal amplifier successively through an electron transfer lens, a semi-spherical electronic energy analyzer and a channel electron multiplier. The detector and signal amplifier output a dynamic strain value epsilon of the sample in real time through an auger strain algorithm module and a calculating output system.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to a strain testing device and method, in particular to a high-precision strain testing device and method for testing semiconductor materials. Background technique [0002] The test of strain in solid or thin film materials generally adopts the following three methods: 1) use the lattice constant change obtained by XRD measurement to estimate the size of the strain; 2) calculate the strain according to the frequency shift of the Raman spectrum; 3) use HRTEM measures changes in atomic lattice spacing to calculate strain. XRD or Raman spectroscopy is used to measure lattice constants to estimate strain. Due to the difficulty of focusing light waves and the fact that light spots are generally on the order of microns or submicrons, it is difficult to achieve nanometer-level resolution testing; and there are many test conditions, such as Raman spectroscopy. Fluorescence must be avoided, and a microscope must be used to focus the light...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G01B15/06
CPCG01B15/06
Inventor 郑锦坚郑清团王星河康俊勇
Owner 常州满旺半导体科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com