Methods and circuitry for driving display devices
A display device, drive circuit technology, applied in the direction of static indicators, instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
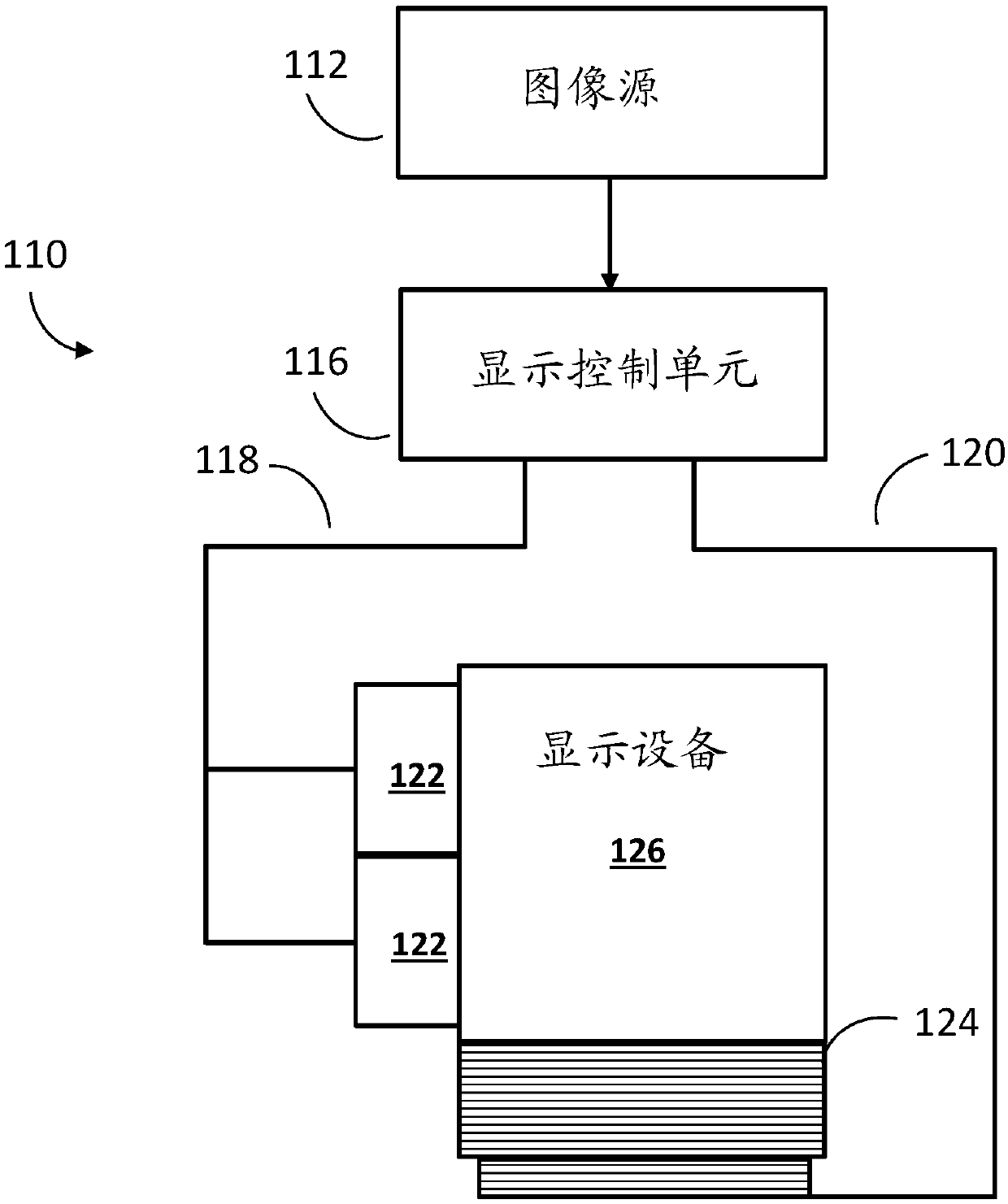
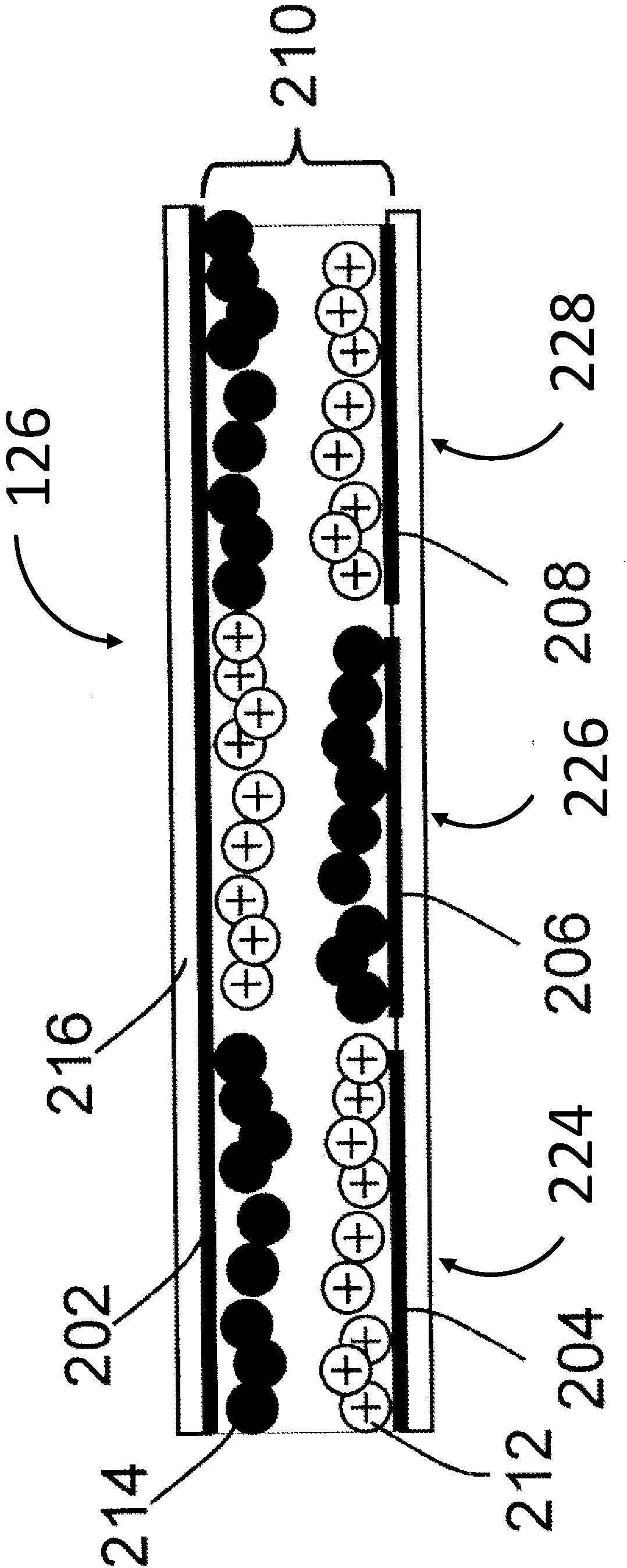
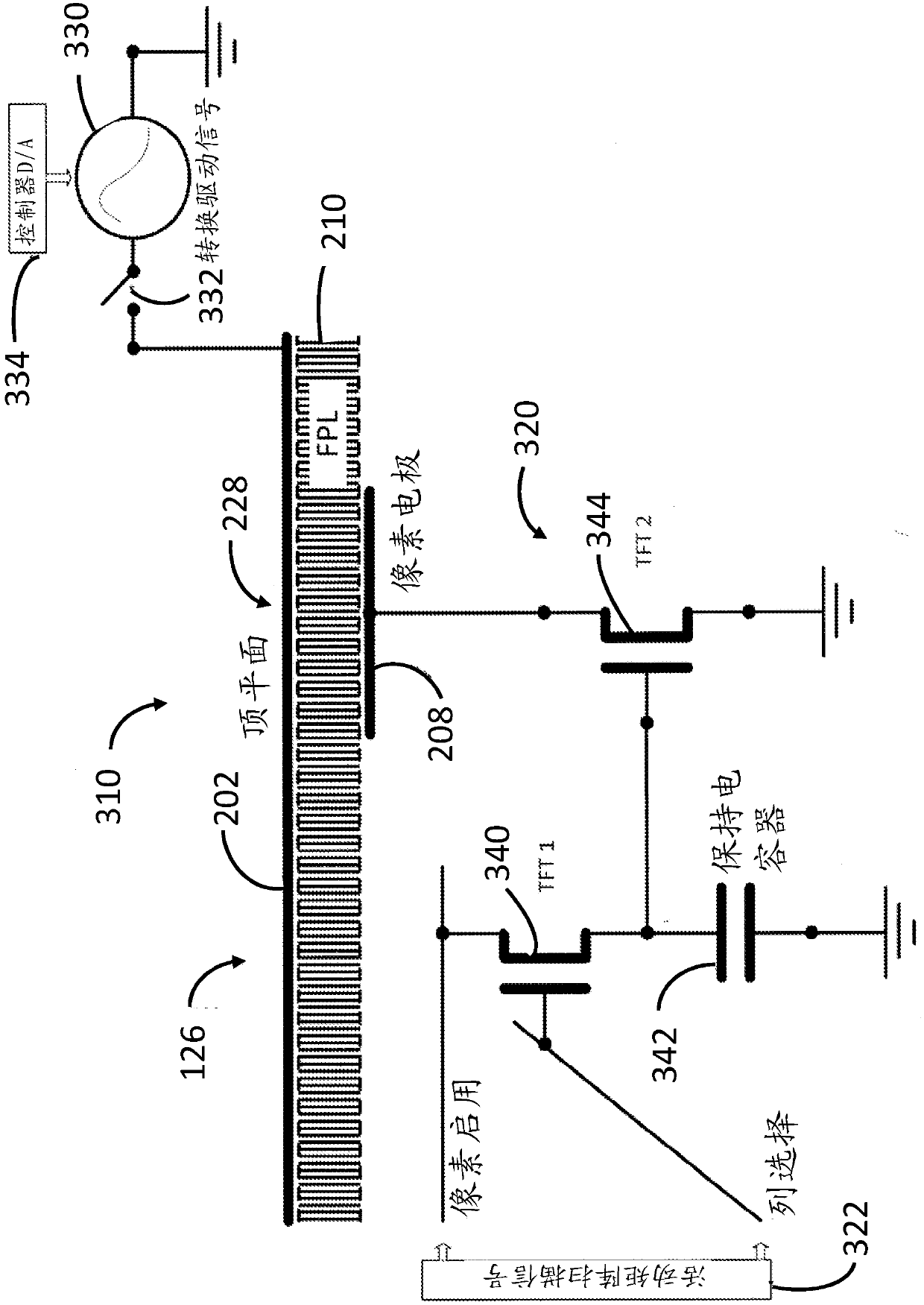
[0022] The term "electro-optic" as applied to materials or displays is used herein in its conventional meaning in the field of imaging to refer to materials having first and second display states that differ in at least one optical property, obtained by applying an electric field to Material to change the material from its first display state to its second display state. While an optical property is generally color perceived by the human eye, it can be another optical property such as light transmission, reflectivity, fluorescence, or in the case of displays intended for machine reading, electromagnetic waves outside the range of visible light False color in the sense of long reflectivity changes.
[0023] The term "gray state" is used herein in its conventional meaning in the imaging field to refer to a state intermediate between two extreme optical states of a pixel, and does not necessarily imply a black-and-white transition between these two extreme states. For example, s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com